The history of climate change is one of people slowly coming to terms with the truth. None but a small minority still question whether it’s real and caused by humans. Now most grapple with the reality of trying to slow down catastrophic warming, and the difference between solutions and false hope. The concept of climate overshoot is the next thing we will need to get to grips with.
Unless urgent action is taken, emissions are expected to cause the planet to continue heating rapidly over the next few decades, prompting the global average temperature to overshoot the Paris agreement’s target, which aimed to limit warming to between 1.5°C and 2°C. A period of higher temperatures will occur in the middle of this century as a result. Then, the idea goes, new but yet unproven technologies and techniques for pulling greenhouse gases from the atmosphere will eventually bring temperatures back down to a safer level.
Until now, scientists were unsure what temporarily overshooting (and then boomeranging back below) the Paris agreement’s temperature target would entail for nature. So, for the first time, we studied the consequences of allowing Earth’s temperature to exceed these precautionary limits, then fall below them again, for marine and land-based life. In other words, we looked at how damaging the journey of overshooting the 2°C temperature target would be, and not just the destination itself.
The results suggest that a temporary overshoot would cause waves of irreversible extinctions and lasting damage to tens of thousands of species. This is what the world can expect if humanity fails to make deep emission cuts this decade, and relies instead on future technologies to remove emissions later.
Harm arrives fast and leaves slowly
Our study modelled the impact of global temperatures exceeding 2°C for around 60 years between 2040 and 2100 on over 30,000 species that live on land and in the sea. We looked at how many of them would be exposed to temperatures that could hinder their reproduction and survival, and how much time they would be exposed to this risk.
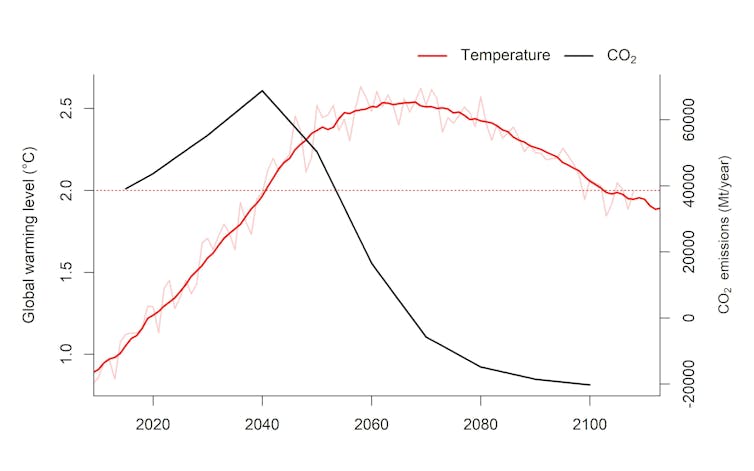
Harm would be fast to arrive and slow to disappear for nature, even after temperatures fall again. Just a few years of global temperatures above 2°C could transform the world’s most important ecosystems. Take the Amazon basin, for example. Some species would remain exposed to dangerous conditions long after the global average temperature stabilised – with some remaining exposed as late as 2300. This is because some species, especially those in the tropics, live closer to the limit of heat they can tolerate and so are sensitive to relatively small changes in temperature. And while global average temperatures may return to safer levels eventually, local temperature changes might lag behind.
The consequences of this exposure could be irreversible and include the tropical forest turning into savanna. The world would lose a critical global carbon sink, leaving more planet-warming gases in the atmosphere.
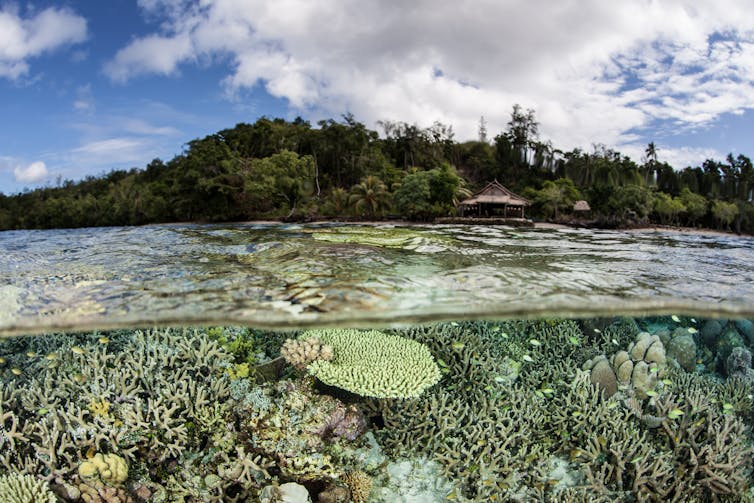
The Coral Triangle in the western Pacific Ocean is one of the most species-rich marine ecosystems and home to many reef-building corals, sea turtles, reef fish and mangrove forests. Our modelling showed that in some communities, all or most of the species would be exposed to dangerous conditions simultaneously for at least a few decades and as much as two centuries. As well as disrupting a source of food for millions of people, disappearing corals and mangroves would remove a natural barrier protecting coastal towns and villages from rising seas and worsening storms.

No way home
The consequences of overshooting 2°C for the survival of species have been neglected by policymakers. Our analysis indicates that it cannot be assumed that life will simply recover once temperatures fall below 2°C again. We found that 3,953 species will have their entire population exposed to temperatures outside the range they evolved in for more than 60 consecutive years. The Philippine porcupine will be exposed for 99 years, and the Mawa clawed frog for an astonishing 157 years. Surviving this length of exposure is a stern challenge for any species.
Relying on carbon dioxide removal and so-called negative emissions technologies to lower greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over several decades is too risky to contemplate. Some of this technology, like carbon capture and storage, hasn’t yet been shown to work at the scale needed. Other techniques have negative effects on nature, such as bioenergy, where trees or crops are grown and then burned to generate electricity. Rolling out vast plantations at the same time as temperatures overshoot the internationally agreed “safe” limit would leave species reeling from a hotter climate and shrinking natural habitat.
Delaying drastic cuts to emissions will mean the world overshooting 2°C is a best-case scenario. This overshoot would come at an astronomical cost to life on Earth that negative emission technologies will not reverse. The effort to stop temperatures rising isn’t an abstract attempt at bending curves on a graph: it’s a fight for a liveable planet.

Don’t have time to read about climate change as much as you’d like?
Get a weekly roundup in your inbox instead. Every Wednesday, The Conversation’s environment editor writes Imagine, a short email that goes a little deeper into just one climate issue. Join the 10,000+ readers who’ve subscribed so far.
Joanne Bentley received funding as a result of a collaboration between the UK Royal Society and the African Academy of Sciences.
Alex Pigot receives funding from the Royal Society and the Natural Environment Research Council.
Andreas L. S. Meyer received funding as a result of a collaboration between the UK Royal Society and the African Academy of Sciences.
Christopher Trisos is an author for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







