Intel on Wednesday said that its 3nm-class process technology called Intel 3 has entered high volume production at two sites as well as provided some additional details about the new production node. The new process brings in both higher performance and higher transistor density as well as supports voltages of 1.2V for ultra-high-performance applications. The node is aimed at Intel's own products as well as at foundry customers. It will also evolve over the coming years.
"Our Intel 3 is in high volume manufacturing in our Oregon and Ireland factories, including the recently launched Xeon 6 'Sierra Forest' and 'Granite Rapids' processors," said Walid Hafez, Foundry Technology Development Vice President at Intel.
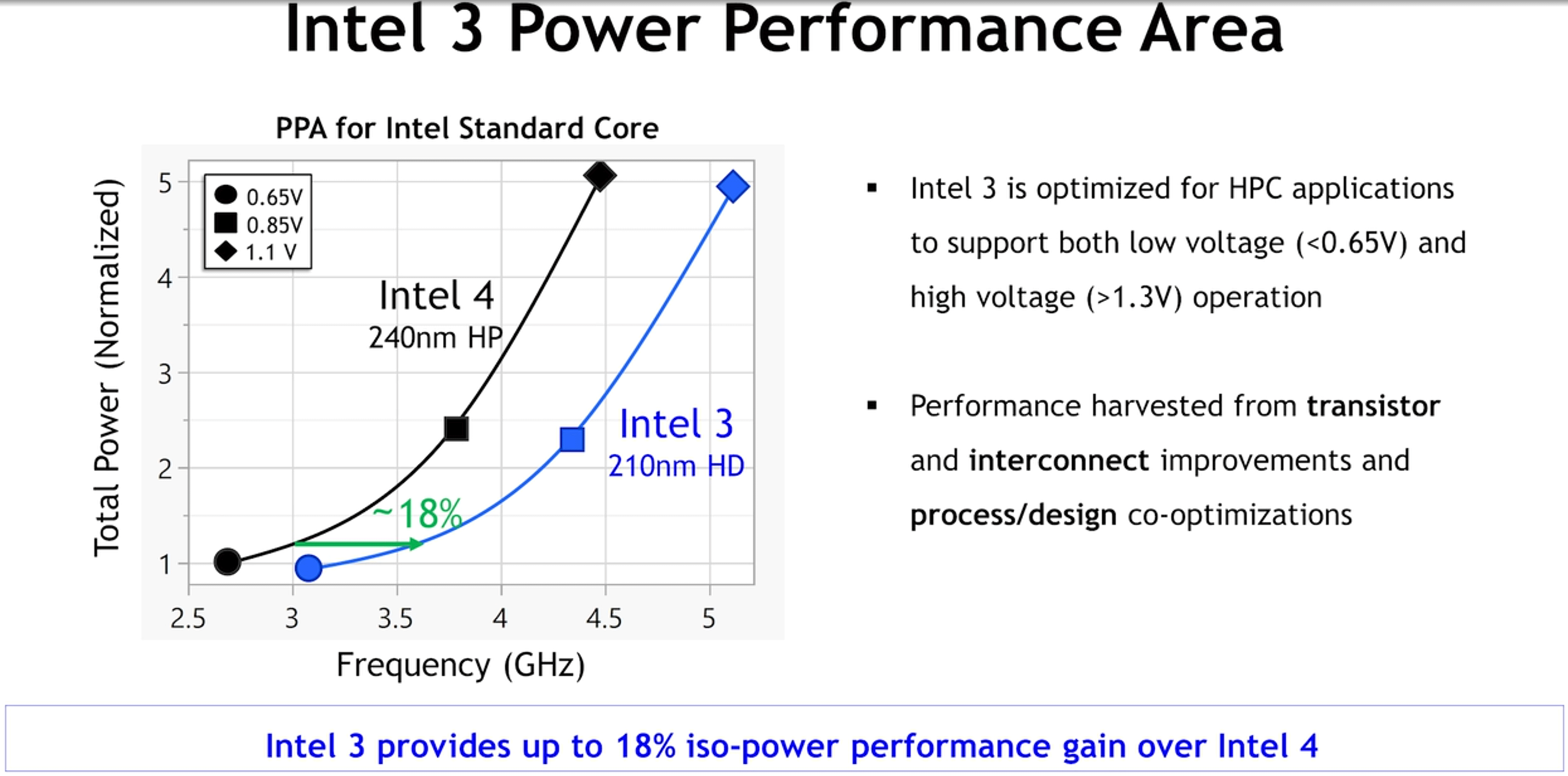
Intel has always positioned its Intel 3 fabrication process to be aimed at datacenter applications that require leading-edge performance enabled by revamped transistors (compared to Intel 4), their power delivery circuitry with reduced transistor via resistance, and design co-optimization. The production node supports both <0.6V low voltage as well as >1.3V high voltage for maximum loads. When it comes to performance, Intel promises that the new node will enable 18% higher performance at the same power and transistor density compared to Intel 3.
