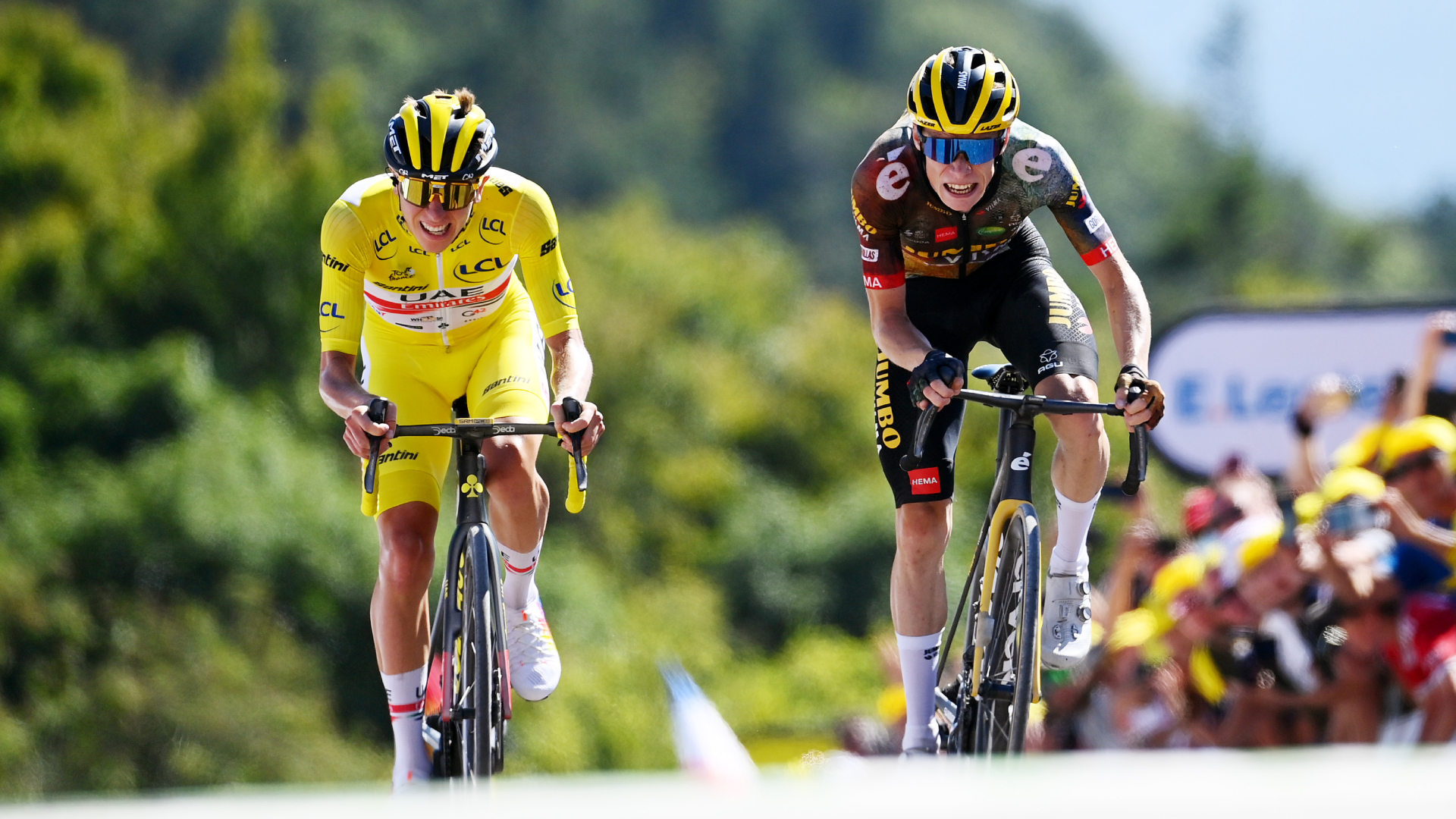
The Tour de France is an almighty undertaking. This year’s edition packs in 3,404km over 21 stages, with an accumulated elevation total in excess of 56,000 metres. Just getting selected for the start requires all the riders to be in peak physical condition, but winning the biggest race of all demands an even more finely turned body. The general classification (GC) contenders are arguably the fittest athletes on the entire planet – but what exactly does it take, in terms of talent and training, to get there? In other words, what makes them the best of the best?
The basic description of a Tour de France winner – the last being Jonas Vingegaard (Jumbo-Visma) – won’t shock anyone: almost always European, typically aged between 24 and 34; usually with a height between 175 and 185cm (5ft 9in and 6ft 1in), and low body weight of between 60 and 66kg. But there have been exceptions: two-time champion Tadej Pogačar (UAE Team Emirates) was only 21 when he claimed his first title in 2020 – 98 years after the race’s oldest winner, 36-year-old Firmin Lambot, took the title in 1922. The race’s first ever winner in 1903, Maurice Garin, was a petite 162cm (5ft 4in), while 2012 winner Bradley Wiggins was 190cm (6ft 3in). On the scales, five-time winner Miguel Induráin was 80kg, some 28kg heavier than his Spanish compatriot Luis Ocaña who won in 1973. As for non-Europeans, there have been three: American Greg LeMond won in 1986, 1989 and 1990; Australian Cadel Evans won in 2011; and Colombian Egan Bernal became the first South American winner in 2019.
