In the U.S., 26 states provide for a statewide initiative process, referendum process, or both. Washington, D.C. also has an initiative and referendum process. These types of ballot measures are known as citizen-initiated ballot measures. Conversely, 24 states do not provide for statewide citizen-initiated ballot measures. However, municipal and local governments provide for local initiatives in some of these states.
- The initiative process allows citizens to collect signatures to place a new statute or constitutional amendment on the ballot.
- The veto referendum process allows citizens to collect signatures to ask voters whether to uphold or repeal an enacted law.
The initiative process can be direct or indirect and amend statutes or constitutional laws. This can be explained with a fourfold table:
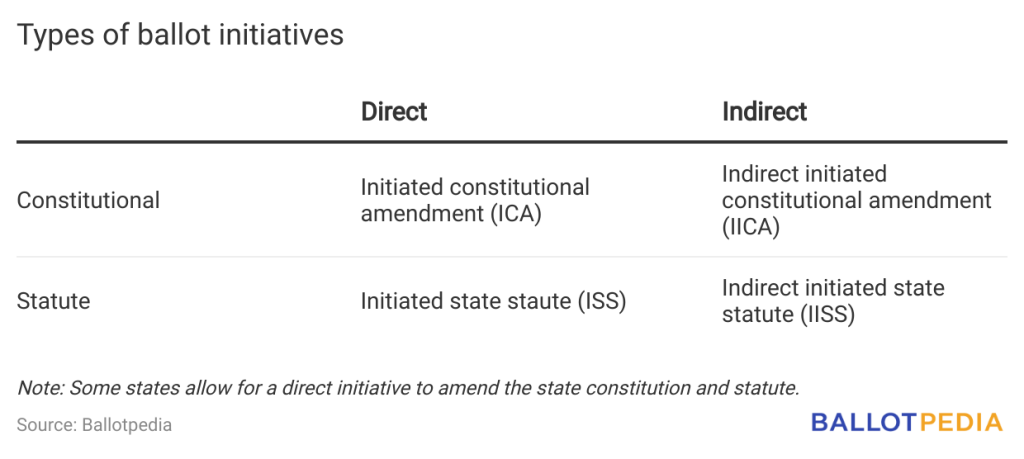
California and Colorado also allow for initiatives to address both constitutional and statutory changes.
While a direct initiative is placed on the ballot once supporters file the required number of valid signatures, an indirect initiative is first presented to the state legislature. Legislators have a certain number of days, depending on the state, to adopt the initiative into law. Should legislators take no action or reject the initiative, the initiative is put on the ballot for voters to decide.
Initiated constitutional amendments
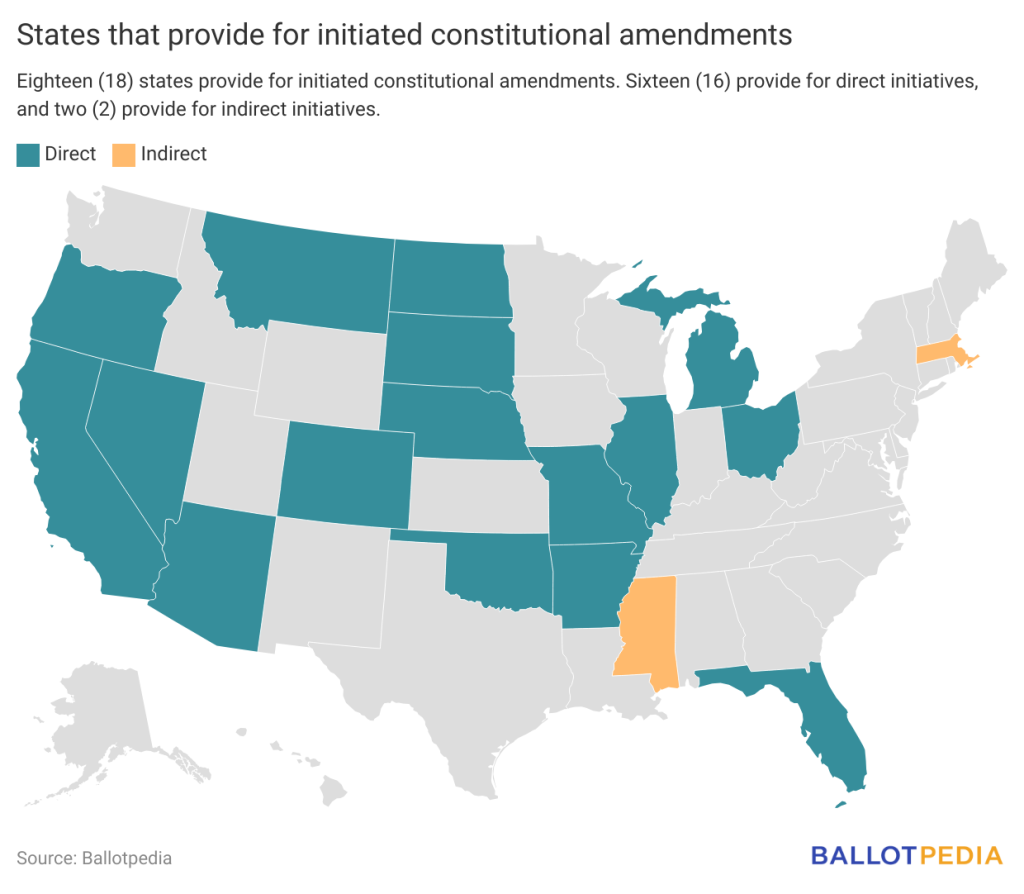
An initiated constitutional amendment is a citizen-initiated ballot measure that amends a state’s constitution. Eighteen (18) states allow citizens to initiate constitutional amendments. The process is direct in 16 states and indirect in two states.
