Global sea levels rose more slowly in 2022 than models predicted. But there's no reason to celebrate, according to NASA. The minor deviation from a decades-long trend was caused by the cooling effects of the La Niña climate pattern, and we are no doubt set to see faster sea level rise again in the coming years.
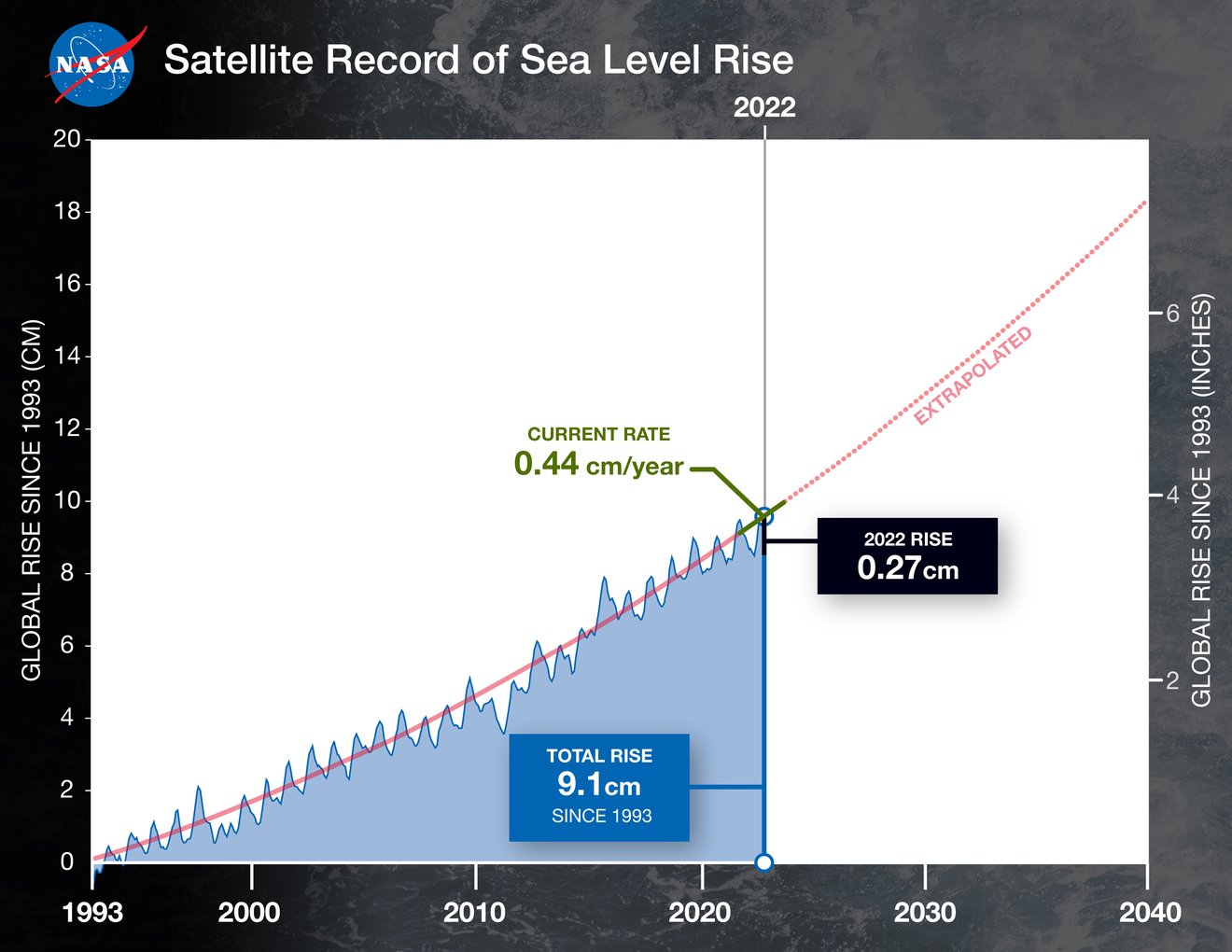
Between 2021 and 2022, global oceans absorbed the equivalent of a million Olympic-size swimming pools of water, which added 0.11 inches (0.27 centimeters) to average global sea levels. This increase is 0.05 inches (0.17 cm) lower than the projected 0.17-inch rise (0.44 cm) that scientists expected last year.
However, despite such fluctuations, 30 years' worth of satellite measurements reveal a trend of sea level rise acceleration that is only expected to speed up. While in the 1990s, global sea levels were rising at 0.08 inches (0.20 cm) per year, by 2050, three times as much water will be added to the global oceans on a yearly basis.
Related: Sea levels might rise much faster than thought, data from Greenland suggest
Scientists link the slow-down observed in 2022 to the La Niña climate pattern, the cold counterpart of El Niño. During La Niña years, sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean drop, and this change has widespread effects on weather around the world including on the amount of rainfall above the oceans, NASA said in a statement. But weather forecasters expect the warming El Niño to return in 2023 and with it, the sea level rise is set to speed up again.
NASA's data reveal that since 1993, global sea levels have risen by 3.6 inches (9.1 cm). NASA has been monitoring sea surface height since it launched the first satellite capable of measuring sea levels in 1992 in cooperation with its French counterpart CNES. The view from space allowed scientists for the first time to gain a detailed and global overview of what was happening with the world's oceans.
"We have this clear view of recent sea level rise — and can better project how much and how quickly the oceans will continue to rise — because NASA and CNES have gathered decades of ocean observations," Karen St. Germain, director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in Washington, said in the statement. "By combining that data with measurements from the rest of the NASA fleet, we can also understand why the ocean is rising."
Although natural weather fluctuations such as La Niña can have an effect on sea surface height, scientists know that the main contributor to the accelerating sea level rise is human-made climate change. Because of rising temperatures, ice sheets and glaciers melt faster, and more fresh water flows into the seas. On top of that, the warmer temperatures lead to the expansion of sea water, which further exacerbates the rise of sea levels.
Follow Tereza Pultarova on Twitter @TerezaPultarova. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.





