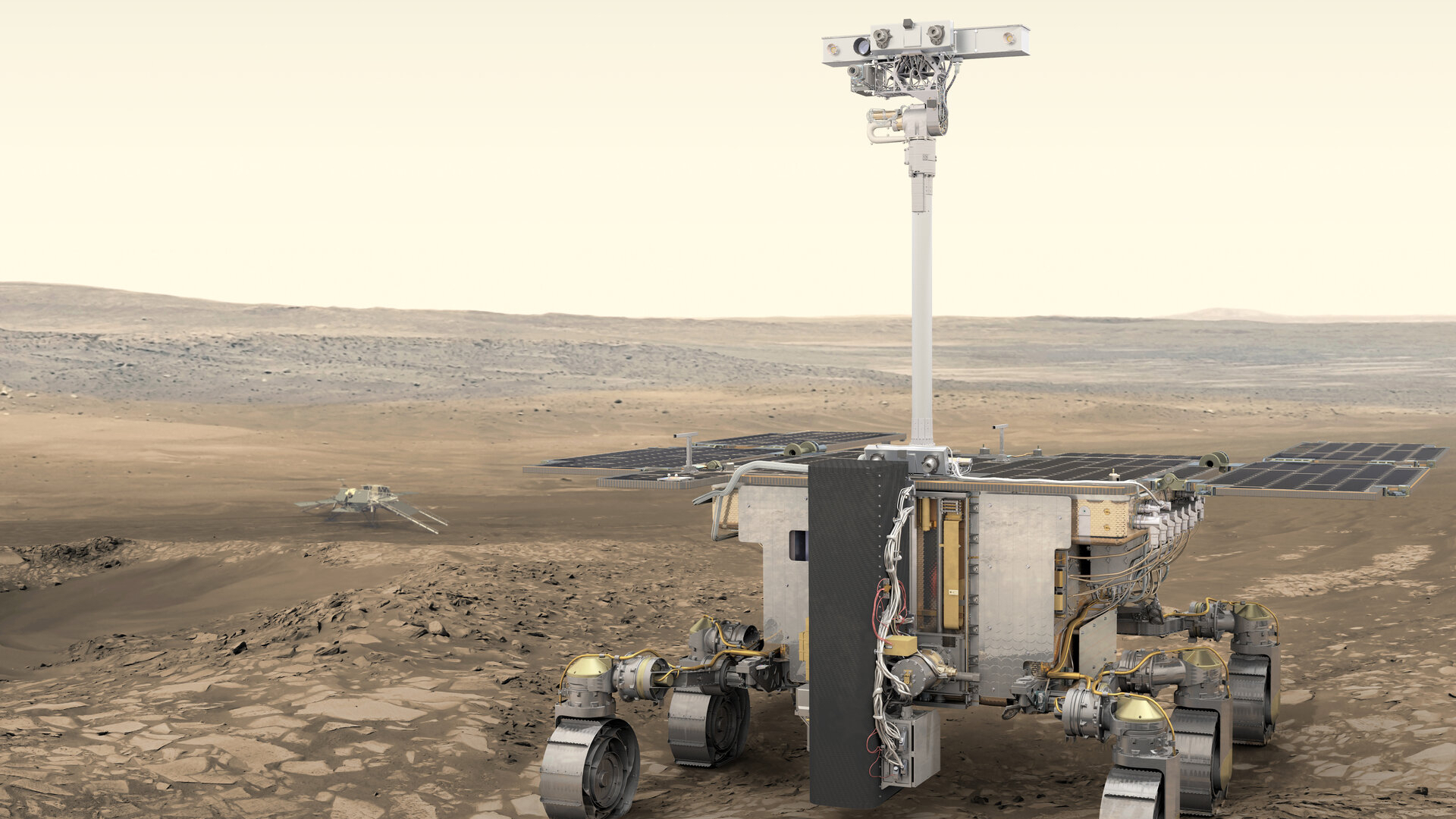
Europe's long-delayed ExoMars rover mission to the Red Planet just got a boost for its projected launch in 2028.
NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) inked a memorandum of understanding on Thursday (May 16), thereby officially joining forces on the endeavor, which will send a life-hunting rover named Rosalind Franklin to Mars.
Two years ago, ESA cut ties with Russia's space agency Roscosmos, the former main partner on ExoMars, due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. As a result, the mission missed its intended launch window and now must wait for 2028. (Mars and Earth align properly for interplanetary missions just once every 26 months.)
Now ESA, its member states and European industry, along with NASA, are hammering out new synergies and partnerships.
Related: ExoMars: Europe's astrobiology missions to Mars
U.S. contributions
Here’s the new deal for ExoMars:
NASA's Launch Services Program will procure a commercial U.S. rocket to launch Rosalind Franklin. The U.S. space agency will also provide part of the propulsion system needed to get the rover down safe and sound on Mars, as well as heater units for the robot.
Those last elements will be lightweight radioisotope heater units (RHUs), provided by NASA in partnership with U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). In parallel, work on the development and certification of a European RHU to fly on the mission will continue, led by the U.K., according to ESA officials.
Called the ESA GSTP/ENDURE program (ENDURE standing for "European Devices Using Radioisotope Energy"), the U.K. work is focused on delivery of an end-to-end European capability for radioisotope heat and power systems by the end of this decade.
Drilling down — politically and scientifically
Rosalind Franklin is built to drill to a depth of up to 6.5 feet (2 meters) below the Martian surface. Doing so will allow access to samples of Mars that have been protected from surface radiation and extreme temperatures.
ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher spotlighted ExoMars in an exclusive interview with Space.com last month at the Space Foundation’s 39th Space Symposium, held in Colorado Springs.
"ExoMars started around 2010-201l, with NASA originally a partner. But budget issues had NASA drop out. So then in working with Russia it moved forward for about 10 years. With war in Ukraine and the sanctions that our member states imposed on Russia, I could not finish the program," Aschbacher said.
"And this is something quite drastic," he added. "The ExoMars rover was finished and ready for launch in September 2022. The war started in February 2022, so I stopped and terminated the cooperation with Russia."

Finding some microbes?
As for how important ExoMars is in the ongoing study of the Red Planet, Aschbacher is ready for new, prime-time revelations.
"It will drill into the surface, which is quite unique. There’s no chance to find life on the surface. You have to go down, and exobiologists are saying at least 1.5 meters, and we go down 2 meters," said Aschbacher.
"Can you imagine how exciting this will be?" the ESA chief added. "Just imagine finding some microbes of life and to analyze whether there is DNA or no DNA. Would the DNA be similar to ours or not? Unimaginable … and we just don’t know."







