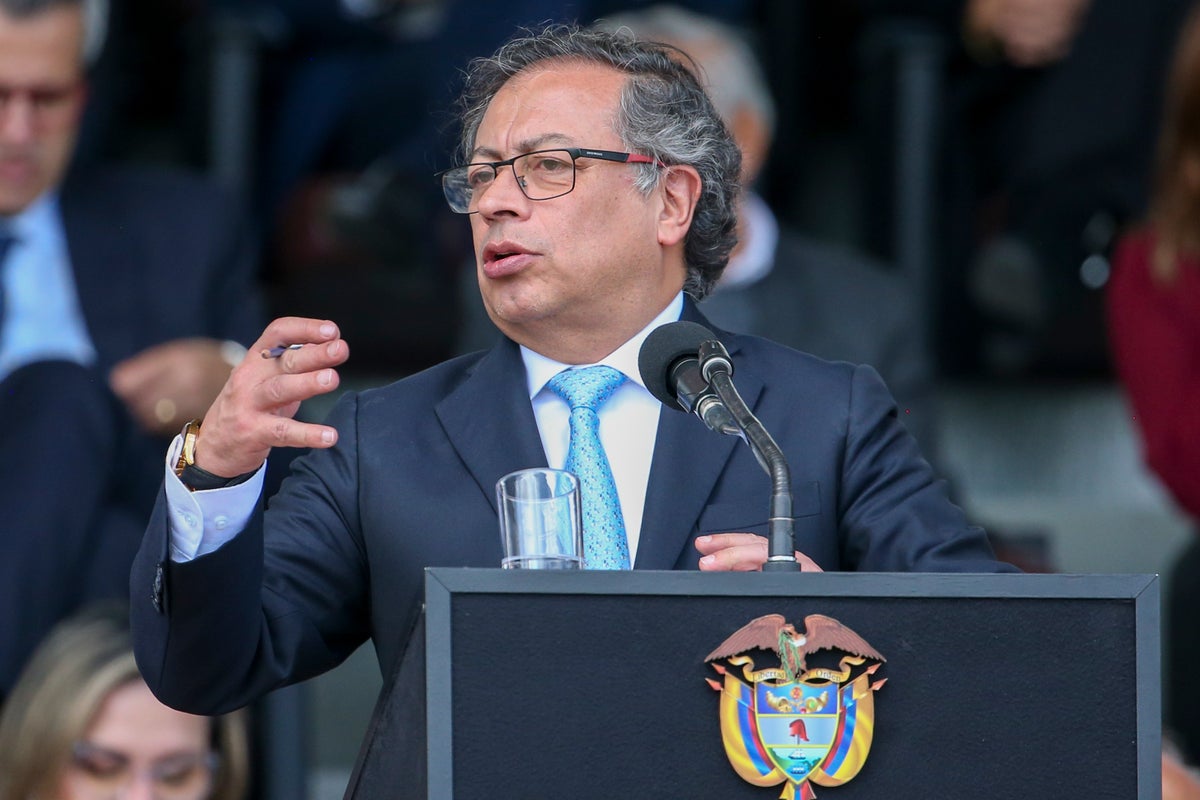
Colombian rebel leader Pablo Beltran said on Tuesday that peace talks between his National Liberation Army and the government have been put “on pause” due to remarks made last week by President Gustavo Petro.
Petro questioned whether members of the rebel group's delegation in Cuba could effectively control the actions of their own commanders on the battlefield. He also said the younger leaders of the group, known as the ELN, were motivated not by political goals, but by drug trafficking profits.
In an interview published on Youtube by the ELN’s communication team, Beltran said that delegations from both sides would have to meet to “examine” the comments by Colombia's president before issues like a ceasefire and rural development schemes can continue to be discussed. The negotiations began in November and have failed to produce any major breakthroughs so far.
The ELN was recognized as “an armed rebel group” by Colombia’s government during the last round of talks which took place in Mexico, a designation that enables it to seek policy changes in peace talks instead of just negotiating reduced sentences for their crimes. Beltran argued that Petro’s recent comments are putting its status as a “political organization” in jeopardy.
“If they are saying one thing in the negotiations, while the president says another we feel like we are stuck in the middle,” Beltran said. “So we are asking for an explanation.”
During a speech to military officers on Friday, Petro described members of the ELN’s peace delegation as “elderly” leaders who were interested in discussing political changes. But he questioned whether younger ELN commanders who lead troops on the ground have the same kind of goals.
“They may use the same banners,” Petro said. “But what motivates them is (profiting from) illicit economies.” Petro added that elderly leaders like Beltran were “willing to sit down and talk. But are they really in charge?”
The ELN was founded in the 1960s by union leaders, students and priests inspired by the Cuban revolution. It is Colombia’s largest remaining rebel group and has been notoriously difficult for previous Colombian governments to negotiate with.
In 2016, Colombia’s government signed a peace deal with the larger FARC group that ended five decades of conflict in which an estimated 260,000 people were killed. But violence has continued to affect rural pockets of the country where the ELN has been fighting the Gulf Clan and FARC holdout groups for the control of drug trafficking routes and other resources.
Petro promised during his presidential campaign that he would seek peace deals with all of Colombia’s major armed groups by rolling out a strategy he described as “total peace.”
But the Gulf Clan recently gave up on the peace talks, while negotiations with FARC holdout groups are still in preliminary stages.