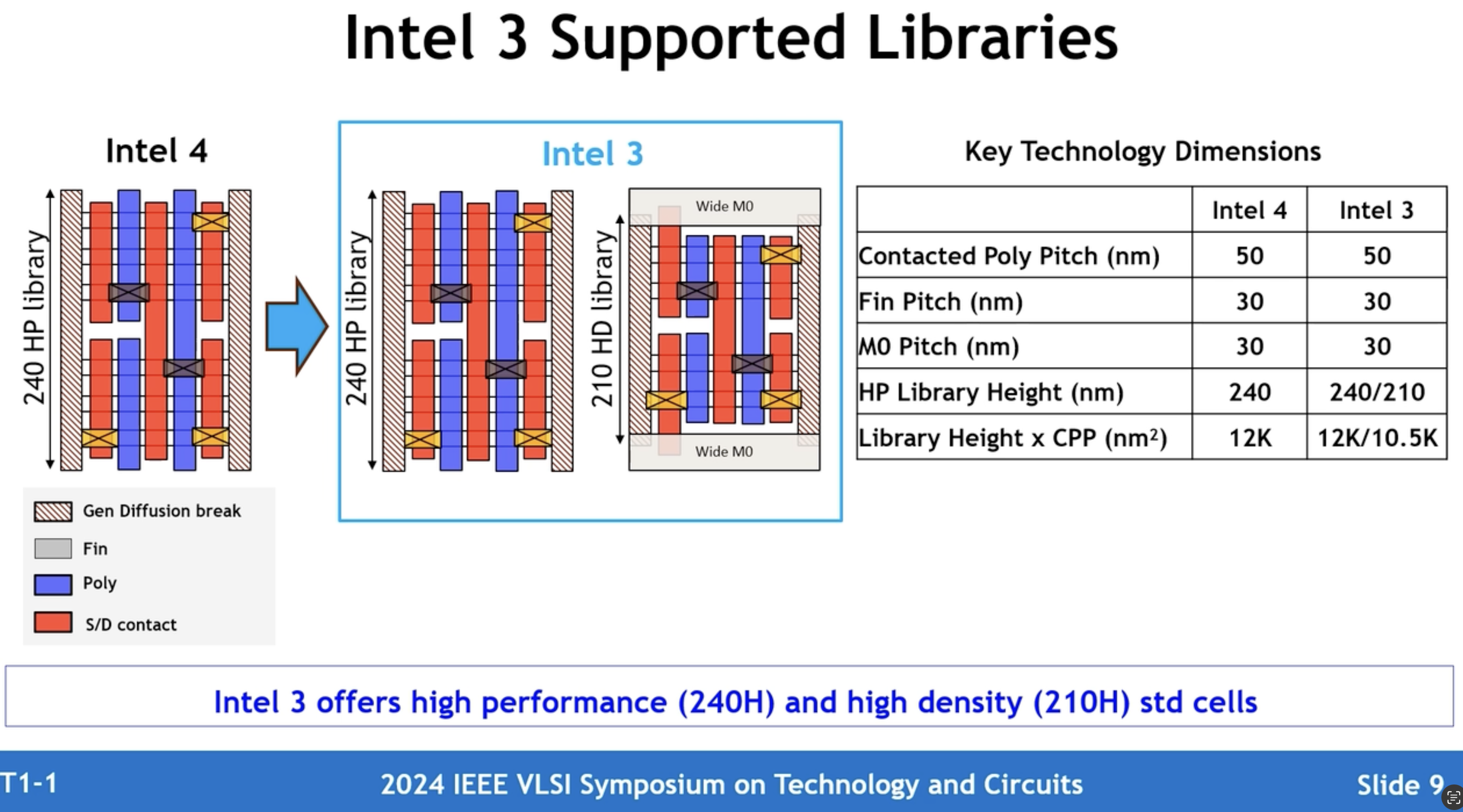
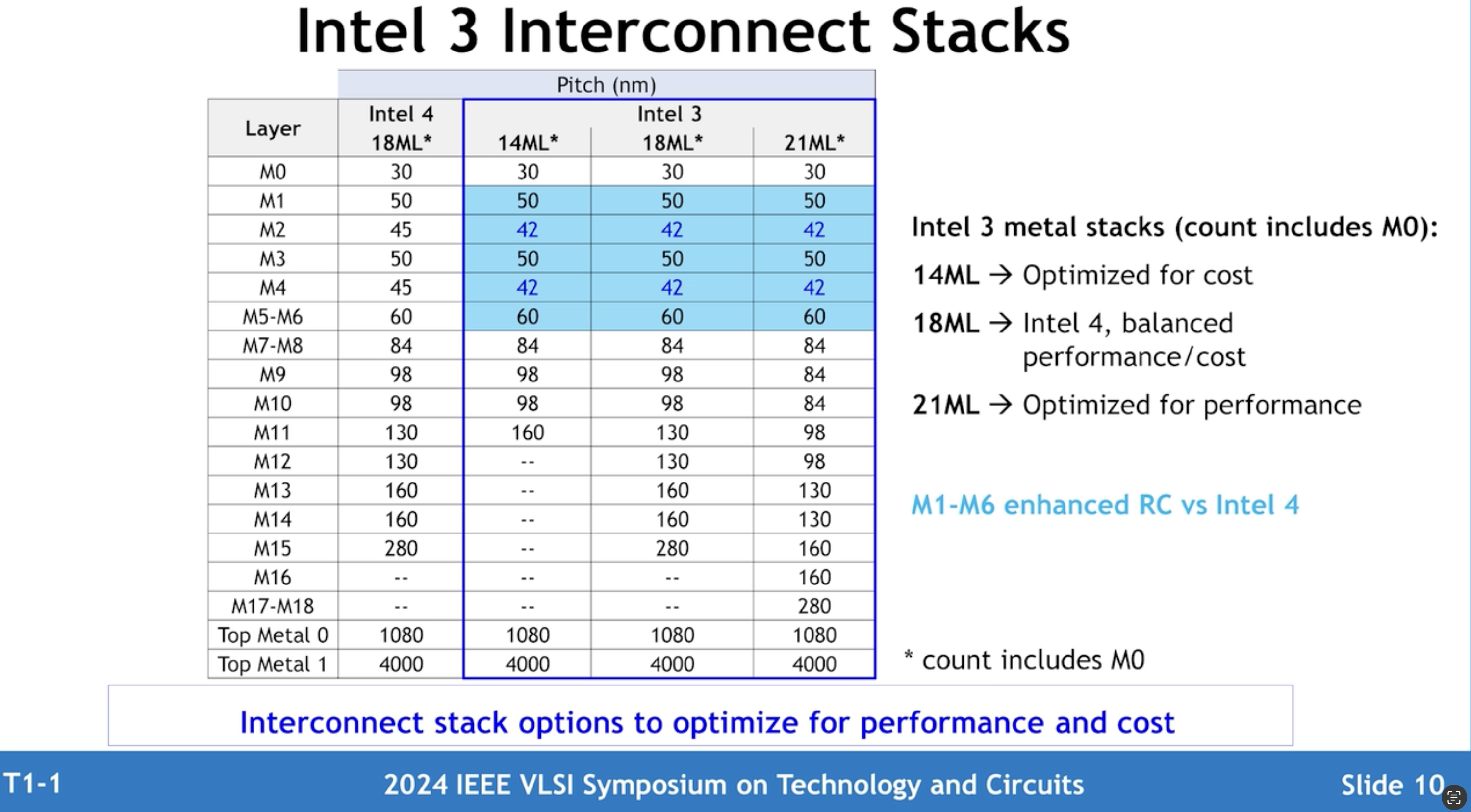
To get the best combination of benefits for performance and density, chip designers will have to use a combination of 240nm high performance and 210nm high density libraries. Furthermore, Intel clients can choose between three metal stacks: 14 layers for costs, 18 layers for an optimal balance between performance and cost as well as 21 metal layers for higher performance.