There are clearly no strict physical parameters, at least not on the surface, so what do we know about their habits – their monk-like devotion to their single objective – and how they get their bodies ready for the biggest challenge in sport?
1. Unbreakable work ethic
The road to a Grand Tour starts all the way back in the dark, cold winter months, when riders log 30-hour training weeks of low-intensity rides, building aerobic efficiency and reinforcing the body’s ability to burn fuel as fat – to push hard while using as little energy as possible. As spring nears, more tempo, sub-threshold and threshold work are introduced, and the work becomes ever more tailored and specific.
“There are no sessions specifically for GC riders, but what is most important for them is that they’re able to recover from big loads,” says Bora-Hansgrohe’s head of performance, Dan Lorang. “GC riders will train in a three-to-one rhythm: three weeks of load, one week of recovery. These riders do a lot more climbing, and they train to reproduce high-intensity efforts after four to five hours.” Putting in hard efforts after many hours of steady riding is bread-and-butter for prospective Tour winners. “An example would be four hours of training at Zone 2, finishing off with 30 minutes of threshold climbing to simulate a final climb,” adds Lorang. “GC guys also train on their time trial bikes two or three times a week.”
To simulate Grand Tour demands, many GC riders train intensely before heading straight into a one-week stage race, or extend a heavy block of training to imitate three weeks of racing. Two weeks before the Tour, they begin their taper with more rest periods and less intense work.
2. World-beating watts per kilo
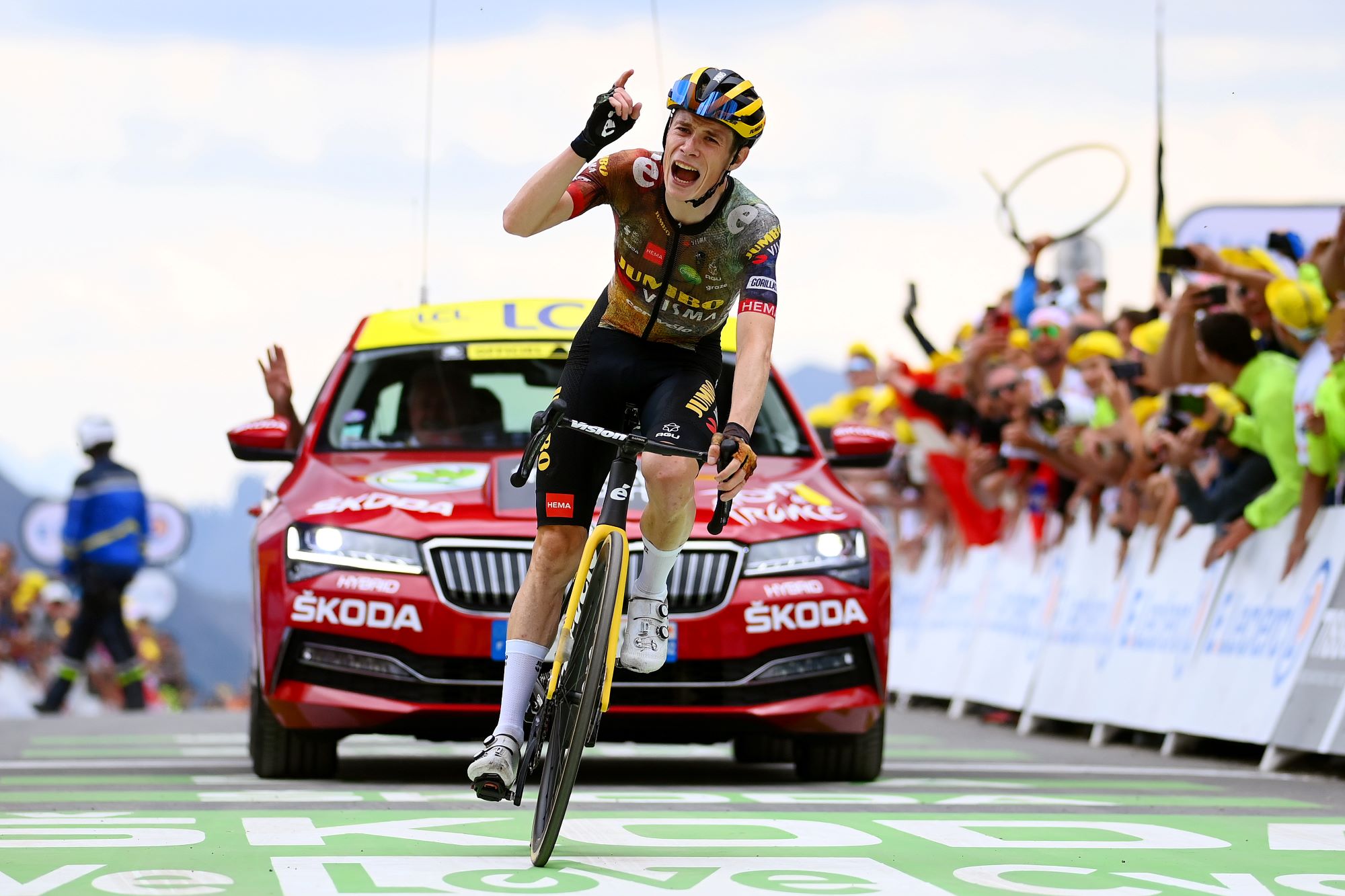

To think of cycling as solely a watts per kilogram game removes the romance and the panache, but time gaps are made in the mountains and in time trials thanks to a rider’s power output. Put simply, if a rider wants to win the Tour de France, they need to be able to maintain an exceptional power output over a sustained period of around 30 minutes after several hours of attritional, varied-intensity riding. Not just exceptional, but better than every other cyclist in the world.
