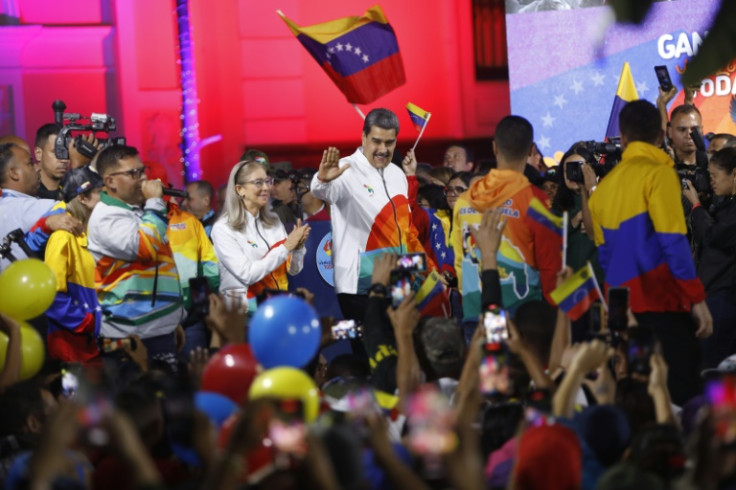
Guyana said Monday it would remain "vigilant" after Venezuelans voted overwhelmingly in favor of claiming an oil-rich border region that makes up more than two-thirds of its territory.
"We have to always remain vigilant. Of course, our monitoring must be always at a high level. President Maduro, while we don't believe he will order an invasion... can do something that can be very unpredictable," Foreign Minister Hugh Todd told AFP.
Earlier, Caracas said more than half of eligible Venezuelan voters had taken part in the referendum that yielded a 95 percent "yes" outcome.
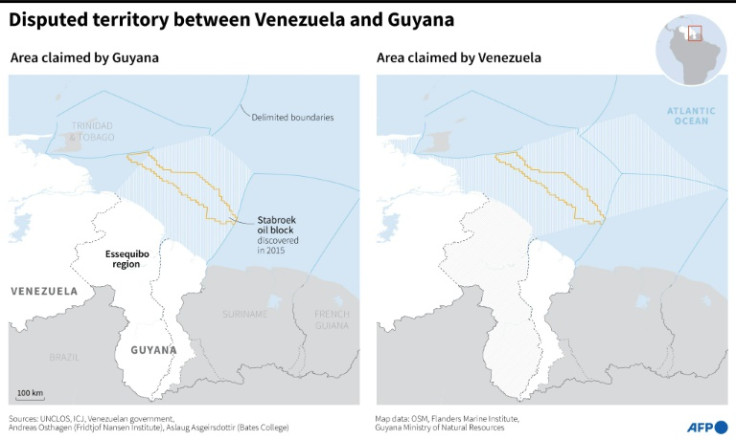
Venezuela has for decades laid claim to Essequibo, which Guyana has administered for over 100 years and is home to 125,000 of its 800,000 citizens.
Litigation is pending before the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in The Hague over where the borders should lie.
Guyana, a former British and Dutch colony, insists the frontiers were determined by an arbitration panel in 1899.
But Venezuela -- which does not recognize the ICJ's jurisdiction in the matter -- claims the Essequibo River to the region's east forms a natural border and had historically been recognized as such.
The dispute has intensified since ExxonMobil discovered oil in Essequibo in 2015.
Caracas called Sunday's referendum after Georgetown started auctioning off oil blocks in Essequibo in August.
Voters were asked five questions in Sunday's referendum, including whether or not Venezuela should reject the 1899 arbitration decision as well as the ICJ's jurisdiction.
They were also asked whether or not Venezuelan citizenship should be granted to the people -- currently Guyanese -- of a new "Guyana Esequiba State."
There was a massive campaign for Venezuelans to vote "yes," but none against the measure.
More than 10.4 million out of 20.7 million eligible voters cast their ballots, National Electoral Council president Elvis Amoroso said Monday, seeking to lay to rest initial doubts over the turnout.
The initial tally had been met with suspicion by opposition politicians and analysts, who said it appeared voters' responses to each of five questions on the referendum may have been counted as separate ballots cast.
Low voter turnout was observed at polling stations in Caracas and other cities, fueling doubts.
The figure of 10.4 million announced Monday by Amoroso, accompanied by President Nicolas Maduro, is the highest turnout ever in a Venezuelan election.
Maduro has hailed an "overwhelming victory."
"We have taken the first steps of a new historic stage in the struggle for what belongs to us, to recover what the liberators left us," he said.
The referendum raised fears in Guyana, and further afield, about Venezuela's ultimate intentions for the contested territory.
Todd told AFP Guyana would maintain defense cooperation with the United States and other strategic partners and continue diplomatic efforts to persuade Venezuela to let the ICJ make the final determination.
"We have already made it clear that we will abide by the ruling of the court," he said.
Guyana had asked the ICJ to block Sunday's vote.
On Friday, the court urged Caracas to take no action that might affect the disputed territory, but did not grant Georgetown's request for urgent intervention.
Guyana said the referendum posed an "existential" threat to the country as it could pave the way for Venezuela to "unilaterally and illegally" seize the region.