Yao Ruyan paced frantically outside the fever clinic of a county hospital in China’s industrial Hebei province, 70 kilometers (43 miles) southwest of Beijing. Her mother-in-law had COVID and needed urgent medical care, but all hospitals nearby were full.
“They say there’s no beds here,” she barked into her phone.
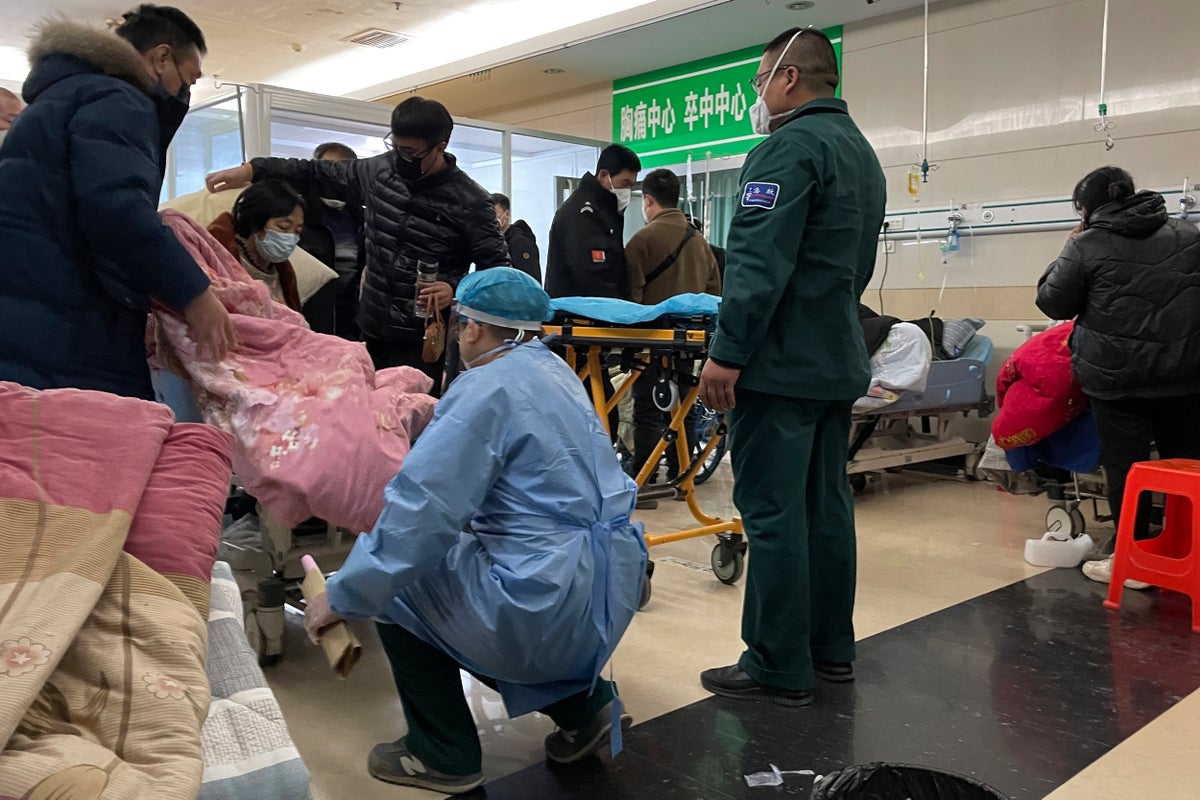
As China grapples with its first-ever national COVID wave, emergency wards in small cities and towns southwest of Beijing are overwhelmed. Intensive care units are turning away ambulances, relatives of sick people are searching for open beds, and patients are slumped on benches in hospital corridors and lying on floors for a lack of beds.
Yao’s elderly mother-in-law had fallen ill a week ago. They went first to a local hospital, where lung scans showed signs of pneumonia. But the hospital couldn’t handle COVID cases, Yao was told. She was told to go to hospitals in adjacent counties.
As Yao and her husband drove from hospital to hospital, they found all the wards were full. Zhuozhou Hospital, an hour’s drive from Yao’s hometown, was the latest disappointment.
“I’m furious,” Yao said, tearing up, as she clutched the lung scans from the local hospital. “I don’t have much hope. We’ve been out for a long time and I’m terrified because she’s having difficulty breathing.”
