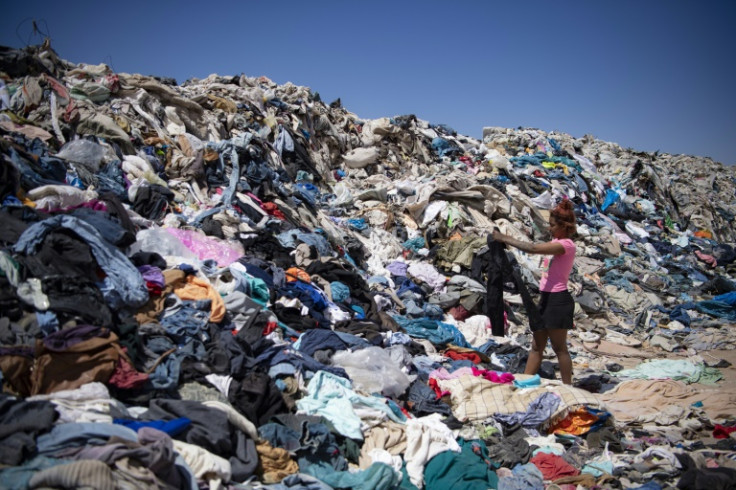
The fashion industry's enormous waste problem is pushing governments, particularly in Europe, towards ambitious recycling targets.
The problem is that recycling textiles is a highly complex task and technical solutions are still in their infancy.
NGOs warn the real problem is over-production, and that tech innovations may just provide cover for brands to continue pumping out billions of new clothes.
But the pressure to start recycling at massive scale is happening now.
"Brands need to get to high levels of recycling at super-speed, and if they don't, the EU will be giving them massive fines," said circular economy consultant Paul Foulkes-Arellano.
AFP spoke to multiple experts to see which ideas could make a difference.
Many will fail, but here is a snapshot of current contenders that illustrate the different challenges in textile recycling.
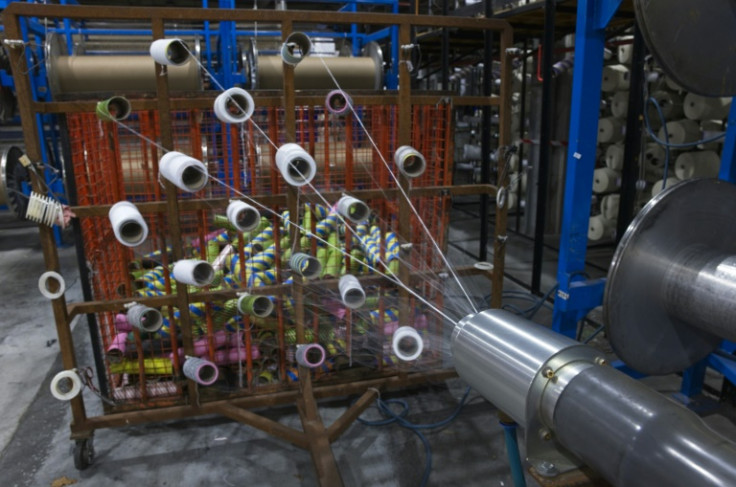
Most clothes are a blend of materials, making them hard to recycle. US-based Circ has invented a chemical solution to separate the most common blend, polycotton, into its constituent parts.
It uses a hydrothermal process to liquify the polyester and separate it from the cotton.
Both can then be turned into new fibres. Zara used them for a clothing line released in April.
The world lacks the infrastructure to collect and sort large amounts of old clothes, which must be kept clean and separate from other waste.
SuperCircle brings together delivery firms, warehouses and tracking systems to streamline and cheapen the process.
They hope to change public attitudes with in-store drop-off bins, free shipping labels and other encouragements.
"We need ease, convenience and incentives for consumers so that when they are done with an item, the first thing they think is end-of-life recycling," said co-founder Stuart Ahlum.
Starting with their own brand, Thousand Fell, they have rapidly expanded and now handle all recycling logistics for multiple companies and sectors, including Uniqlo North America.
Saentis Textiles already helped solve one key challenge with a patented machine that can recycle cotton with minimal damage to the fibres, so it can make quality new textiles.
Its recycled cotton is used by brands including IKEA, Patagonia and Tommy Hilfiger.
Now it is selling its machine to textile companies so they can install one directly in their factories, allowing them to chuck in cut-offs and scraps for recycling on the spot.
Unspun says it has invented the world's first 3D weaving machine, capable of creating a custom-sized pair of jeans directly from yarns in under 10 minutes.
Currently building its first micro-factory in Oakland, California to prove the concept, the machine could remove the need for brands to keep large stockpiles of inventory, cutting down on waste and transport.
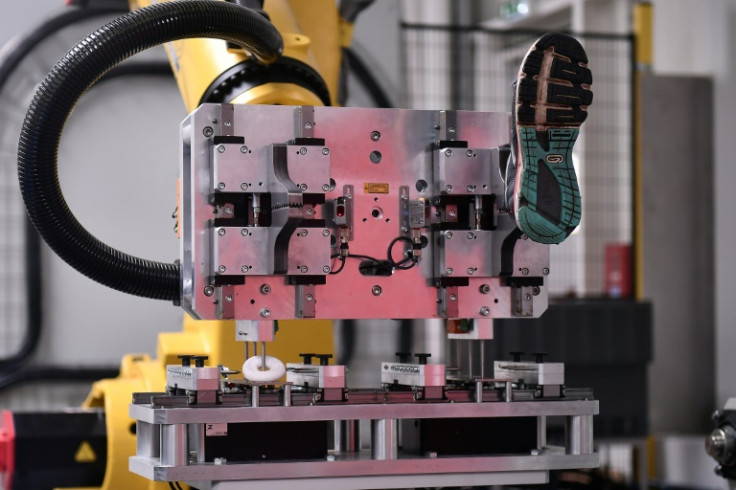
Clothes must be prepared before they can be recycled, and this is the specialty of France-based Cetia.
Some of its machines are simple, like one that yanks the soles off shoes.
Others are more complex. One uses AI to recognise hard points such as buttons and zippers, and then a laser to slice them off without damaging the item.
Rubi Labs has come up with a way to capture waste carbon dioxide from factories and turn it into cellulose, similar to the way that plants grow.
The resulting cellulose pulp can then be used to make yarn.
Whether it can be done at affordable scale remains to be seen, but in July Rubi Labs announced a pilot project with retail behemoth Walmart to test its innovation.