Witches, ghosts, and ghouls don’t just appear on Halloween night — they haunt the cosmos, too.
From eerie nebulae to zombie stars, here’s a collection of the most spine-chilling images from space to add a cosmic scare to your Halloween.
Related: Best space horror movies
Ghostly hand
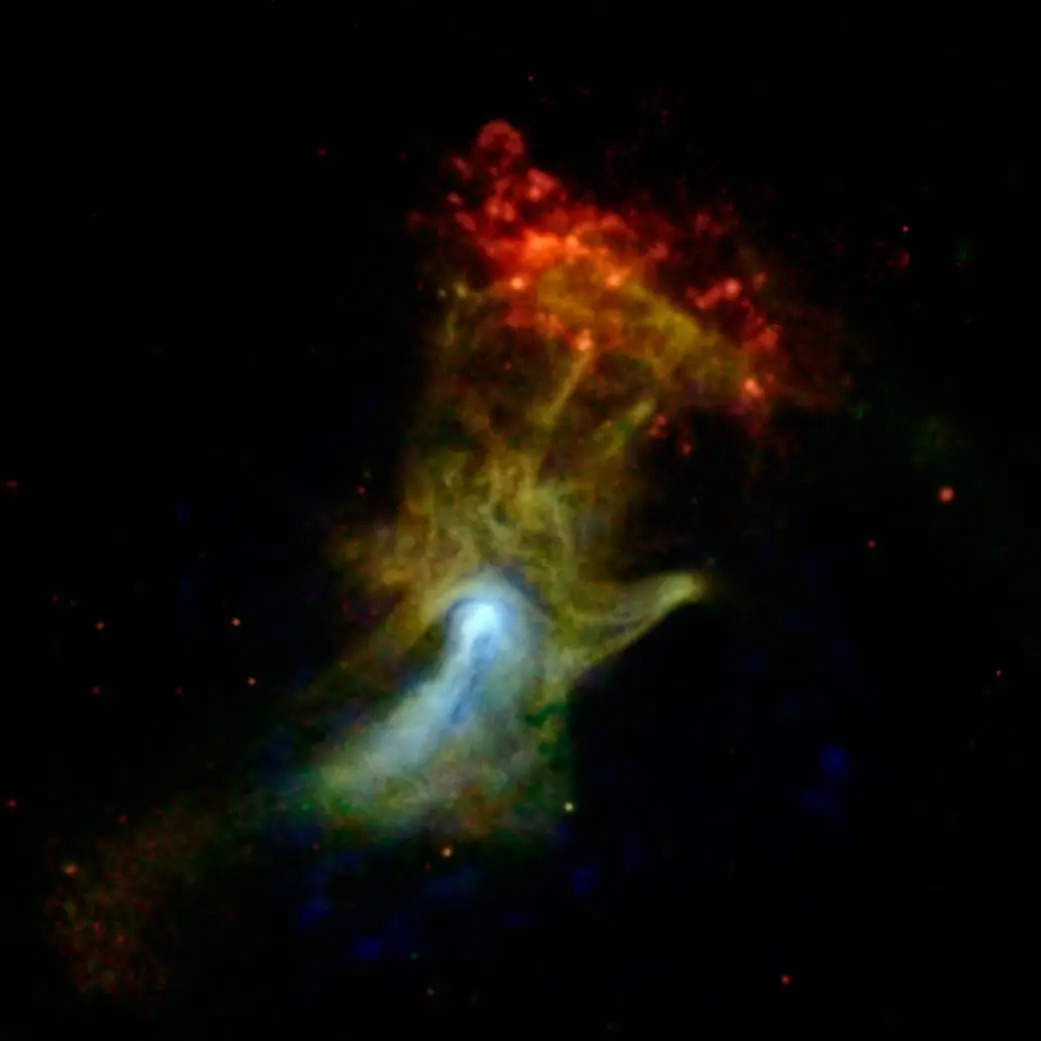

This glowing, green zombie-like hand reaches through the depths of space to grab a bright-red cloud of light. Is this a giant space zombie grabbing some dinner? Not quite — NASA calls this nebula the "Hand of God." It is actually a pulsar wind nebula, produced by the dense remnant of a star that exploded in a supernova.