The numbers are mind-boggling. When Jonas Vingegaard crushed the field on Stage 11 to win atop the Col du Granon (11.3km at 9.2% gradient) at last year’s Tour, he averaged 6.1W/kg for 35 minutes 52 seconds. No one has gone faster. Six days later, on Stage 17, Brandon McNulty (UAE Team Emirates) climbed the Col d’ Azet (8.34km, 7.9%) averaging 6.58W/kg for a time of 22:24. Again, it was the fastest time ever recorded.
Jump on Zwift and try riding at 6.5W/kg – then imagine sustaining it for 20 minutes. You’ll get a taste for just how hard GC riders are able to push. Over shorter periods of around 10 minutes, some riders, including former Tour winner Chris Froome (Israel-Premier Tech), have registered eye-popping figures of around 7.5W/kg.
During a normal stage before any attacks go off, riders generally pedal along at 220 to 250 watts. That’s a stout effort for most of us amateurs, but bear in mind that Tadej Pogačar’s functional threshold power (FTP) – the highest power he can sustain for one hour – is as high as 415 watts.
3. Oxygen-burning furnaces
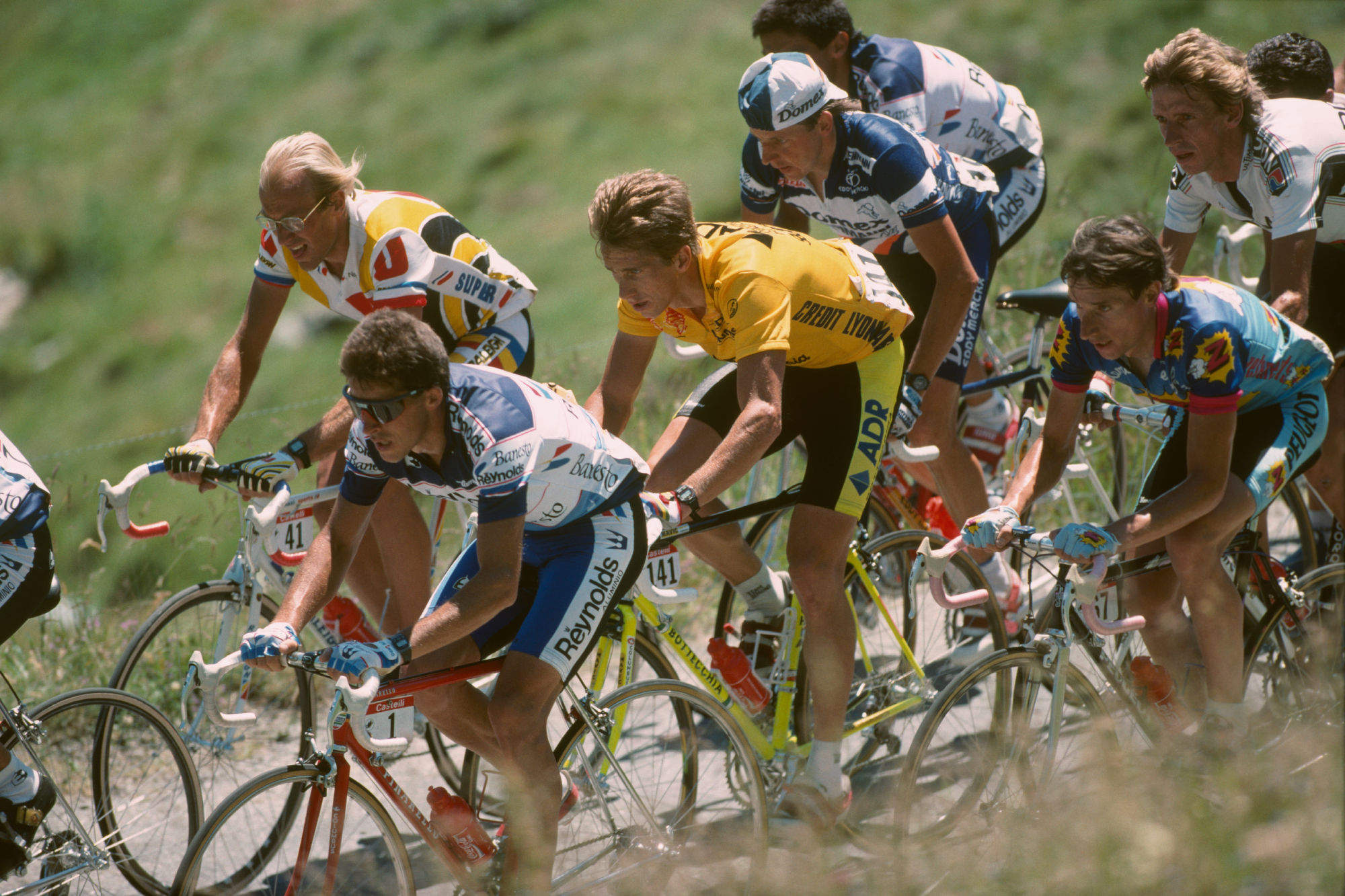

VO2max – very simply put – is the maximum rate at which the body can use oxygen during exercise, so it is used to measure an individual’s aerobic capacity. Measured in millilitres of oxygen per kilogram per minute, the relative figure in an averagely fit 30-year-old male is usually in the upper 40s. It can be improved substantially with training.
What about VO2max in those who win the yellow jersey? Way, way higher. When Chris Froome was dominating Tours, he could intake 88.2ml/kg/min. Remarkably, that’s not the best. American Greg LeMond, winner of the Tour on three occasions, had a reported VO2max of 92. If your VO2max isn’t in the 70s, at least, you’re probably not going to the Tour.
4. Lionhearted beats
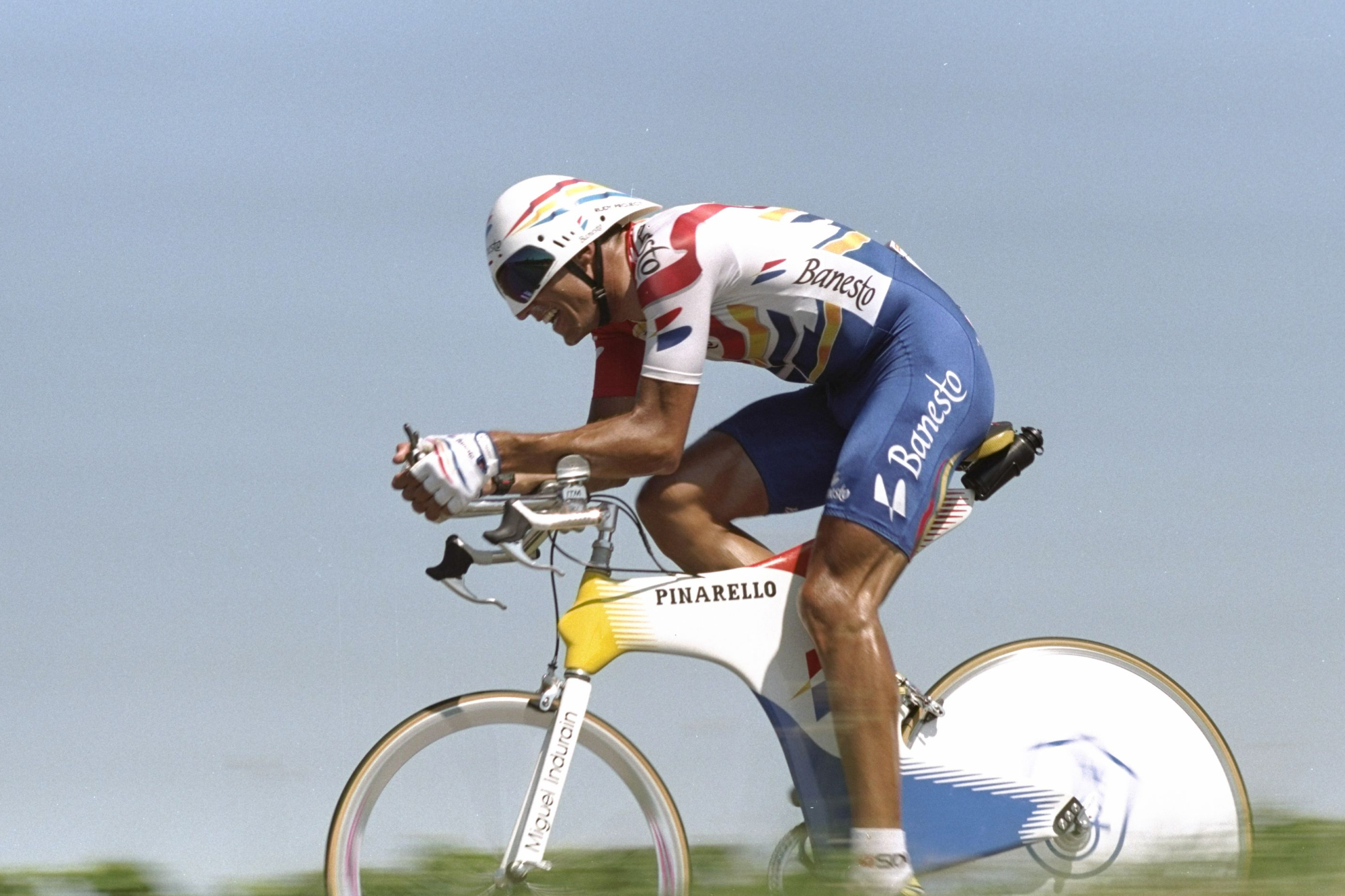