Mississippi is one of these 18 states; however, the process has been de facto suspended because the signature requirement cannot be met. Signatures need to be collected from five congressional districts in Mississippi, but the state has had just four since 2001.
As of Feb. 4, 2024, the following initiated constitutional amendments have qualified for this year’s ballot:
- California Pandemic Early Detection and Prevention Institute Initiative (2024)
- California Two-Thirds Legislative Vote and Voter Approval for New or Increased Taxes Initiative (2024)
- Colorado Property Tax Revenue Cap Initiative (2024)
- Nevada Question 3, Top-Five Ranked-Choice Voting Initiative (2024)
Initiated state statute
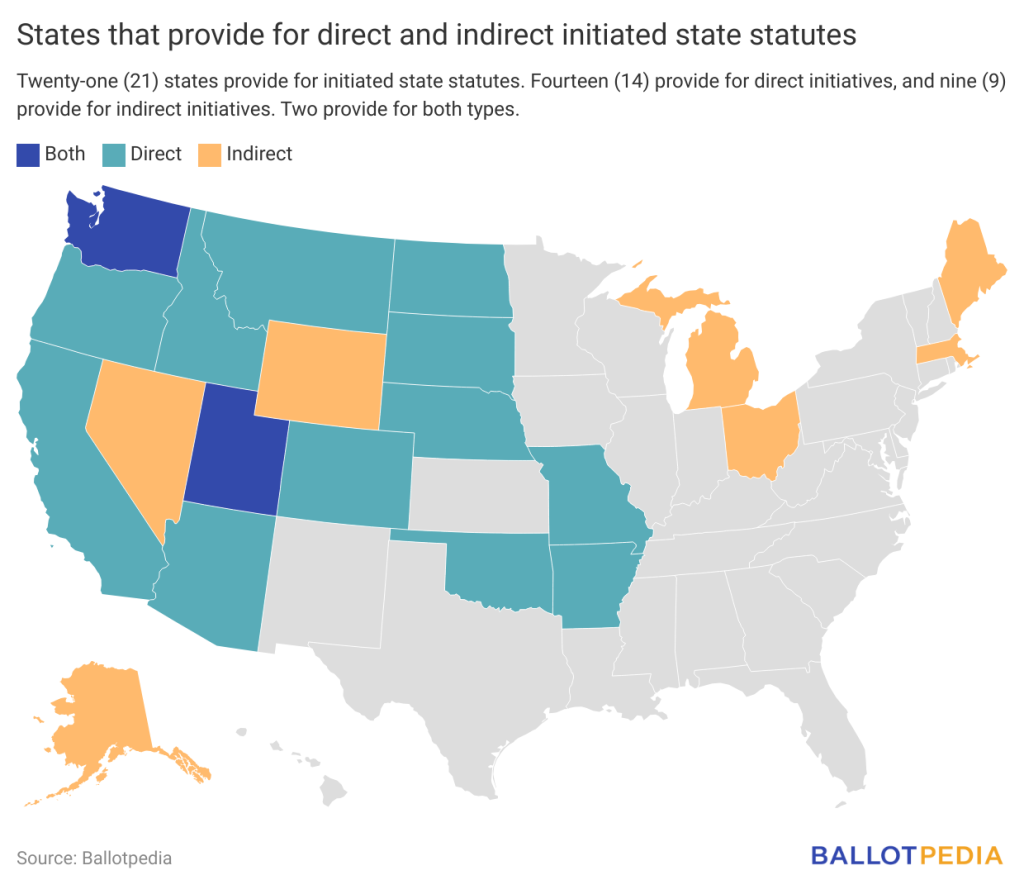
An initiated state statute is a citizen-initiated ballot measure that amends a state statute. Twenty-one (21) states allow citizens to initiate state statutes, including 14 that provide for direct initiatives and nine (9) that provide for indirect initiatives (two provide for both).