Screaming skull
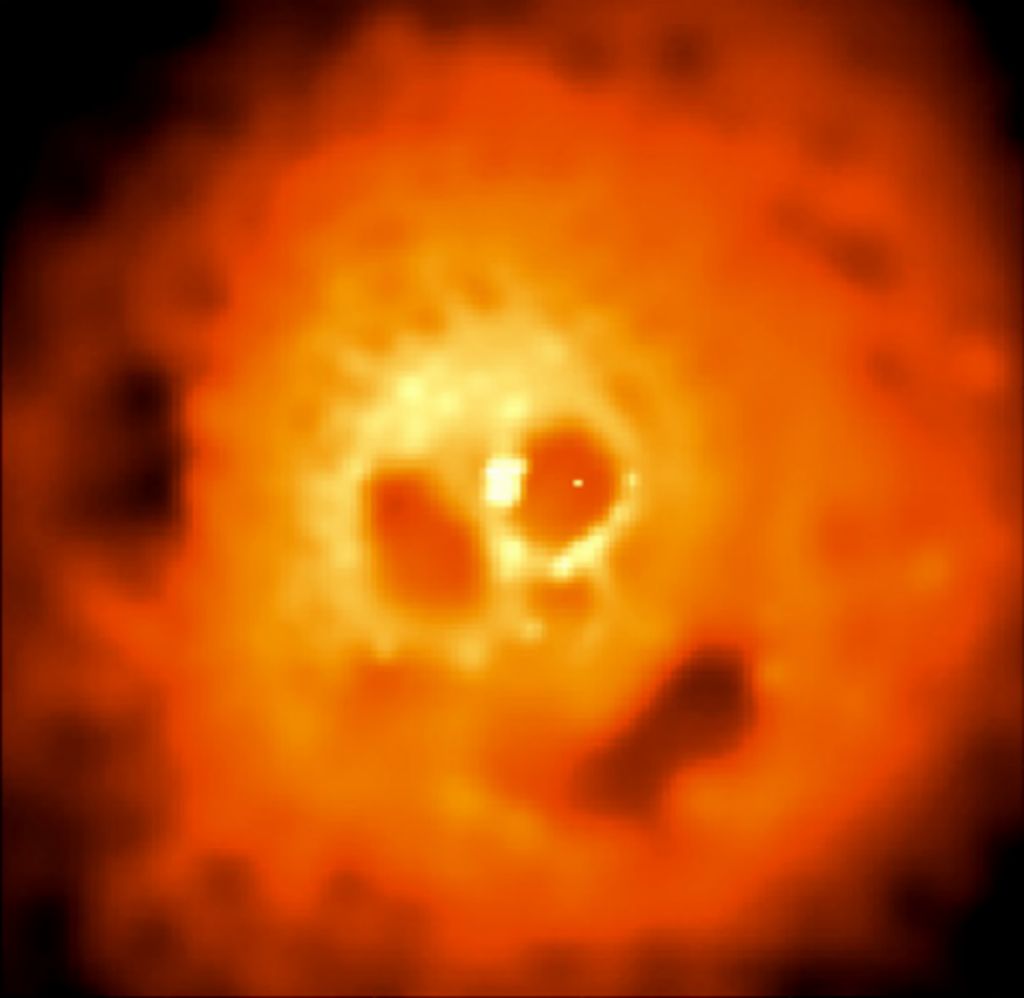

Yikes! This ghastly face in space appears to be screaming while suffering through a miserable, fiery death. But no real skulls were harmed in the making of this photo. It's actually an X-ray image of a cluster of galaxies known as the Perseus Cluster, captured by the Chandra Observatory.
Space ghosts
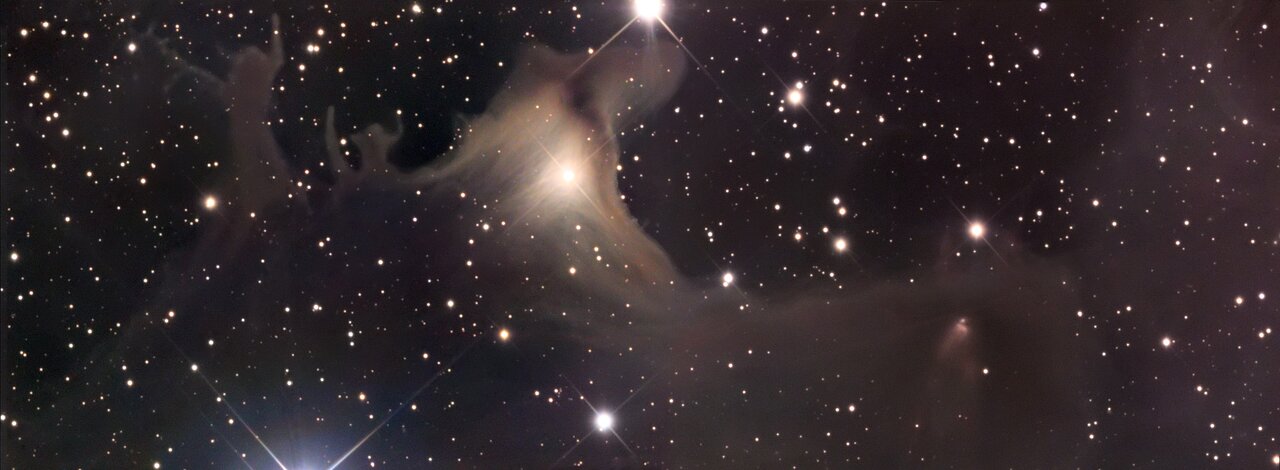

Ghastly figures appear to be fighting to escape from this cloud of interstellar gas and dust called SH2-136. The illuminated dark nebula is about 1,200 light-years away, towards the constellation Cepheus.
