When they lived: 700,000 years ago to 4,000 years ago
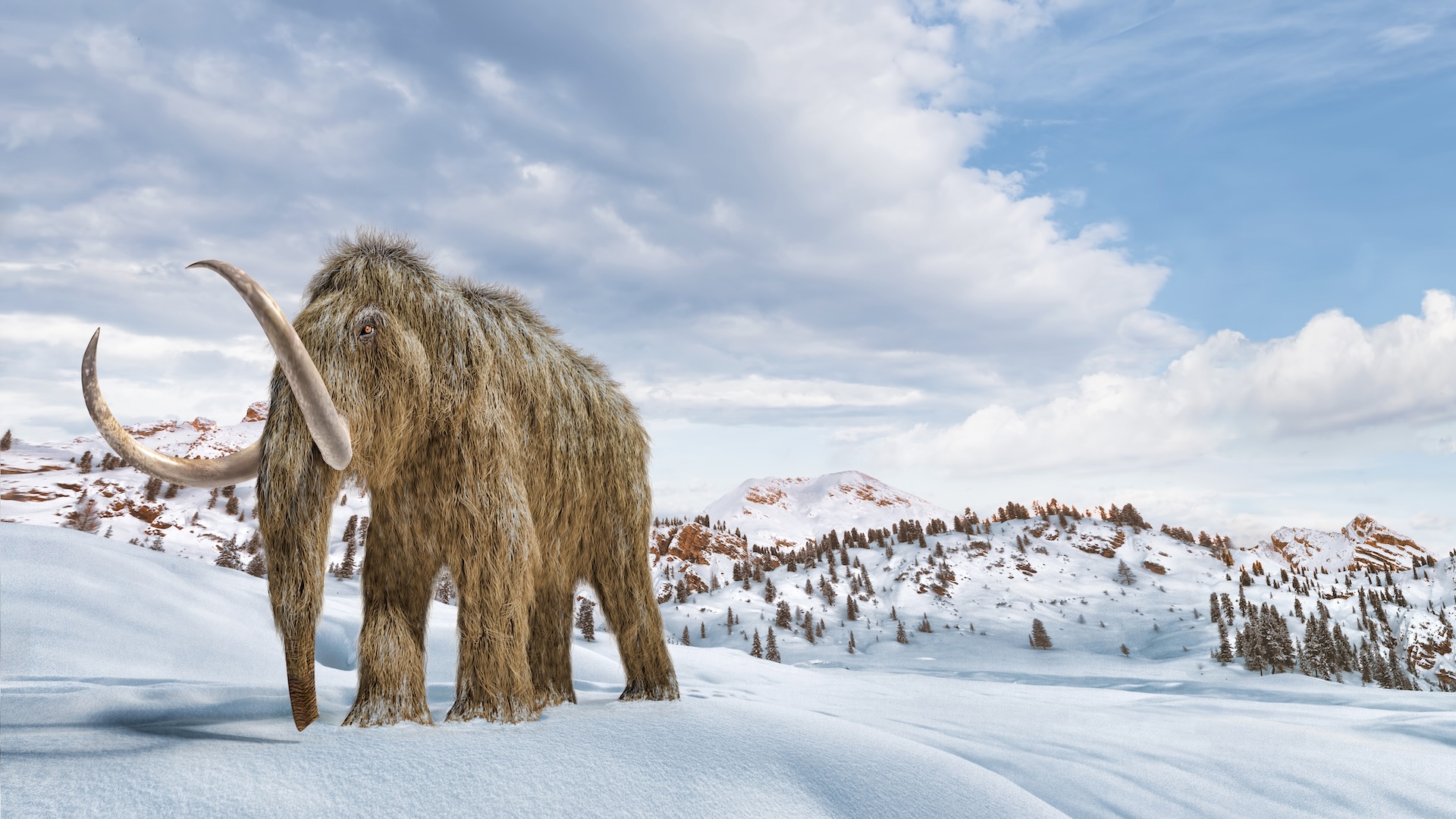
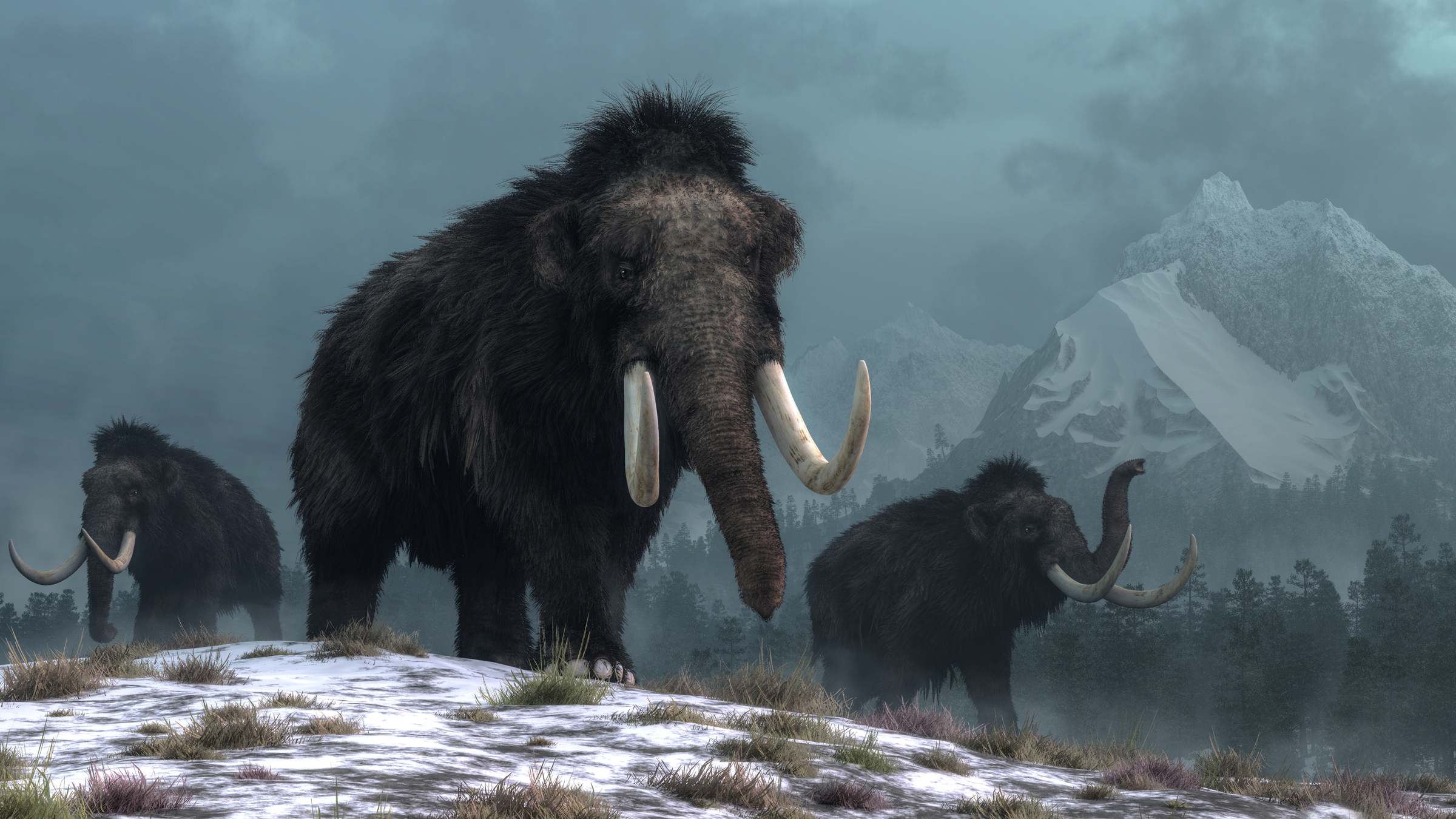
What they looked liked: They had shaggy hair, fatty humps and curved tusks
Size and weight: up to 11 feet and 12,000 pounds
Babies' weight: Around 200 pounds
Where they lived: Eurasia and North America
Woolly mammoths were extinct, shaggy beasts that were relatives of today's Asian elephants (Elephas maximus). They lived across North America and Eurasia for about 700,000 years and went extinct around 4,000 years ago.