Over two days, AP journalists visited five hospitals and two crematoriums in towns and small cities in Baoding and Langfang prefectures, in central Hebei province. The area was the epicenter of one of China’s first outbreaks after the state loosened COVID controls in November and December. For weeks, the region went quiet, as people fell ill and stayed home.
Many have now recovered. Today, markets are bustling, diners pack restaurants and cars are honking in snarling traffic, even as the virus is spreading in other parts of China. In recent days, headlines in state media said the area is “ starting to resume normal life.”
But life in central Hebei’s emergency wards and crematoriums is anything but normal. Even as the young go back to work and lines at fever clinics shrink, many of Hebei’s elderly are falling into critical condition. It could be a harbinger of what's to come for the rest of China.
The Chinese government has reported only seven COVID deaths since restrictions were loosened dramatically on Dec. 7, bringing the country’s total toll to 5,241. On Tuesday, a Chinese health official said that China only counts deaths from pneumonia or respiratory failure in its official COVID-19 death toll.
Experts have forecast between a million and 2 million deaths in China next year, and the World Health Organization warned that Beijing’s way of counting would “underestimate the true death toll.”
At Baoding No. 2 Hospital, in Zhuozhou, Wednesday, patients thronged the hallway of the emergency ward. Patients were breathing with the help of respirators. One woman wailed after doctors told her that a loved one had died.
At the Zhuozhou crematorium, furnaces are burning overtime as workers struggle to cope with a spike in deaths in the past week, according to one employee. A funeral shop worker estimated it is burning 20 to 30 bodies a day, up from three to four before COVID measures were loosened.
“There’s been so many people dying,” said Zhao Yongsheng, a worker at a funeral goods shop near a local hospital. “They work day and night, but they can’t burn them all.”
Over two hours at the Gaobeidian crematorium on Thursday, AP journalists observed three ambulances and two vans unload bodies.
“There’s been a lot!” a worker said when asked about the number of COVID deaths, before funeral director Ma Xiaowei stepped in and brought the journalists to meet a local government official.
As the official listened in, Ma confirmed there were more cremations, but said he didn’t know if COVID was involved. He blamed the extra deaths on the arrival of winter.
But even as anecdotal evidence and modeling suggests large numbers of people are getting infected and dying, some Hebei officials deny the virus has had much impact.
“There’s no so-called explosion in cases, it’s all under control,” said Wang Ping, the administrative manager of Gaobeidian Hospital, speaking by the hospital’s main gate.
Wang said only a sixth of the hospital’s 600 beds were occupied, but refused to allow AP journalists to enter. Two ambulances came to the hospital during the half hour AP journalists were present, and a patient’s relative told the AP they were turned away from Gaobeidian’s emergency ward because it was full.
In Bazhou, a city 100 kilometers (60 miles) east of Gaobeidian, a hundred or more people packed the emergency ward of Langfang No. 4 People’s Hospital on Thursday night.
Guards worked to corral the crowds as people jostled for positions. With no space in the ward, patients spilled into corridors and hallways. Sick people sprawled on blankets on the floor as staff frantically wheeled gurneys and ventilators. In a hallway, half a dozen patients wheezed on metal benches as oxygen tanks pumped air into their noses.
Over two hours, AP journalists witnessed half a dozen or more ambulances pull up to the hospital’s ICU and load critical patients to sprint to other hospitals, even as cars pulled up with dozens of new patients.
A beige van pulled up to the ICU and honked frantically at a waiting ambulance. “Move!” the driver shouted.
“Let’s go, let’s go!” a panicked voice cried. Five people hoisted a man bundled in blankets out of the back of the van and rushed him into the hospital.
The guard asked a patient to move, but backed off when a relative snarled at him. The bundled man was laid on the floor instead, amid doctors running back and forth.
Medical workers rushed over a ventilator. “Can you open his mouth?” someone shouted.
As white plastic tubes were fitted onto his face, the man began to breathe more easily.
Others were not so lucky. Relatives surrounding another bed began tearing up as an elderly woman’s vitals flatlined. A man tugged a cloth over the woman’s face, and they stood, silently, before her body was wheeled away. Within minutes, another patient had taken her place.