During the 2020 Tour de France, the WorldTour team now known as EF Education-EasyPost released data on each of their riders’ heart rates and heart rate variability. Among their roster of eight, the average resting heart rate was 42bpm before the race began. During the race, this rose to 51bpm ahead of the first rest day, but after a day off it dropped to 40bpm, highlighting the power of recovery.
Chris Froome had a reported resting heart rate of 29bpm, and Miguel Induráin’s was claimed to be even lower, at 28bpm – about half the speed of a typical adult’s heart rate. A pro rider’s cardiovascular system is so efficient that this plodding heart rate is fast enough, at rest, to supply their body with all the blood and oxygen it needs.
On intense days in the mountains, with full-throttle racing, GC riders spend as much as 50% of their day performing in the upper heart rate zones, at 80-90% of their maximum heart rate.
5. Jack Sprat fat levels
You only need to look at a Tour de France rider to know that they aren’t carrying so much as a twig’s worth of spare timber. A ‘normal’ man usually has body fat of between 18 and 24% – but for our Grand Tour cyclists, determined not just to make it over the mountains but to triumph up them, their body fat needs to be as low as possible, around 5-6%.
There is a danger, however, in going too low. The body needs between 3% and 5% of body fat to protect organs and to regular body temperature, so while there have been some reported cases of riders competing with less than 5% of body fat, that is the lowest they can go without jeopardising their health.
6. Endless appetite

It’s become a cycling press cliche to quantify a Tour de France rider’s daily calorie intake by showing the equivalent number of McDonald’s Big Macs. Oh go on, then: it’s 12 to 18 Big Macs, depending on the stage.
A Tour rider shovels anywhere between 6,000 and 9,000kcal of food down them per 24 hours during a stage race. While racing, up to six hours per stage, they burn around 1,000kcal per hour. Unsurprisingly, riders are prone to losing weight and shedding fat during a three-week race, since consuming enough – in food and carb-laden drinks – isn’t easy.