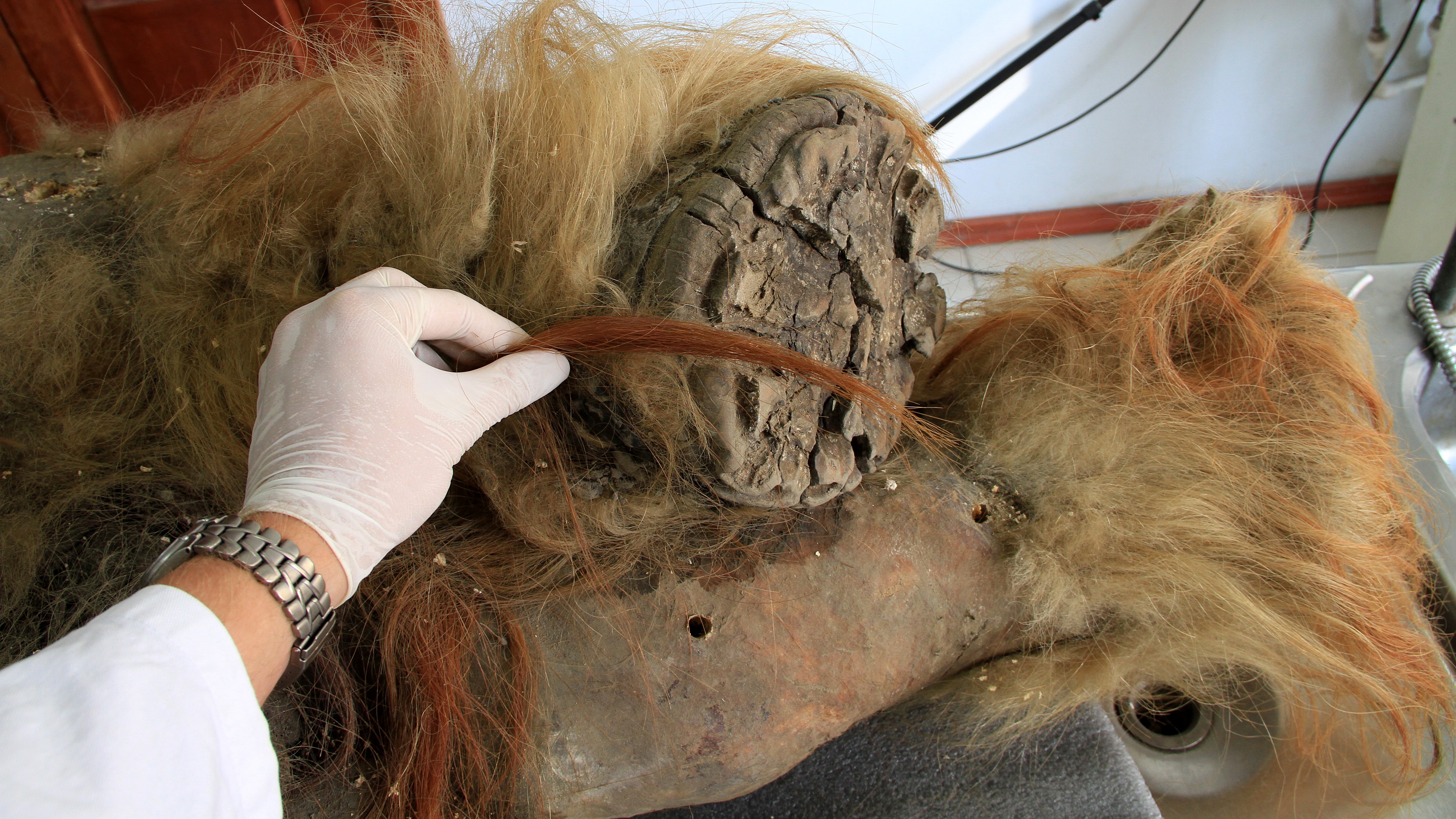
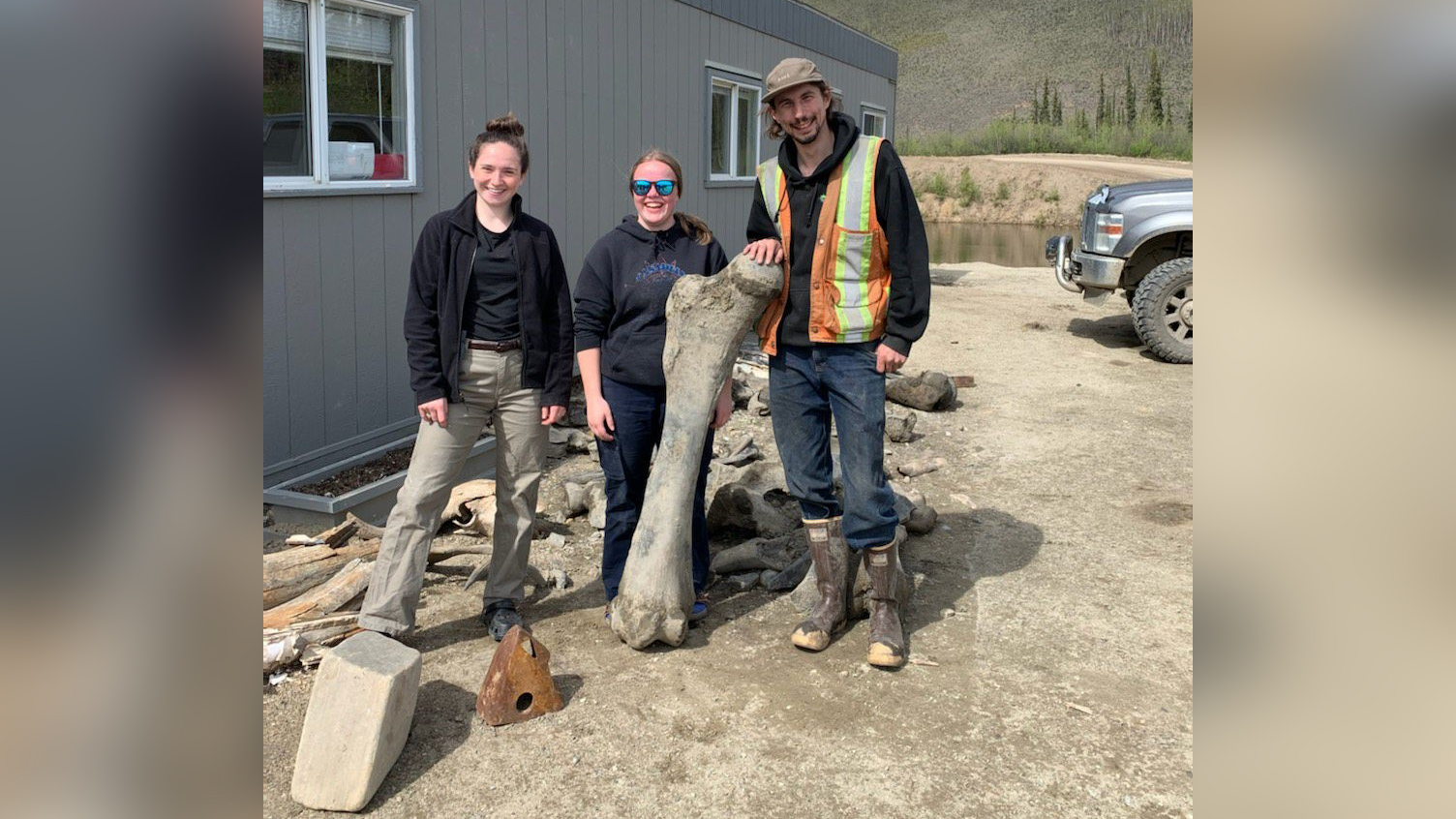
Scientists know so much about these elephant-relatives because many of their bodies have been found, frozen and preserved in the ground in Siberia, Alaska and Canada. Some of these mammoths look like they died only recently, with fresh-looking skin, hair and tusks. From these amazing finds, we know what adults and babies ate, how far they walked, how they died, and how they're different from modern-day elephants.
Even though they're long gone, some scientists are trying to clone the ice age beasts. They hope to bring the mammoths back to places like Siberia and Alaska, where they once lived.
3 fun facts about woolly mammoths
- Mammoths walked huge distances: If woolly mammoths walked in a straight line they could have circled the Earth twice
- Necropsies, or autopsies for animals, show that babies drank their mother's milk. But they also ate grass and even poop. And mammoths also ate flowers that were packed with protein
- They had tiny ears — about the size of dinner plates — compared with their relatives that lived in warm places. Smaller ears meant less surface area to lose heat, so their ears shrunk over time to adapt to living in colder places.
Everything you need to know about woolly mammoths
What did mammoths look like?