Asteroid skull
How did this skull wind up in space? A radar image of asteroid 2015 TB145, which NASA says is likely a dead comet, was captured using the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico on Oct. 30, 2015. Astronomers determined that the asteroid likely completes one rotation every 2.94 hours and that it reflects just 5 or 6 percent of the sunlight that hits it.
Solar jack-o'-lantern
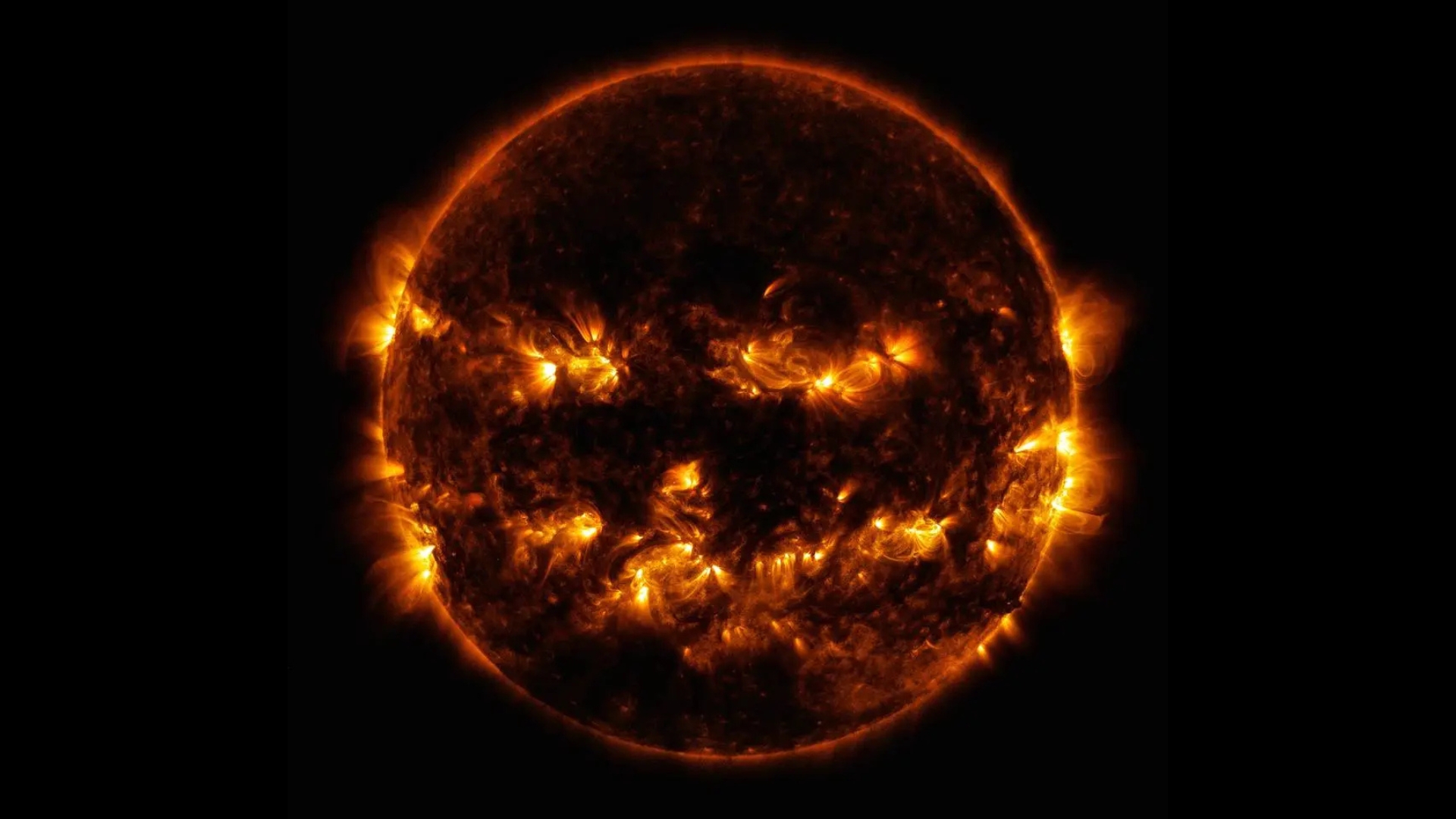

This striking NASA image shows the sun with an eerie jack-o'-lantern-like grin. Captured by the Solar Dynamics Observatory on Oct. 8, 2014, this composite photo reveals bright magnetic hotspots that form the "face"—two eyes, a nose, and a wide, spooky smile, with faint “ears” on each side.