Dropping a little weight is sometimes in the plan: at the 2018 Giro, Chris Froome only ate 2,500 calories on stage 11 as he was attempting to drop to his ideal weight of 68.5kg in time for his famous late-race assault that secured him the maglia rosa.
7. Brimming carb tanks
Riding relentlessly hard for three weeks is only possible to endlessly consuming huge amounts of carbohydrate – before and during each stage. Iñigo San Millán is UAE-Team Emirates’ head of performance: “A rider needs to absorb 500 grams of glycogen [stored carbohydrate] before the race starts,” he says. “They should be completely full before the race, and empty afterwards.”
Filling up the proverbial tank relies on mammoth breakfasts containing 200g carbs – equivalent to about 13 slices of bread – with similarly gut-busting amounts for dinner once the day is done. During the race they replenish their energy stores with about 100g carbs per hour, in various forms including energy gels, carb drinks and rice cakes. Over the course of a day, a rider imbibes a massive carb load of about 1,200g – compared to about 300g in a normal diet.
8. Solid sleep patterns
“Sleep is the most important recovery resource for people in general, but especially for cyclists who use their bodies so intensively,” says Jumbo-Visma’s head of performance, Mathieu Heijboer. “The enormous effort during a race damages the body… [and] physical recovery is therefore the most important thing. Deep sleep is essential. If it is disturbed, it is at the expense of recovery, which slows down reaction times, causes memory problems and has a negative effect on motor coordination.”
Getting a good amount of shut-eye, night after night, is essential for someone who wants to win the world’s biggest race. Some teams carry their own mattresses and bedding, such is the emphasis on good sleep. On average, riders in a Grand Tour sleep for eight hours, with most going to bed at 11.30pm and waking up at 8am. If that sounds late, it’s because stages don’t start until around 1pm, and dinner is often not served until 9pm.
