NASA has invested in an innovative superalloy as part of its Technology Transfer Program, a program that allows technology built for missions to be utilized for other commercial purposes.
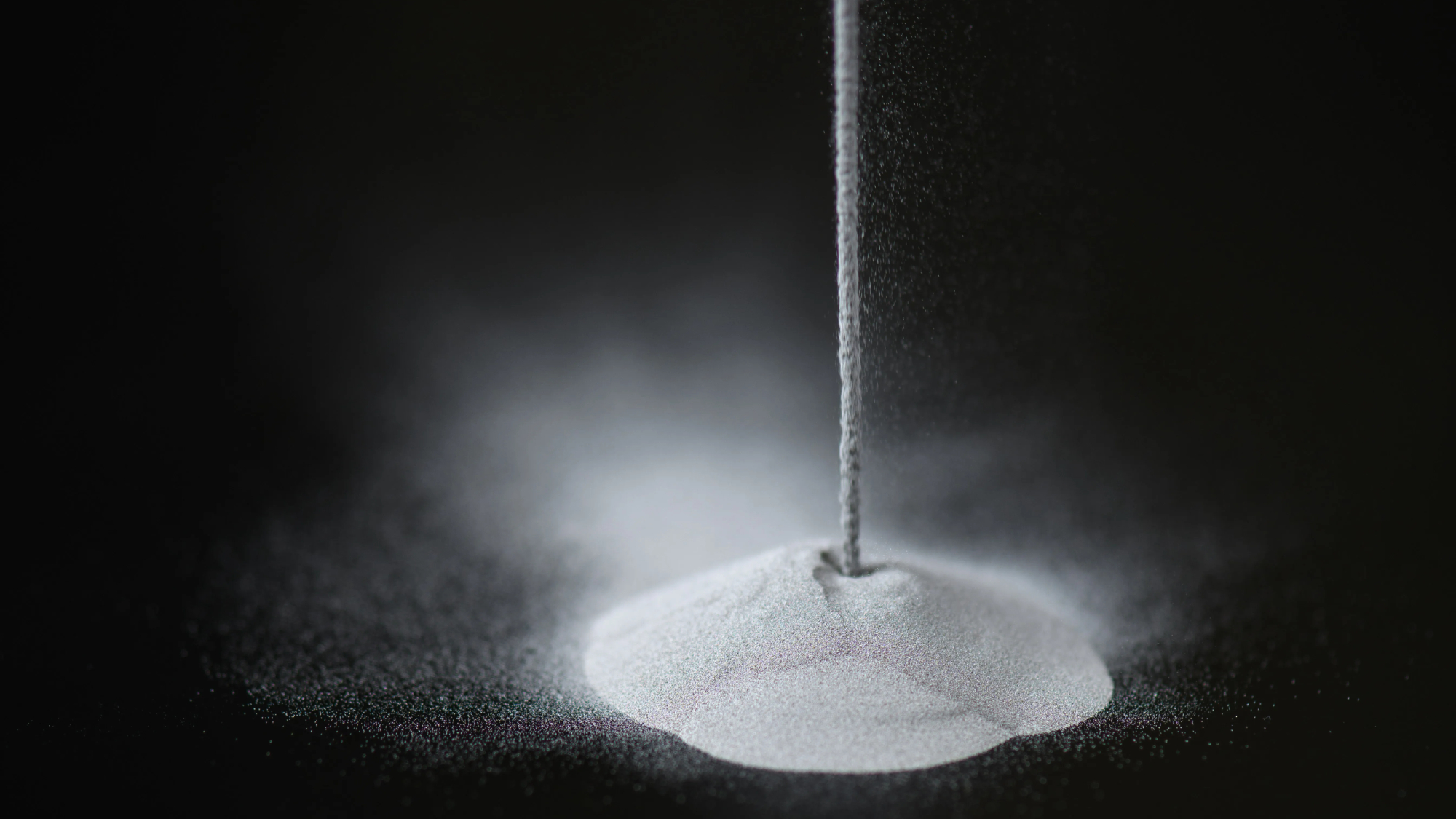
The superalloy is known as GRX-810 and consists of a 3D-printable, high-temperature material that has the potential to make airplane equipment and spacecraft parts more heavy duty. Items built with this material will be able to withstand a wide range of severe conditions, including intense temperatures, both in the air and in space. As of now, the superalloy is licensed to four American companies; going forward, it could result in positive commercial dividends, NASA says, and benefit the overall U.S. economy.
The four companies selected are Carpenter Technology Corporation of Reading, Pennsylvania, Elementum 3D, Inc. of Erie, Colorado, Linde Advanced Material Technologies, Inc. of Indianapolis, and Powder Alloy Corporation of Loveland, Ohio.
Related: 10 everyday NASA inventions and spin-offs you can find in your home
Through each co-exclusive license agreement, the companies will be able to create and sell GRX-810 to airplane and rocket equipment manufacturers, as well as other companies part of aviation or spaceflight supply chains. "NASA invests tax dollars into research that demonstrates direct benefit to the U.S. and transfers its technologies to industry by licensing its patents," Amy Hiltabidel, a licensing manager at NASA's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, OH, said in a statement.
