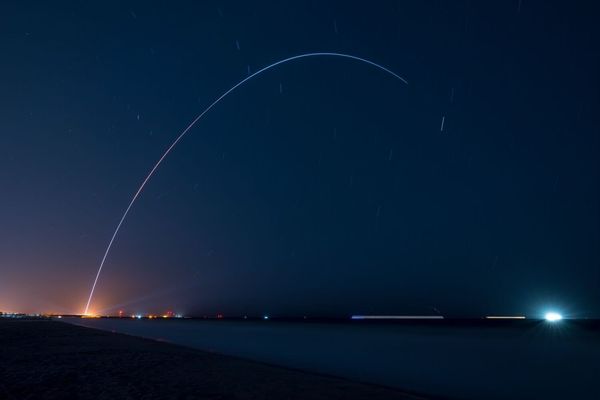
Washington (AFP) - The world's first 3D printed rocket is scheduled to make its third attempt to lift off on Wednesday for the maiden flight of an innovative spacecraft billed as being less costly to produce and fly.
The unmanned rocket, Terran 1, had been scheduled to launch on March 8 from Cape Canaveral, Florida, but it was postponed at the last minute because of propellant temperature issues.
A second attempt on March 11 was scrubbed due to fuel pressure problems.
Relativity Space, the California private aerospace startup that built the rocket, is hoping that the third time's the charm.
The company's three-hour launch window begins at 10:00 pm Eastern Time on Wednesday (0200 GMT Thursday).
Once it does take off, Terran 1 is set to reach low Earth orbit after eight minutes on a voyage intended to gather data and demonstrate that a 3D-printed rocket can withstand the rigors of liftoff and space flight.
If the rocket manages to attain low Earth orbit, it will be the first privately funded vehicle using methane fuel to do so on its first try, according to Relativity.
Terran 1 is not carrying a payload for its first flight, but the rocket will eventually be capable of putting up to 2,755 pounds (1,250 kilograms) into low Earth orbit.
The rocket is 110 feet (33.5 meters) tall with a diameter of 7.5 feet (2.2 meters).
Eighty-five percent of its mass is 3D printed with metal alloys, including the nine Aeon 1 engines on its first stage and the one Aeon Vacuum engine on its second stage.
It is the largest ever 3D printed object, according to the Long Beach-based company, and is made, it says, with the world's largest 3D metal printers.
Built in 60 days
Relativity's goal is to produce a rocket that is 95 percent 3D printed.
Terran 1 is powered by engines using liquid oxygen and liquid natural gas -- the "propellants of the future," capable of eventually fueling a voyage to Mars, Relativity says.
SpaceX's Starship and Vulcan rockets being developed by United Launch Alliance use the same fuel.
Relativity is also building a larger rocket, Terran R, capable of putting a payload of 44,000 pounds (20,000 kg) into low Earth orbit.
The first launch of a Terran R, which is designed to be fully reusable, is scheduled for next year.
A satellite operator can wait for years for a spot on an Arianespace or SpaceX rocket, and Relativity Space hopes to accelerate the timeline with its 3D-printed rockets.
Relativity said its 3D-printed rockets use 100 times fewer parts than traditional rockets and can be built from raw materials in just 60 days.
Relativity has signed commercial launch contracts worth $1.65 billion, mostly for the Terran R, according to CEO Tim Ellis, who co-founded the company in 2015.