9. A-head for heights
Several times a season, riders go on altitude camp to increase their blood haemoglobin levels – the component of blood that carries oxygen and gives blood its red colour. Having more haemoglobin allows riders not only to perform better at higher elevations but to use oxygen more efficiently at sea level too.
Bora-Hansgrohe’s Dan Lorang: “For a rider wanting to win a Grand Tour, I would recommend that they spend two 18-day periods at altitude, and then one block of 15 days before the Grand Tour.” This approach is mirrored across the WorldTour. The final altitude block has to finish as close as possible to the start of the race, as half of the haemoglobin increase disappears after a week, and returns to normal after a fortnight. If the altitude camp is too early, “the effect evaporates,” according to Professor Lars Nybo of the University of Copenhagen. “High-altitude camps conducted in the winter or pre-season will almost certainly have no direct effect on performance several months later.”
10. CAN stand the heat
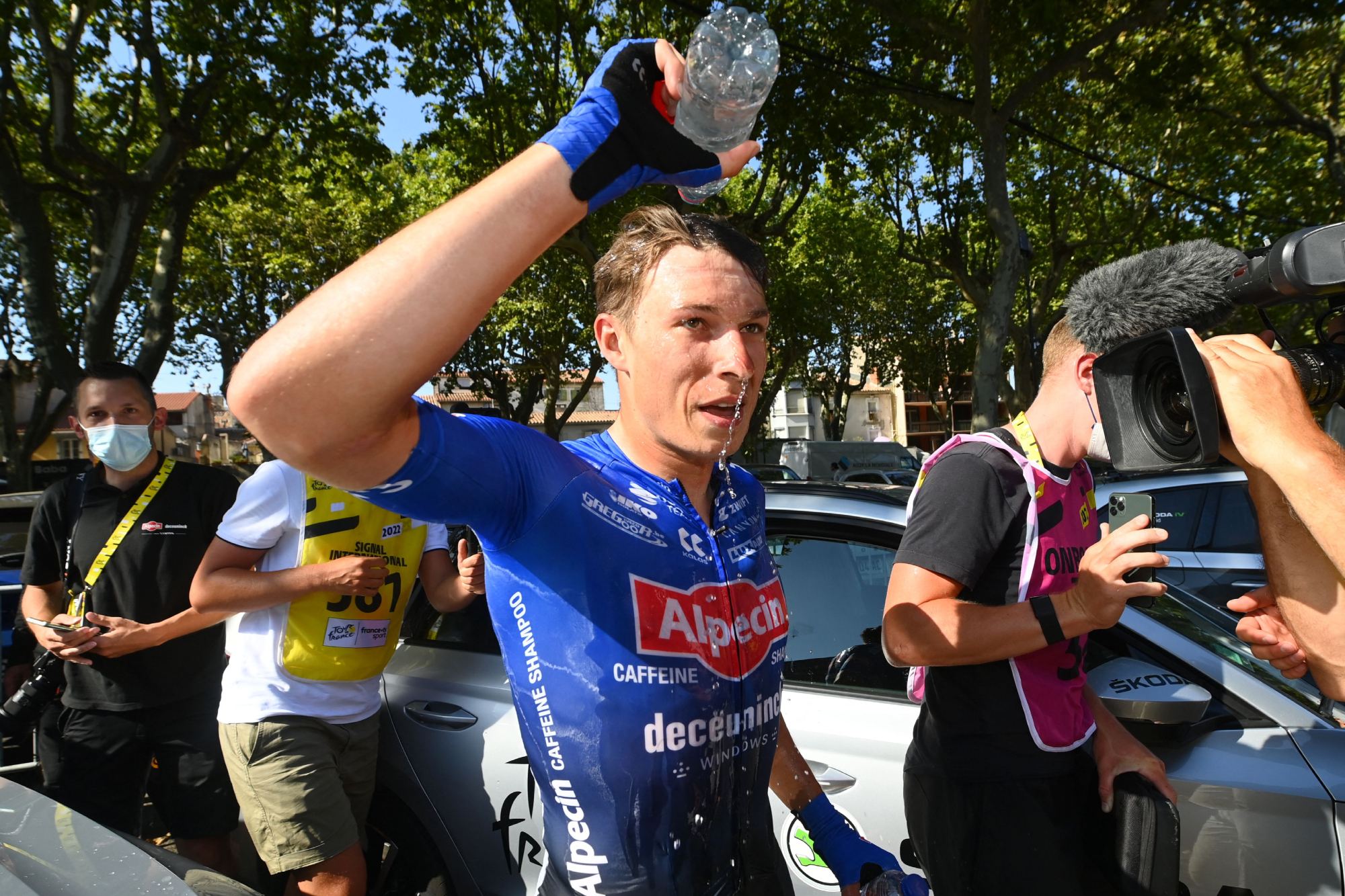

Temperatures on Stage 15 of last year’s Tour de France got close to 40ºC, putting riders under even greater strain. As summer temperatures climb ever higher, Ineos Grenadiers have begun to perfect cooling strategies, having realised that excessive heat can have a direct effect on a rider’s power output. “A one degree increase in core temperature results in a 1% drop in gross efficiency, which means about a 10-12 change in watts,” says Dan Bigham, Ineos’ performance engineer.