Zombie Pac-Man nebula
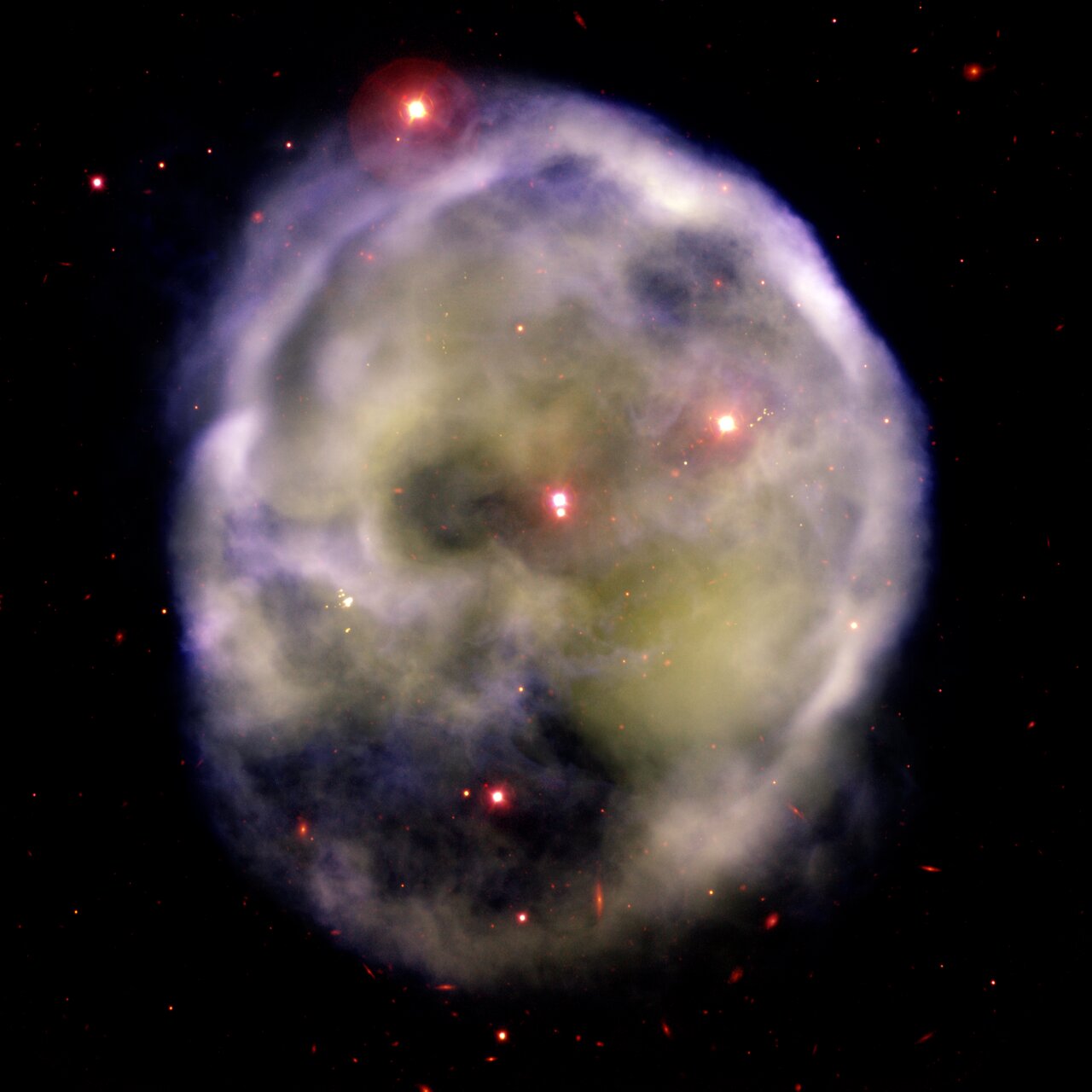
An ominous-looking nebula named NGC 246 lurks in the constellation Cetus about 1,600 light-years away from Earth. It is nicknamed the "Skull Nebula," but some astronomers call it the "Pac-Man Nebula." It appears to be taking a bite out of space.