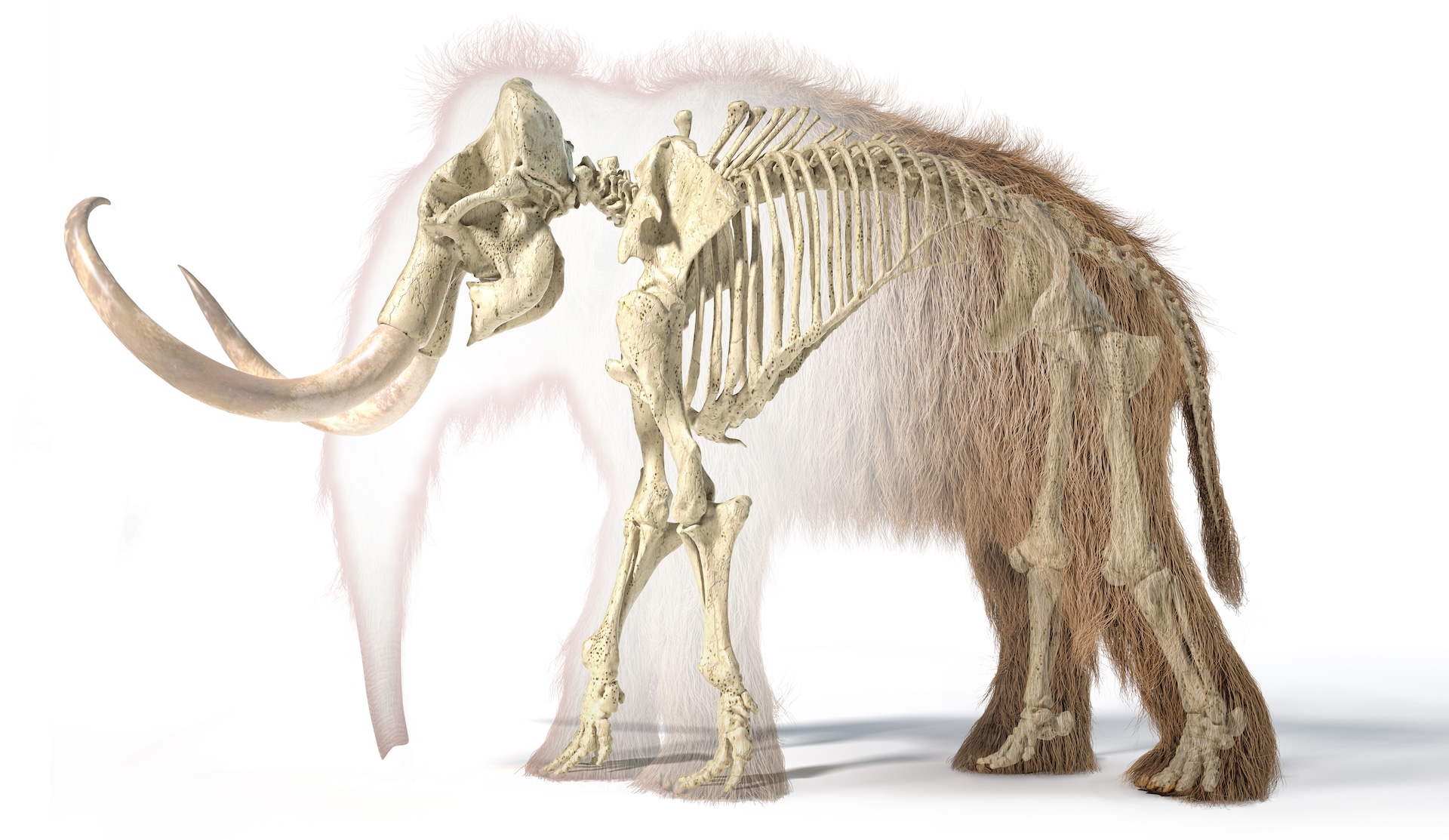
Woolly mammoths (Mammuthus primigenius) looked a lot like their modern elephant cousins, but they had special fat deposits and were covered in thick brown hair. This helped keep them warm in frigid Arctic regions, such as Siberia and Alaska, where they roamed. Males had large, curved tusks, which they probably used to fight over mates. Female woolly mammoths also had tusks, but they tended to be straight and much smaller than males' tusks.
When did woolly mammoths go extinct?
Woolly mammoths existed as a species for about 700,000 years and went extinct about 4,000 years ago.
Most woolly mammoths died off by the time the last ice age ended 11,700 years ago, when the frozen grasslands they inhabited changed into warmer ecosystems. Scientists disagree about when mammoths disappeared from the mainland of North America. Fossils suggest they were gone by 10,500 years ago, but traces of DNA in ancient permafrost (ground that is permanently frozen) hint that the animals may have survived in the Yukon until 5,000 years ago.