As of Feb. 4, 2024, the following initiated state statutes have qualified for this year’s ballot:
- California $18 Minimum Wage Initiative (2024)
- California Employee Civil Action Law and PAGA Repeal Initiative (2024)
- California Prohibit State Limitations on Local Rent Control Initiative (2024)
Veto referendum
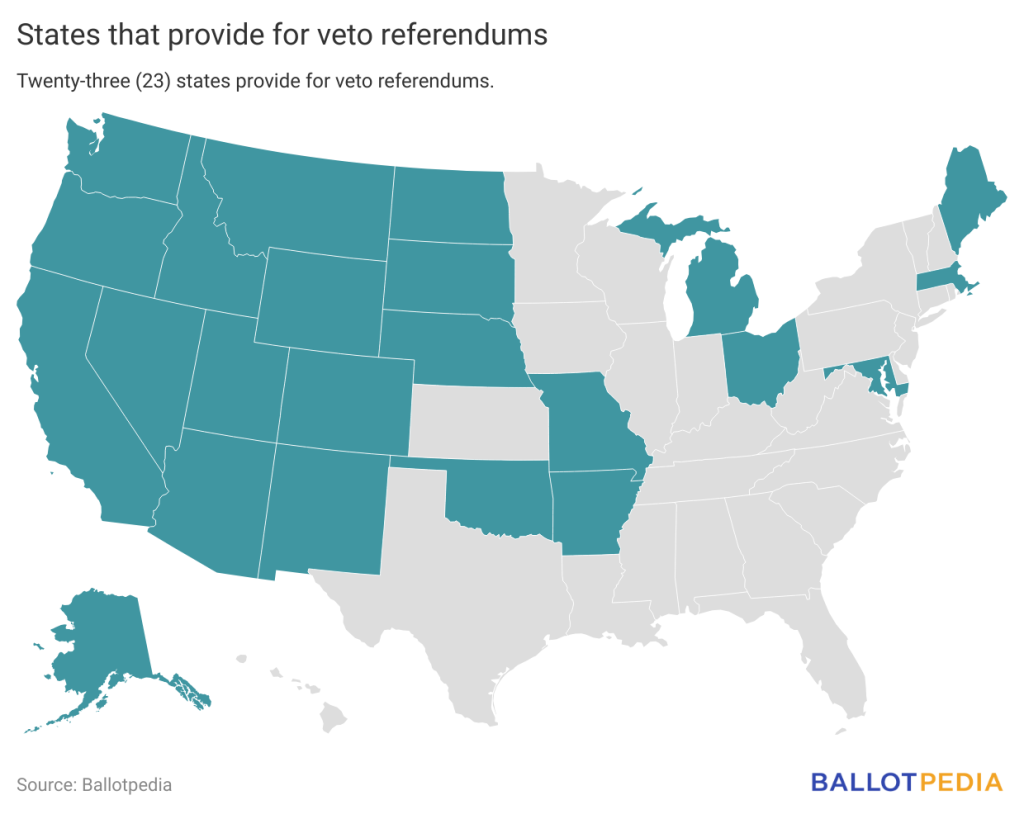
A veto referendum is a citizen-initiated ballot measure that asks voters whether to uphold or repeal an enacted law. This type of ballot measure is also called statute referendum, popular referendum, people’s veto, or citizen’s veto. Twenty-three (23) states allow citizens to initiate veto referendums. Proponents of a veto referendum collect petition signatures from a certain minimum number of registered voters in a state. Two states—Maryland and New Mexico—allow for veto referendums but not initiated laws.
As of Feb. 4, 2024, the following veto referendums have qualified for this year’s ballot:
- California Oil and Gas Well Regulations Referendum (2024)
- Nebraska Education Scholarships Tax Credit Referendum (2024)
The ballot initiative is a state process and, as such, the laws vary by state. The signature-gathering process involves different numbers of signatures required and different circulation periods. They can also involve distribution requirements and various rules for signature gatherers. In turn, the initiative process can be more resource-intensive to use in certain states compared to others.