Witch Head nebula
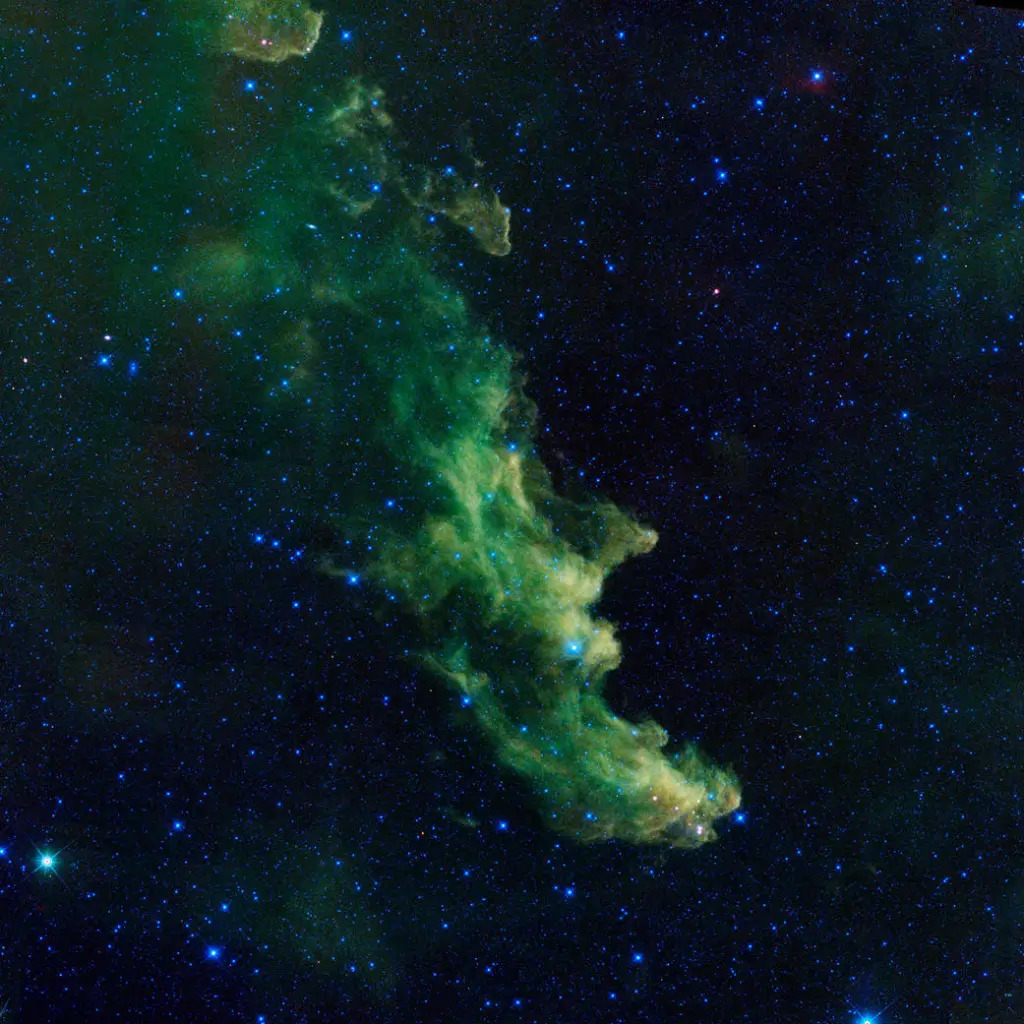

A witch appears to be cackling out into space in this eerie image from NASA's Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. The infrared portrait shows the Witch Head nebula, named after its resemblance to the profile of a wicked witch.
Ever feel like you're being watched?
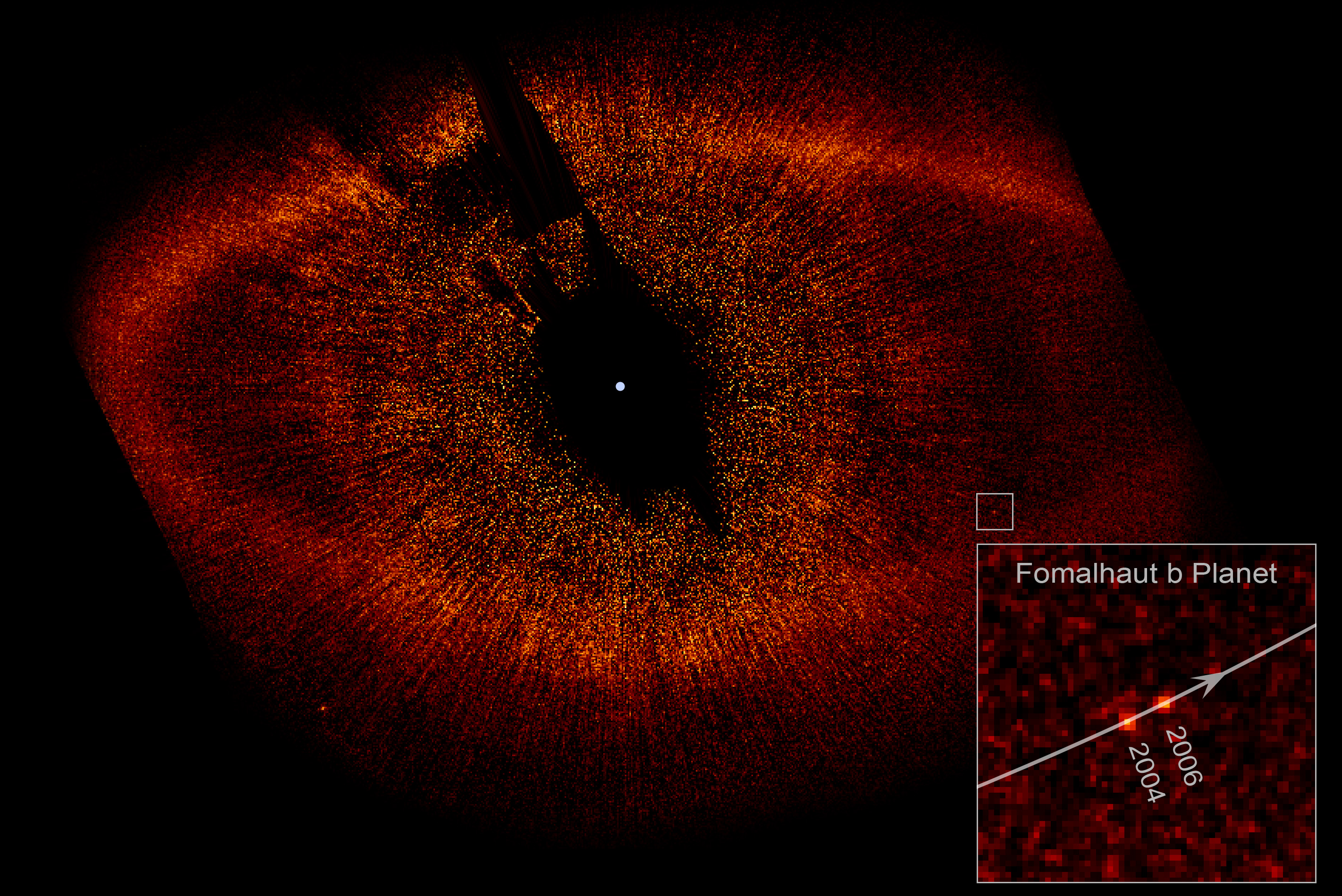
This evil eye-shaped nebula, formally named Fomalhaut, strikes an eerie resemblance to the fearful Eye of Sauron from the Lord of the