Ice vests have become a common sight – for good reason. Studies have shown that a rider’s performance can decline by as much as 16% when not acclimatised to hot conditions. Given at least two weeks getting used to the weather they’ll be racing in, these losses can be reduced to as little as 2%.
What makes Pogačar so special?
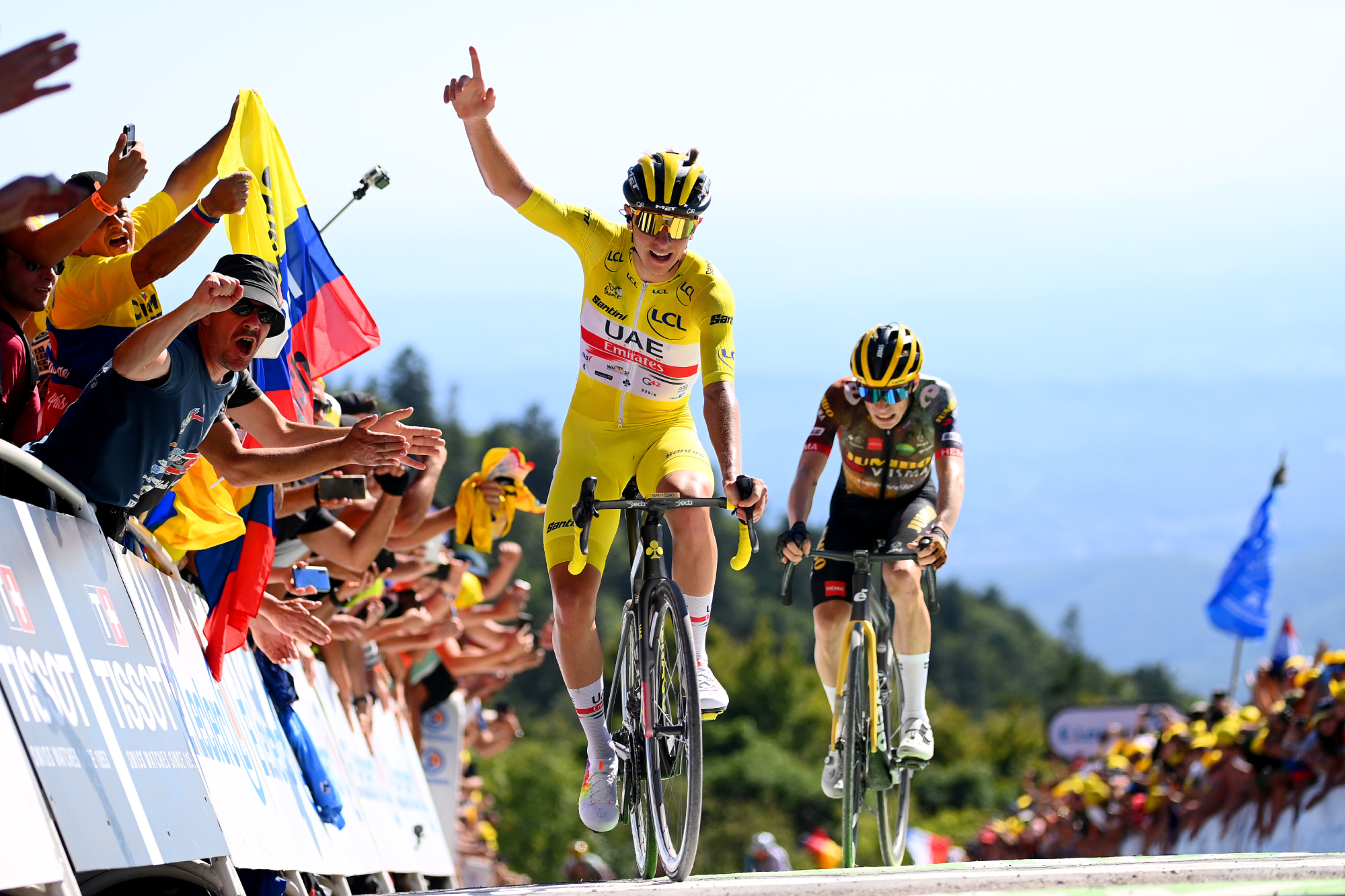

Although Tadej Pogačar isn’t going into this year’s Tour as the defending champion, it is widely accepted that the Slovenian is the greatest bike rider on the planet. Some believe he may even surpass the winning feats of Eddy Merckx. But what makes him so good?