For now, Intel will use its 3nm-class process technology to make its Xeon 6 processors datacenters. Eventually Intel Foundry will use the production node to manufacture datacenter-grade processors for its customers.
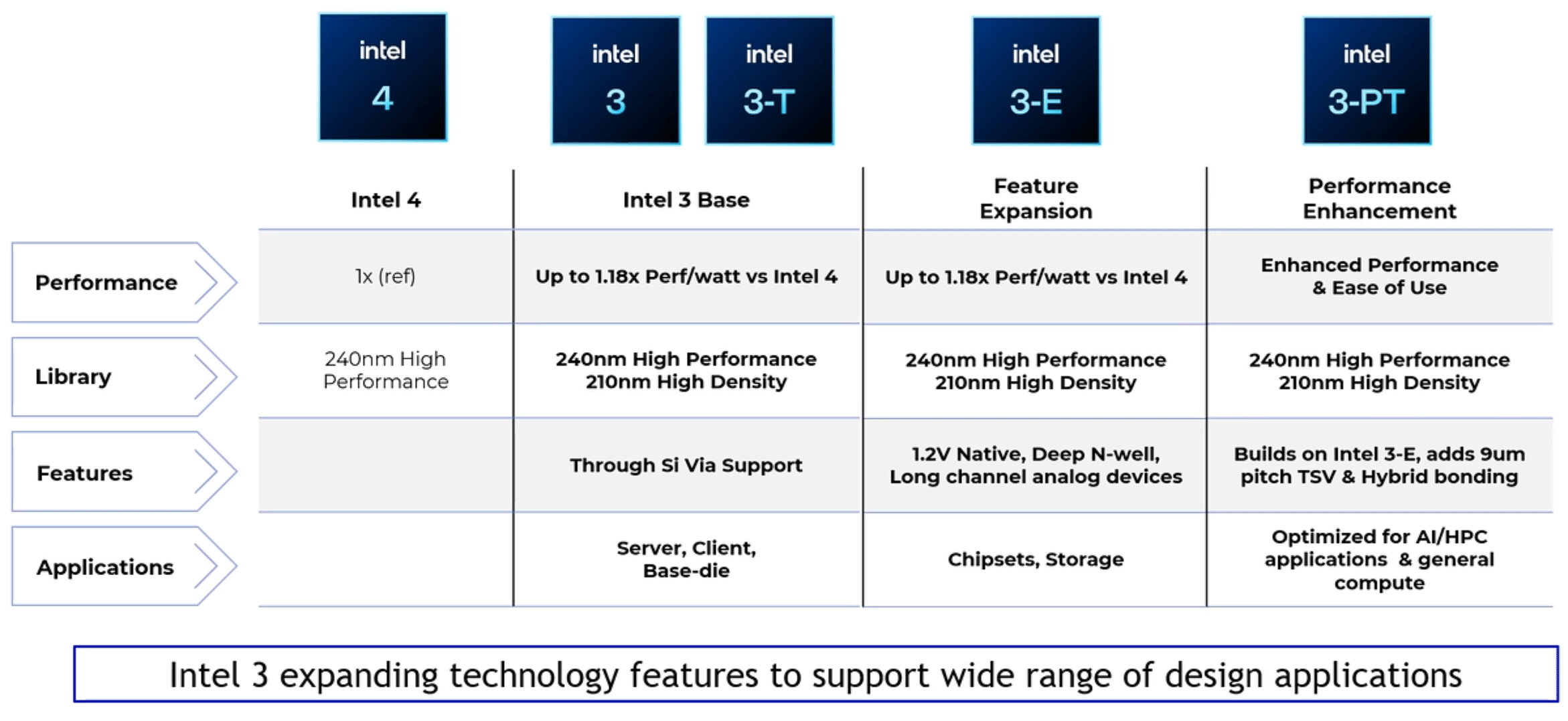
In addition to base Intel 3, the company will also offer Intel 3T that supports through silicon vias and can be used as a base die. In the future, Intel will offer feature-enhanced Intel 3-E for chipsets and storage applications, and performance-enhanced Intel 3-PT that can be used for a wide range of workloads, such as AI/HPC and general purpose PCs.