Rings series. In the books, Tolkien described the eye as being "rimmed with fire... watchful and intent, and the black slit of its pupil opened up on a pit, a window into nothing."
Spooky face on Mars
Though we have yet to find any aliens on Mars, NASA did discover this creepy human face on the Red Planet. The original "Face on Mars" image was taken by NASA's Viking 1 orbiter, in grey scale, on July, 25 1976. NASA assures that the face is simply a peculiar pile of rocks — but that doesn't make it any less spooky!
Ghost Head nebula
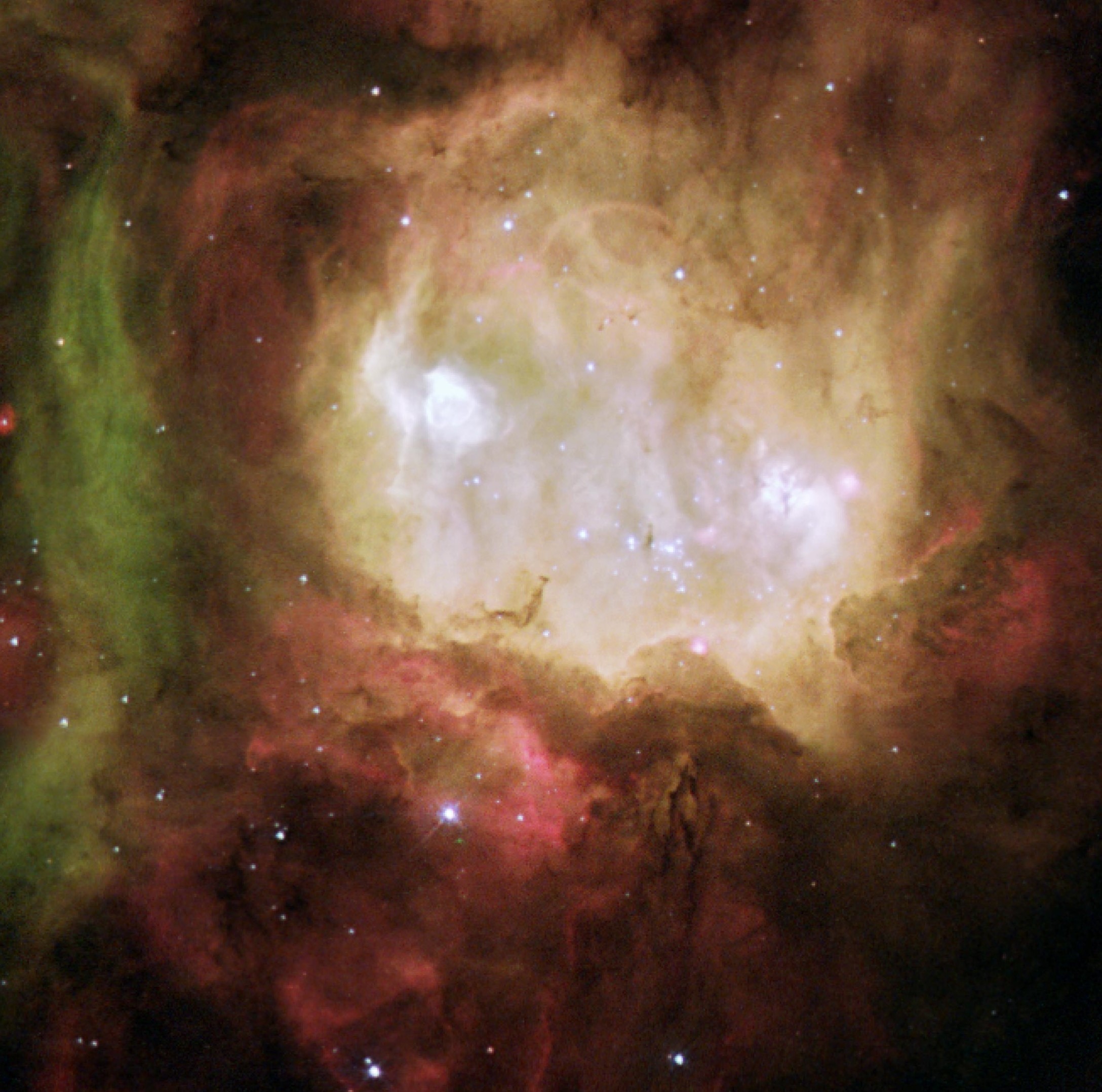

The Ghost Head Nebula's two flaming-hot eyes peer at us all the way from the Magellanic cloud, located about 170,000 light-years away from Earth. Its glowing eyes are star-forming regions with hot blobs of hydrogen and oxygen.
Black Widow nebula
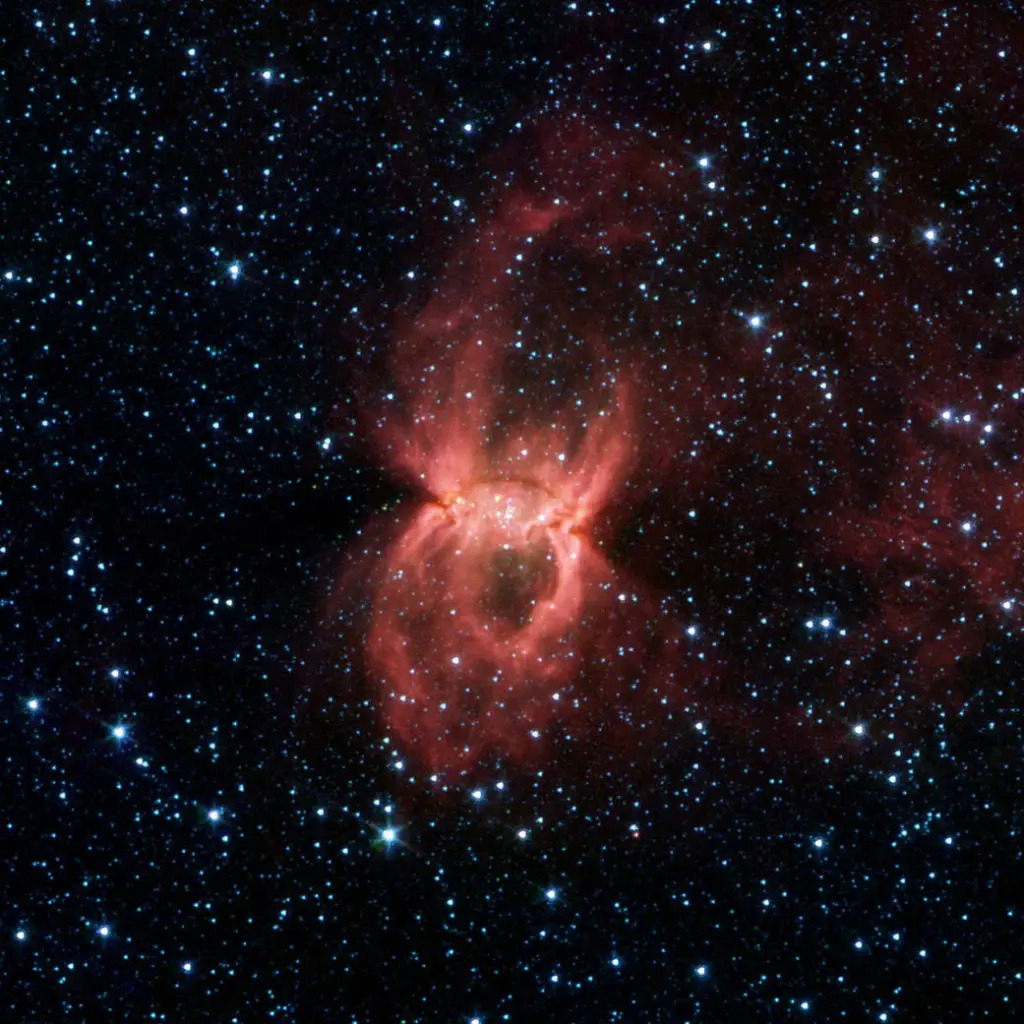

This giant, red space spider is the biggest black widow we've ever seen! But don't worry — it won't bite. It's actually just a nebula, or a cloud of interstellar gas and dust.
