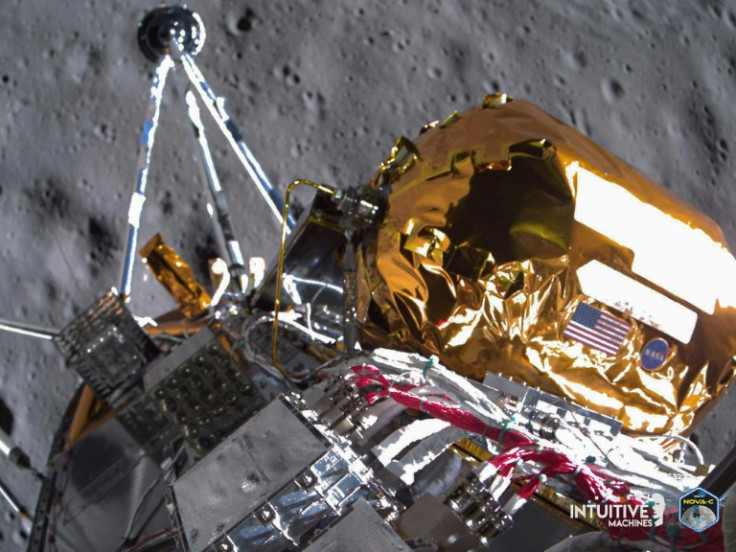
An uncrewed American lander that became the first private spaceship on the Moon has met its ultimate end after failing to "wake up," the company that built it said.
Houston-based Intuitive Machines said late Saturday that the lander, named Odysseus, had not phoned home this week when its solar panels were projected to receive enough sunlight to turn on its radio.
The lander touched down at a wonky angle on February 22, but was still able to complete several tests and send back photos before its mission was determined to have ended a week later, as it entered a weeks-long lunar night.
Intuitive Machines had hoped that it might "wake up" once it received sunlight again, as Japan's SLIM spaceship -- which landed upside down in January -- did last month.
The company said Saturday on X, formerly Twitter, that after several days of waiting, operators had confirmed that the power system of the lander, nicknamed "Odie," would "not complete another call home."
"This confirms that Odie has permanently faded after cementing its legacy into history as the first commercial lunar lander to land on the Moon," it said.
The mission has been hailed as a success by Intuitive Machines and NASA, even as it ran into multiple problems along the way, including the tip-over at landing.
It was also the first lunar touchdown by an American spaceship since the manned Apollo 17 mission in 1972.
NASA is planning to return astronauts to the Moon later this decade. It paid Intuitive Machines around $120 million for the mission as part of an initiative to delegate cargo missions to the private sector and stimulate a lunar economy.
Odysseus carried a suite of NASA instruments designed to improve scientific understanding of the lunar south pole, where the space agency plans to send astronauts under its Artemis program later this decade.
Intuitive Machines has two more Moon missions planned this year, both part of NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, which works with the private sector.
The United States, along with international partners, wants to eventually develop long-term habitats in the region, harvesting polar ice for drinking water -- and to produce rocket fuel for eventual onward voyages to Mars.