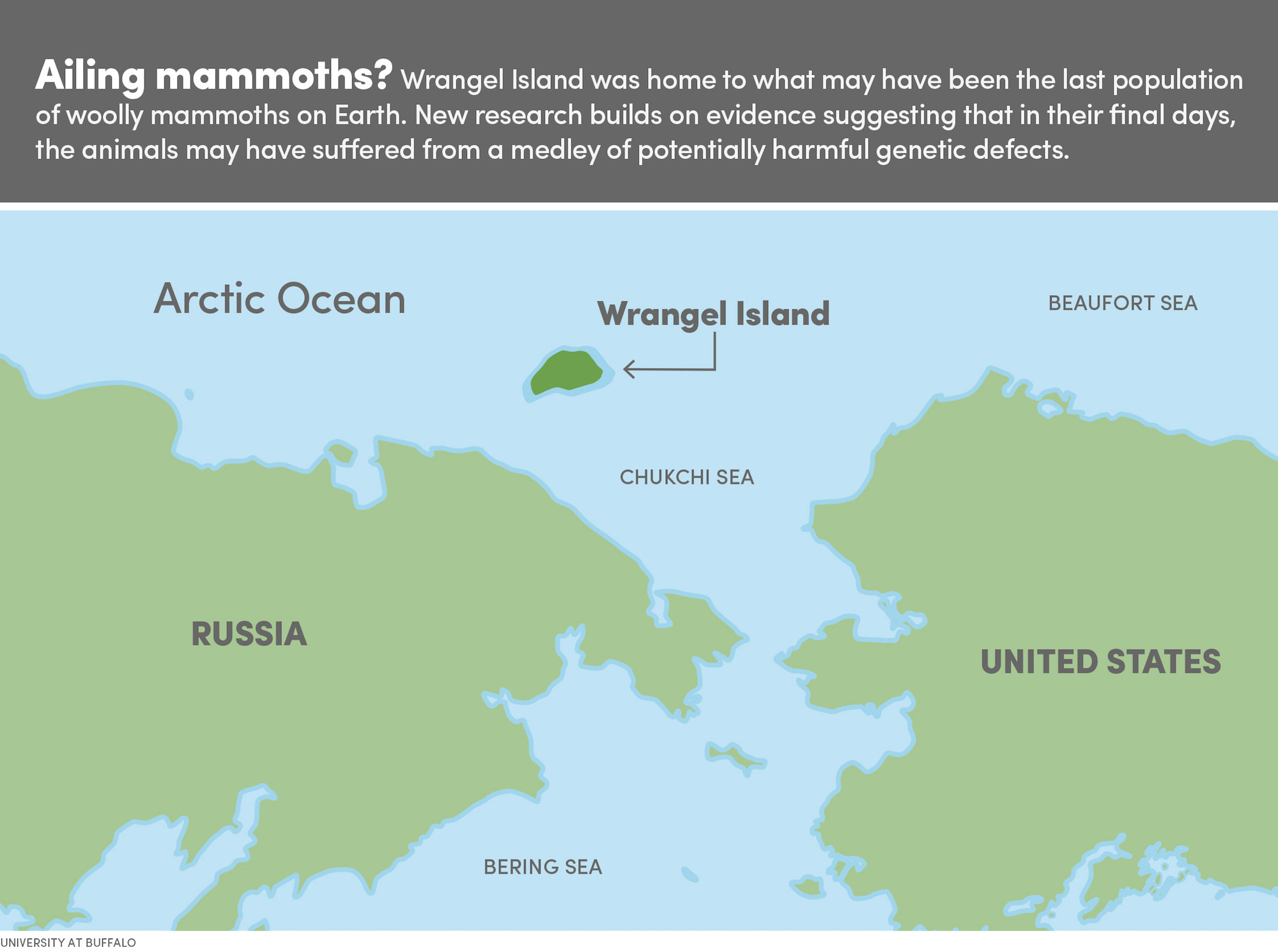
Either way, some mammoths survived on Russia's Wrangel Island, off Alaska, until around 4,000 years ago. It's not clear what eventually killed these mammoths. Some studies suggest the Wrangel Island mammoths were so inbred they became sickly and died out, while others suggest a random mystery event wiped out the last woolly mammoth.
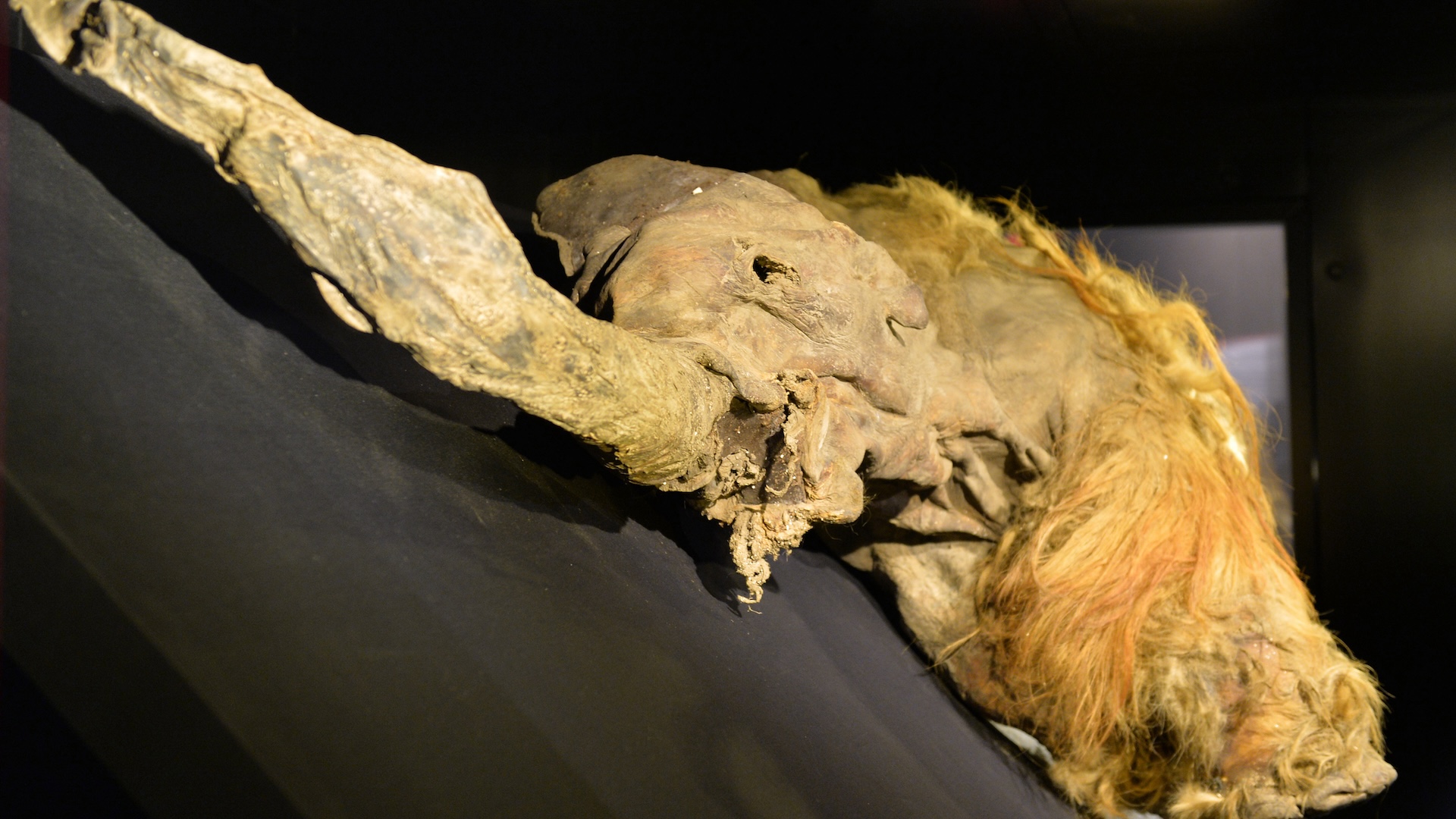

Could we ever clone a woolly mammoth?
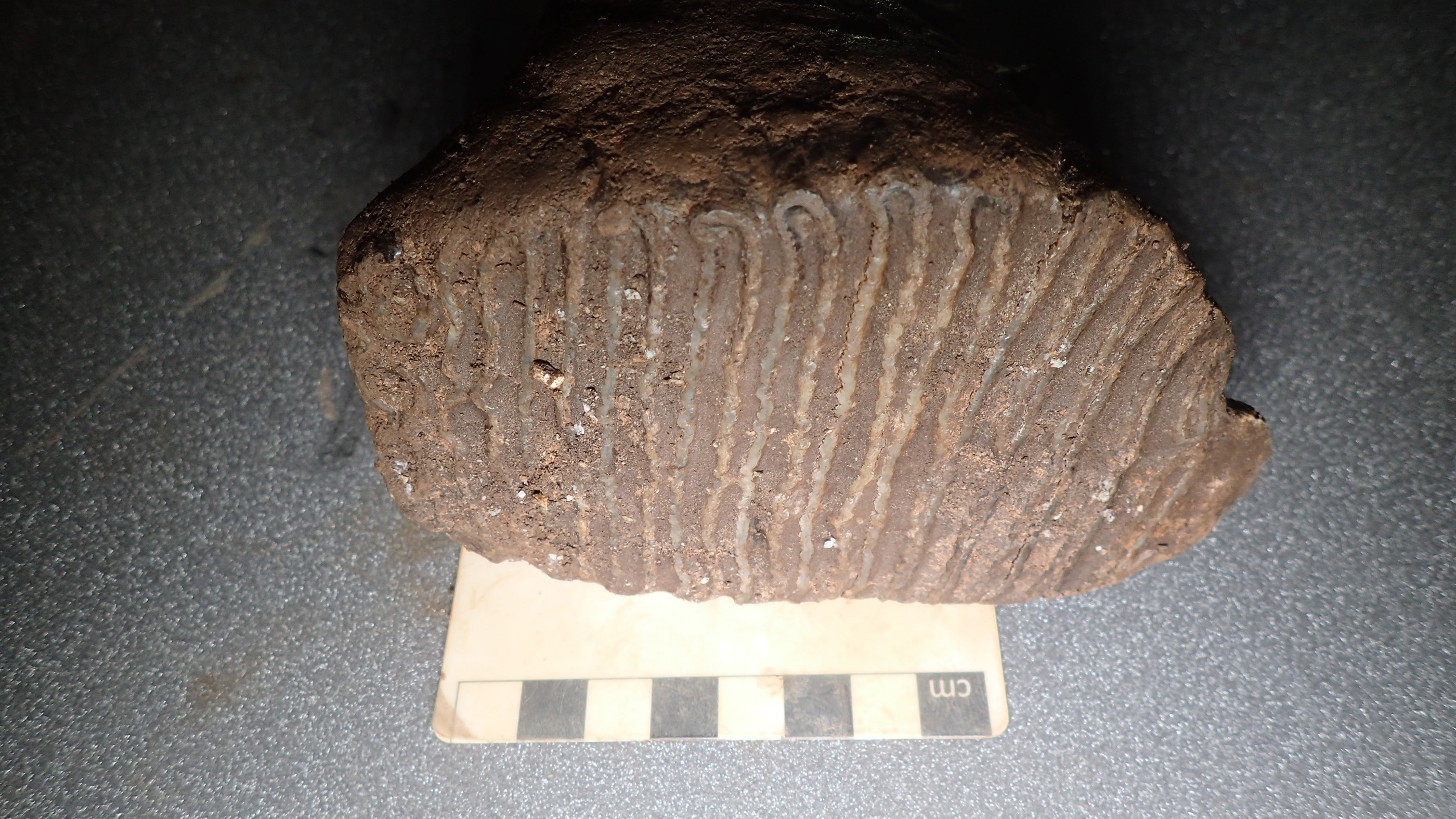
Scientists are trying to clone woolly mammoths and bring them back to places like Siberia and Alaska. Researchers are hopeful they can resurrect the species because the Arctic permafrost preserves mammoth corpses so well. Many of these long-lost beasts have been found with well-preserved teeth and skin that contain usable DNA. In 2024, scientists actually extracted the 3D structure of chromosomes from 52,000-year-old, freeze-dried skin, which they took from a mammoth discovered in 2018 in Siberia. Scientists haven't yet reconstructed the complete genome — all the genetic information — of a woolly mammoth, but that may not be necessary to create creatures that look an awful lot like the shaggy-coated beasts, researchers told Live Science.
