by tupungato from Getty Images; Canva
The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States. It is categorized into three key entities:
- The Board of Governors determines Fed policies, oversees internal operations, and manages the public-facing Federal Reserve system.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) manages open market operations and sets the Fed funds rate, which is the basis for prevailing interest rates.
- The twelve regional Reserve Banks print currency, make loans, and conduct all other fiscal operations.
Even though it works closely with government agencies like the U.S. Treasury, the Fed is considered an independent agency because its decisions do not have to be approved by the U.S. President, and it does not receive funding from Congress.
Why Are Federal Reserve Banks Important?
While many people know about the Fed’s “dual mandate” to promote a healthy economy through stable prices and maximum employment, most think its responsibilities are strictly on the macro-level: formulating and managing monetary policies set through the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), for example.
But the Fed also plays a very hands-on role as chief supervisor and regulator of the nation’s banks—and it literally serves as the bank of the Federal government. Just like businesses and consumers have checking accounts with their local bank, the U.S. Treasury has a checking account with the Federal Reserve, which it uses to process government payments and deposit federal taxes.
In a similar fashion, the regional Federal Reserve Banks serve as the “bank for banks,” and their primary responsibility is to regulate and supervise these financial institutions. They serve as a link between the Federal Reserve and the private sector, reporting critical insights back to the Fed about current economic conditions in different parts of the United States, which are then factored into its policy decisions.
How Many Federal Reserve Banks Are There?
There are 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks and 24 branches. Each Reserve Bank is separately incorporated, and they are governed by a president who is appointed from its nine-person board of directors. Under the terms set forth in the Federal Reserve Act, the president is mandated to have “tested banking experience,” which typically means experience in commercial banking or financial services.
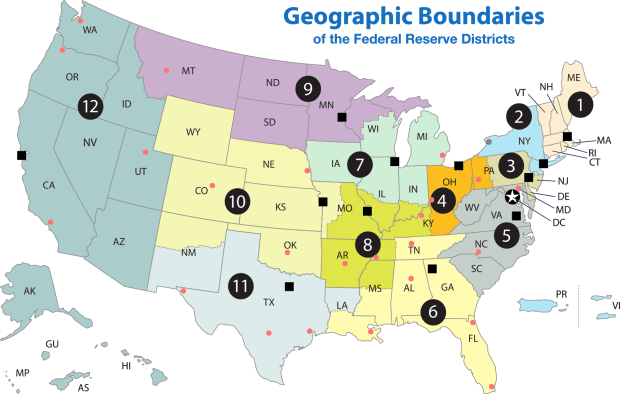
Federal Reserve Bank presidents meet with the Fed’s Board of Governors every six weeks at Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meetings in Washington, DC. These meetings determine whether the Fed funds rate will be raised, lowered, or left unchanged in order to fulfill the Fed’s mandate to promote stable prices and strong employment for the American people. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York is a permanent voting member of the FOMC, while four other Reserve Bank presidents serve on a rotating basis.
In each Federal Reserve District, commercial banks are required to hold stock in their District’s Reserve Bank. They are also responsible for electing six of the Reserve Bank’s directors. The other three Reserve Bank directors receive their appointments from the Fed’s Board of Governors in Washington, DC.
As seen in the graphic above, most of the Reserve Banks have at least one Branch; their Branch directors are appointed by either their District’s Reserve Bank or the Fed’s Board of Governors.
What Are Some Federal Reserve Bank Responsibilities?
Unlike commercial banks, which are operated in the interest of shareholders and clients, Reserve Banks serve the public interest.
Their responsibilities include:
- Supervising state-chartered member banks, thrift holding companies, and other “systemically important” financial institutions
- Ensuring liquidity in the financial system by making loans to depository institutions
- Providing financial services like clearing checks, distributing paper currency and coins, and processing electronic (ACH) payments
- Monitoring commercial banks to make sure they remain in compliance with federal consumer protection and fair lending laws
Every two weeks, each Reserve Bank’s board makes recommendations on the rate offered to depository institutions through its discount window. These recommendations are subject to review by the Board of Governors.
What Is the Fed’s “Beige Book?”
The reports gathered from each Federal Reserve Bank and Branch director are compiled and published eight times per year into a publication known as the “Beige Book,” or by its official name, the Summary of Commentary on Current Economic Conditions. The Beige Book provides updates from each District through narratives from its Bank and Branch directors, interviews with economists and other financial experts, and other timely and relevant sources. The Beige Book gets its name from the color of its cover.







