Diversity, equity and inclusion efforts have become increasingly visible in U.S. workplaces, especially over the past five years. However, DEI has recently come under attack, with companies scaling back their DEI plans.
As a professor of organizational psychology, I believe businesses should refine rather than abandon these efforts. Introducing a powerful concept, “belonging,” could hold the key.
Although people mistakenly use “belonging” and “inclusion” interchangeably, their differences matter a lot – and can have a significant impact on employee satisfaction and organizational success.
What DEI is and why it’s struggling
Diversity initiatives have a long history in American workplaces, but it’s only recently that “DEI” has become a buzzword. DEI refers to policies and initiatives implemented by organizations to ensure fair treatment of and full participation by all people.
Adoption of formal DEI programs has seen significant growth. In 2019, around 64% of organizations had some form of DEI initiative. By 2023, this rose to 89%, demonstrating a clear upward trend.
Research shows that companies with diverse teams are 70% more likely to capture new markets and are 87% better at making decisions. Additionally, 85% of CEOs report diverse workforces improving profitability. Despite this, a trend of businesses and schools significantly or completely eradicating their DEI initiatives has become prevalent in 2024.
What happened? While external factors contributed to the backlash, including political pressure and a changed legal environment, research suggests that problems with how DEI is conceptualized and practiced also bear a fair share of the blame.
Misunderstanding DEI
While diversity and inclusion are often well-intentioned, many organizations that approached change initiatives solely through diversity metrics have failed. Effective DEI strategy focuses on learning and development, mentorship, and allyship, extending beyond race and gender. The challenge comes from narrow views of DEI, driving oversimplifications and zero-sum thinking.
For example, people have multiple intersecting identities, with complex traits that often depend on social context. But some DEI efforts ignore that complexity, reducing employees to a single category, such as gender, race, age or disability status. That leaves people, regardless of whether they feel included in “ingroups” or “outgroups,” feeling diminished.
Similarly, research shows that people’s actions and opportunities are strongly influenced by their environment. But too often, DEI efforts place the responsibility for growth entirely on individuals. That actually reinforces people’s biases because group dynamics and social structures shape collective behaviors.
When models fail to distribute accountability and responsibility effectively, collective behavior will uphold toxic environments.
To be fair, not all organizations have fallen into these traps. Those with leaders that adopted a more contemporary understanding of power and bias have developed more effective strategies for employees to thrive.
My research suggests that for DEI initiatives to succeed, respect and fairness must be present. These requirements are rooted in the foundations of belonging.
DEI’s evolution: Integrating belonging for lasting impact
While belonging is related to inclusion, research shows it’s much more than just a synonym.
Inclusion may focus on being seen, accepted and valued within a team or community. Belonging goes deeper, involving a genuine sense of connection and identity within a group.
To truly experience belonging, it’s not enough to feel included; my research shows that five critical indicators must also be present.
These elements ensure that individuals feel a deep, meaningful attachment to the group, which inclusion alone cannot fully achieve. This distinction underscores that belonging is a unique and essential experience, distinct from inclusion, and critical for fostering a truly cohesive and supportive environment.
So what are the five indicators of belonging? They are comfort, connection, contribution, psychological safety and well-being, and all of them can be measured.
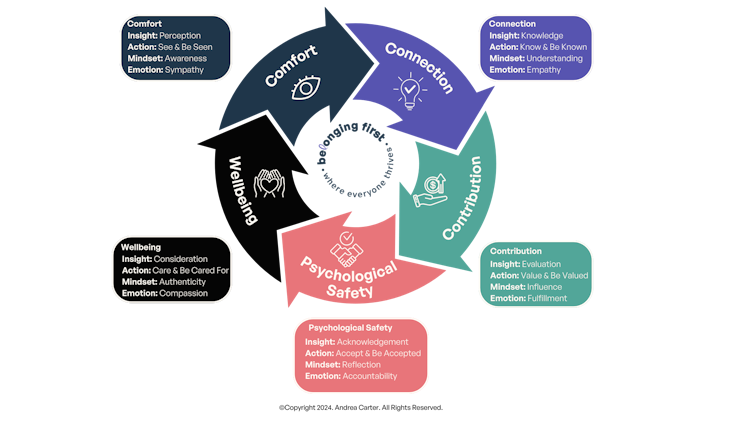
When an environment is high in each of the five indicators, and the measured gap between the ingroup and outgroup is low, it suggests an environment where responsibility for creating opportunities to thrive are shared and balanced. Let’s unpack these concepts:
Comfort. When an organization is high in comfort, people feel seen for who they are. This requires them to accept that others have complex, sometimes contradictory identities, and to adopt a mindset of awareness. Perhaps counterintuitively, achieving comfort requires being a little uncomfortable, too. That’s because respectfully seeing and being seen means acknowledging other people’s discomfort.
Connection. Connection is the need to be known and trusted. For an organization to score high on connection, people will be aligned on values and goals. Connection creates a shared sense of responsibility and accountability. This shared responsibility is a foundation for empathy, since trust and fairness are born from understanding and empathizing with the social and emotional needs of others.
Contribution. An organization high in contribution values its members for the unique and diverse attributes they bring to the table. In belonging environments, an individual’s contribution is evaluated through curiosity and openness; ideas and perspectives are shared to influence and challenge the status quo, driving innovation and creativity. When someone is genuinely acknowledged for their contributions, both they and their team feel fulfilled.
Psychological safety. When a person is genuinely accepted into a group, making a mistake or even failing is seen as a chance to learn and grow, not an opportunity to shame, blame or exclude. This is the essence of psychological safety. In cases where people’s perspectives are dramatically different, psychological safety requires everyone to reflect and put themselves in the shoes of the other to respect their differences and be accountable for behavior.
Well-being. In an organization high in well-being, members’ experiences are considered and cared for. This requires everyone to share responsibility for caring for individuals, groups, teams and the organization as a whole, each with their authentic needs.
Belonging, based on my research, is not just a buzzword; it’s the bedrock of a thriving, innovative workplace. Leaders who understand this and take action can enhance individual well-being while unlocking the full potential of their teams.
By committing to building environments where the indicators of belonging are prioritized, leaders can ignite passion, loyalty and excellence in their workplaces.
Andrea Carter is an Adjunct Professor for Adler University and the CEO and Founder of Belonging First, a consulting firm that advises companies on how to refine their DEI initiatives.
James D. Halbert does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