Zombie star
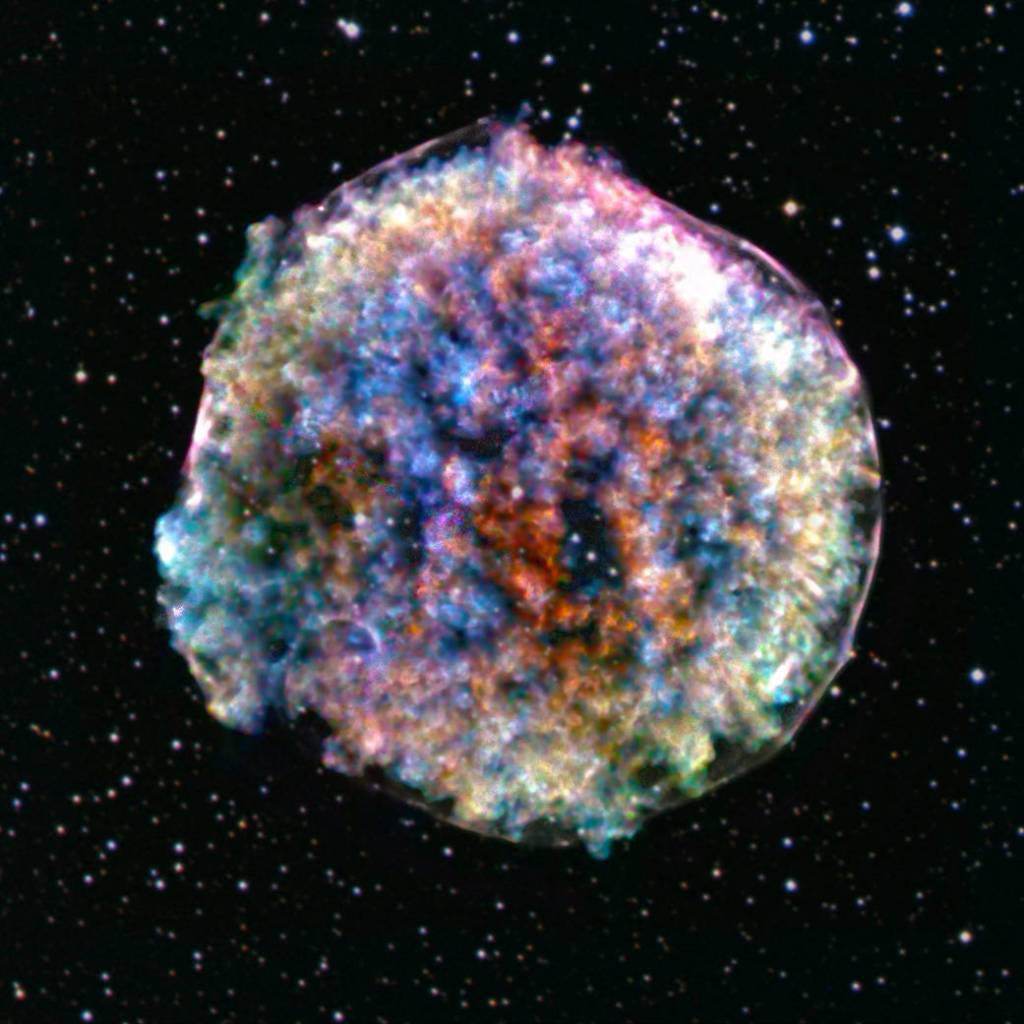
This zombie star named Tycho was once a white dwarf, or the remnants of an exploding supernova. The dead star gobbled up too much mass from another nearby star and exploded again in what's called a Type Ia supernova.
Cosmic jack-o'-lantern

NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope has spotted a cosmic jack-o'-lantern.
Researchers uncovered the grimacing pumpkin while mapping star formation in the outer region of the Milky Way. An animation of the nebula outlines the hollowed-out pumpkin, which appears to be screaming into space.
The carved-out cloud of gas and dust is caused by the outflow of radiation and particles from a massive O-type star that is 15 to 20 times more massive than the sun, according to a statement from NASA.