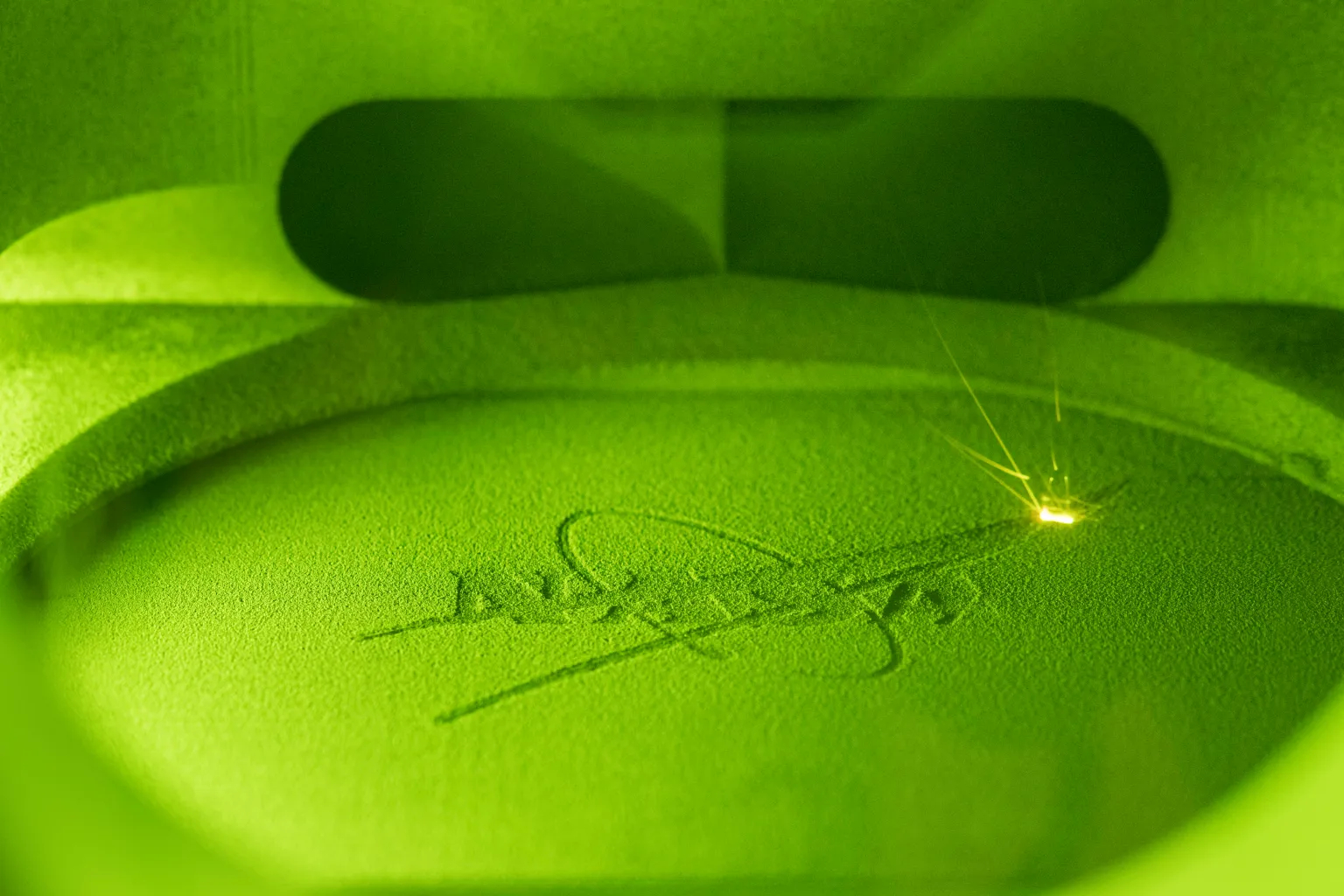

GRX-810 was originally developed with aerospace equipment in mind, including liquid rocket engine injectors, combustors, turbines and hot-section components capable of enduring temperatures over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit (1,093 degrees Celsius), according to a NASA release. The brains behind the superalloy are Tim Smith and Christopher Kantzos, both researchers at NASA Glenn. They say the design was drafted up by pairing computer modeling with a laser 3D-printing process to meld together, layer-by-layer, the metals involved.
"GRX-810 represents a new alloy design space and manufacturing technique that was impossible a few years ago," Smith said in the same statement.
This nickel-based alloy can handle more than most; it can withstand extreme heat, stress, and has double the amount of resistance from oxidation damage.
"Adoption of this alloy will lead to more sustainable aviation and space exploration," Dale Hopkins, deputy project manager of NASA's Transformational Tools and Technologies project, said in the statement. "This is because jet engine and rocket components made from GRX-810 will lower operating costs by lasting longer and improving overall fuel efficiency."