“First things first, he has a massive motor,” says Allan Peiper, his former DS, “and a recuperative power that I’ve never seen before. It’s natural, for sure. There are very few guys who can go into a Grand Tour and get better and keep the motor running, but Tadej’s one of them.
“I’ve been on [UAE-Team Emirates] training camps and riders have ridden themselves into the ground trying to keep up with him and it hasn’t been beneficial for them.”
It’s not just the 24-year-old’s exceptional cardiovascular system. “The other defining thing about Tadej is his approach and outlook on life: he’s always got a positive mindset,” Peiper adds. “He has a way of putting everything into perspective, and that ability to do that when you’re in the hurt box in a Grand Tour keeps you afloat.”
“You can have all these great physical characteristics, but if you’re weighed down by the mental side or overpowered by stress or the fear of failure, it’ll bring you down. Tadej has the physical talent as well as this unbelievable mental side. I have no idea what motivates this kid, but it’s definitely not his ego or by having a chip on his shoulder.”
First-time winners: How did Vingegaard and Remco win Grand Tours last year?
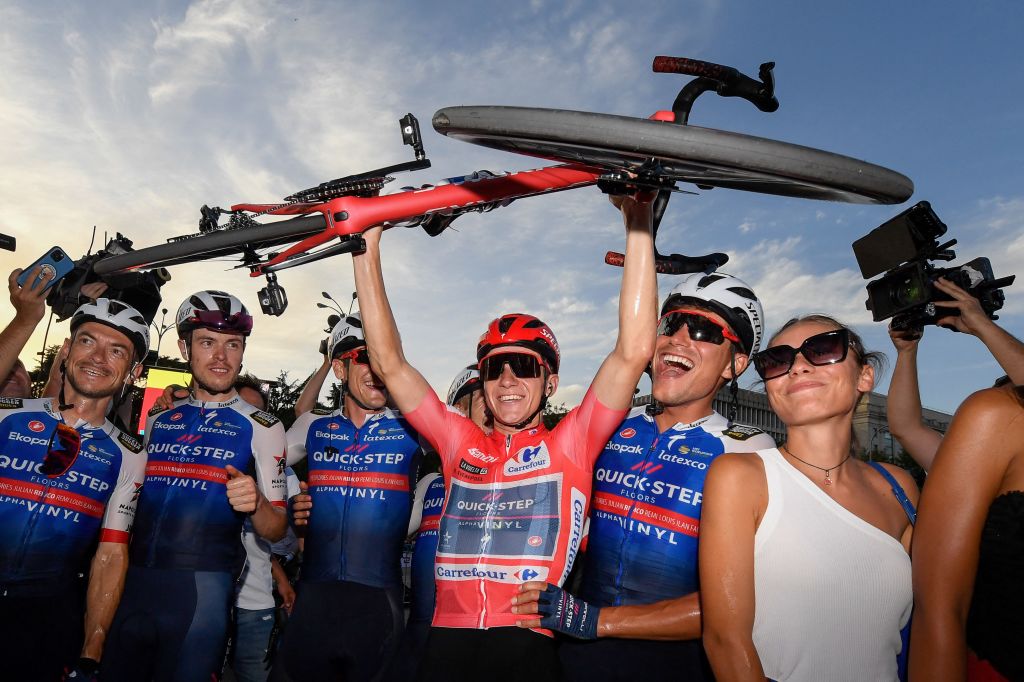

All of last year’s Grand Tours were won by riders who had never before won a three-week race: Jai Hindley in the Giro d'Italia; Jonas Vingegaard in the Tour de France; and Remco Evenepoel in the Vuelta a España.
The latter’s coach, Koen Pelgrim, summarises how the current world champion ensured he was in peak condition to win the Spanish race. “He needed a really good base to be able to work on that to optimise his shape. A few months before we were focusing on shorter work, and then closer to the Vuelta it was about specific and longer efforts so that he could handle multiple consecutive days and multiple efforts.
“The Vuelta had a lot of steep ascents, so he did a lot of efforts on steeper climbs, and he also trained in the middle of the day in Spain so that he was used to the heat. When it’s warm and steep, you suffer more, and we wanted him to be totally acclimatised to that.”
As for 26-year-old Vingegaard, his coach Tim Heemskerk faced a dilemma after the Dane finished second at the Critérium du Dauphiné. “He was in really great shape and I had a choice to make: do I let him have more recovery days or not?” he reflects. “We had three weeks until the Tour, we couldn’t let him get ill, and we couldn’t let him overdo it. This is the time when a coach really has to analyse and manage the situation.
“Getting someone into the best possible shape requires a lot of hard work from the rider, their coaches, the nutritionist and focusing on planning everything correctly. Optimising recovery is really essential.”
This full version of this article was published in the print edition of Cycling Weekly. Subscribe online and get the magazine delivered direct to your door every week.