Instead, researchers are planning to splice, or insert, genes for iconic woolly mammoth features, such as fur, fat and curved tusks, into the genome of a living elephant species. The scientists will then put these modified genomes into the empty egg cells of a living elephant,and grow the mammoth/elephant hybrid in an elephant surrogate, researchers told Live Science.
Where did woolly mammoths live?
Woolly mammoths lived mainly in the Arctic, from Eurasia to North America. At the peak of the last ice age, when glaciers covered a lot of the Northern Hemisphere, they lived as far south as Spain and Illinois.
Woolly mammoths evolved in eastern Siberia, but the ancestors of both mammoths and elephants originally came from Africa. Mammoths only spread into the Northern Hemisphere around 3 million years ago, according to the Natural History Museum in the U.K.
While woolly mammoths preferred the coldest parts of the world, other related species, such as Columbian mammoths (Mammuthus columbi), lived all across North America and Mexico. Columbian mammoths were actually a little bigger than woolly mammoths.
Woolly mammoth taxonomy
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Proboscidea
Family: Elephantidae
Genus: Mammuthus
Species: Mammuthus primigenius
How tall were woolly mammoths?
Woolly mammoths were about as big as today's Asian elephants, according to AZ animals. Males stood about up to about 11 feet tall (3.5 meters) at the shoulder, while females were a bit shorter, at up to around 9.5 feet (3 m).
Woolly mammoths were heavy: Males could weigh in at 12,000 pounds (5,400 kilograms), while females were up to 8,000 pounds (3,600 kg), according to AZ animals.
What did woolly mammoths eat?
Woolly mammoths were foragers and ate grass, as well as small, nutritious flowering plants that flourished in the environment where they lived. They may also have used their curved tusks to dig through trampled snow and eat dead or decaying plants that other foragers couldn't get to. Surprisingly, they may have also eaten their own dung, a 2015 study in the journal Scientific Reports found.
Woolly mammoth pictures




Discover more about woolly mammoths
—How many animal species have humans driven to extinction?
—Pleistocene epoch: The last ice age
—Frozen in time: 10 prehistoric animals found trapped in ice







