What Is Disruptive Innovation?
Disruptive innovation refers to the transformation or tremendous change that occurs due to the introduction or development of a new technology or process.
The term traces its origins to a 1995 issue of the Harvard Business Review in an article in which Harvard Business School authors described it as “any situation in which an industry is shaken up and previously successful incumbents stumble.”
Cathie Wood, who rose to fame with the founding of ARK Invest, makes disruptive innovation the core of the fund-management company’s thematic investing strategy, which is the foundation of her investment objective. ARK defines disruptive innovation as “the introduction of a technologically enabled product or service that potentially changes the way the world works.”
What Are Some Examples of Disruptive Innovation?
Perhaps the greatest opportunity for stock investors is investing early in companies poised to take advantage of emerging themes. There have been many examples of disruptive innovation in the past few decades.
In the late 1990s, Amazon shook up the book market, taking on big brands like Barnes & Noble and selling titles by mail via the internet. Its online platform expanded to selling other goods, and the company eventually created a marketplace that upended the retail market.
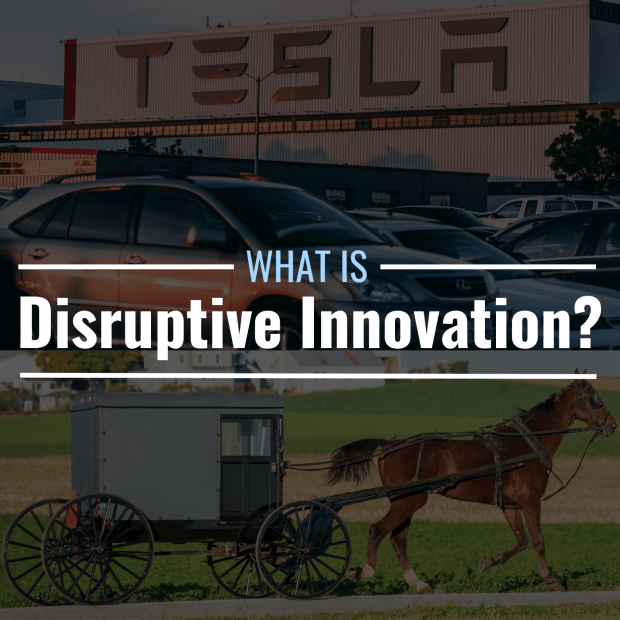
Tesla took on the auto industry by developing and producing electric vehicles at a large scale, beating traditional automakers like Ford Motor and GM as they continued to focus on internal combustion engines.
Nowadays, new entrants are taking advantage of advances in technology—artificial intelligence on information data, and cloud computing on storage data, among them—that many investors believe will provide opportunities as breakthroughs continue to occur.
How to Invest in Disruptive Innovation
Many major money-management companies have mutual funds and exchange-traded funds dedicated to disruptive innovation. Cathie Wood’s ARK Invest funds are dedicated to disruptive innovation, with a number of ETFs focused on certain industries.
How Does Disruptive Innovation Differ From Creative Destruction?
Creative destruction refers to the destruction of old markets to make new ones. Creative destruction was first coined by economist Joseph Schumpeter in his 1942 book titled Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy to describe new markets that are always evolving. That theory is applied to innovations continually replacing established norms—putting those into obsolescence and eventually creating new ones. An example would be turbines, powered first by steam, then by fossil fuels, and then by renewable energy such as solar and wind.
The nuance between creative destruction and disruptive innovation is that creative destruction can arise from the end of an innovation and lead to a new one, whereas, in disruptive innovation, innovation can arise from an existing norm. For example, the creation of the automobile made the horse and buggy obsolete, but disruptive innovation took place when mass production of electric vehicles begins to replace the production of units with the internal combustion engine.
What Is Sustaining Innovation, and How Does It Differ From Disruptive Innovation?
Sustaining innovation is the opposite of disruptive innovation in that sustaining innovation seeks to maintain or improve existing technologies, systems, or products. Apple’s iPhone is a good example of sustaining innovation. The iPhone disrupted the smartphone market following its release in 2007, and it put traditional mobile phones into obsolescence. As new competitors emerged and gained market share, Apple made improvements to the iPhone each year, helping it to maintain market share over the years.