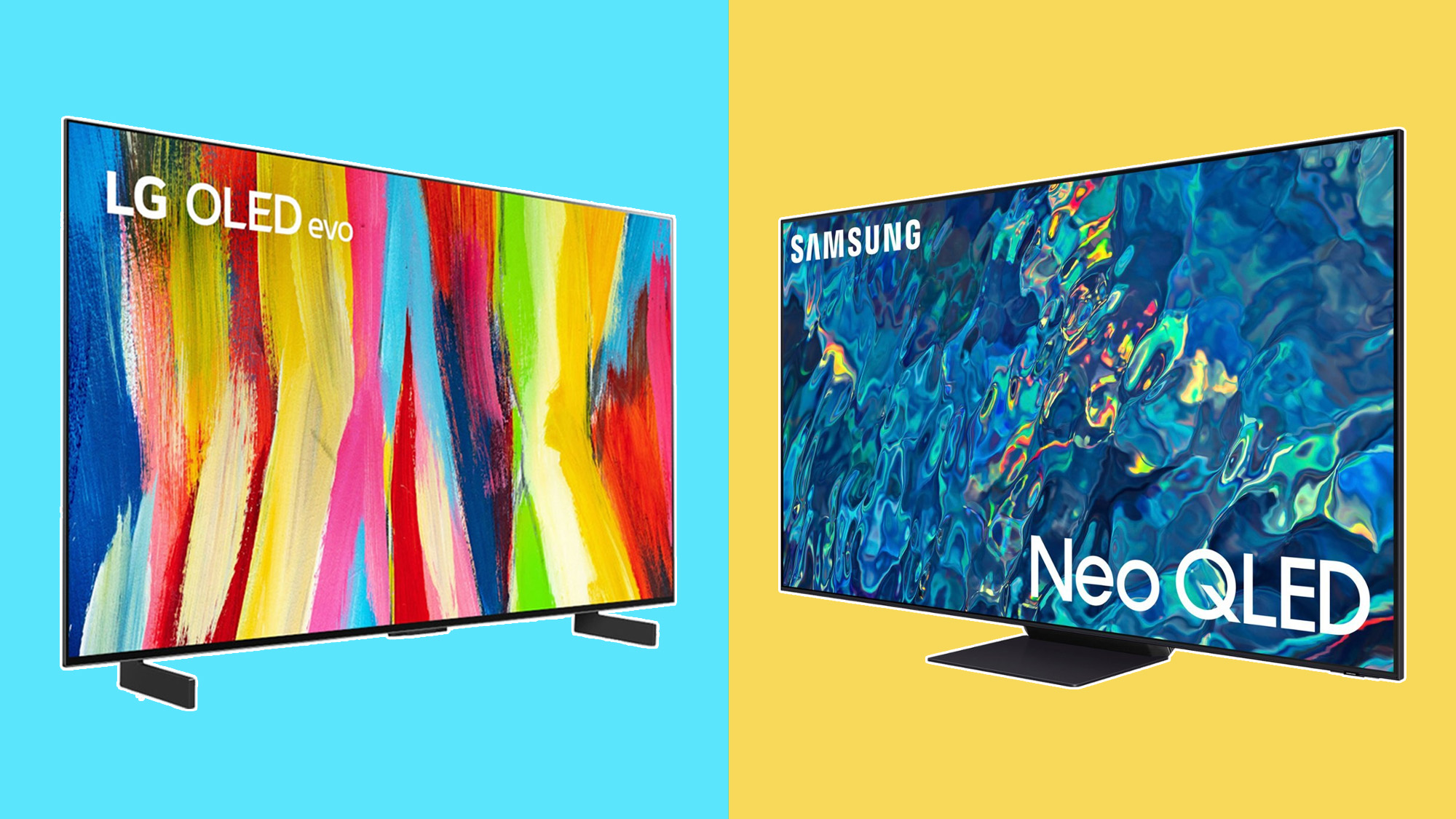
OLED vs Mini-LED is the biggest battle in TV world. If you want one of the best TVs, it's going to come down to one of these display technologies. Both have their pros and cons, which can make it tough to tell which is the better option for you.
Many of the best gaming TVs are OLEDs; it's truly hard to beat the clarity and general performance on these impressive TVs. Case in point: LG's all-new C4 OLED, a powerhouse of a display that comes in a range of sizes, all of them kitted out for gaming.
But Mini-LED TVs have their benefits against OLEDs, primarily better brightness. Thus, you'll have to choose wisely when deciding between OLED and Mini-LED TVs, as even some of the best OLED TVs on the block don't always come equipped with enough brightness to overcome sunny rooms.
Fortunately, with our years of testing TVs and knowhow in the space, we're well equipped to help you get to the bottom of this decision. Here's what you need to know.
OLED vs Mini-LED: What is OLED?

OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode, and it was first released in TVs in the United States in 2013. Until then, TV development was largely focused on refining the traditional LCD. OLED flipped that on its head, as a totally new, totally different display technology.
That’s one of the keys to OLED technology — as it allows images with black to actually be black, since there’s no light in those areas of the image at all.
In OLED displays, each pixel contains an organic material that glows when you apply electricity to it. In fact, the more electricity you apply to the material, the more it glows – which also means that if you apply no electricity to it, it won’t illuminate at all. That’s one of the keys to OLED technology — as it allows images with black to actually be black, since there’s no light in those areas of the image at all.
OLED panels can also be flatter than other display panels because OLEDs can be applied directly to glass, and they don’t require a separate backlight.
That said, it’s important to note that there are a few different ways in which OLED panels create color. Traditionally, many have simply used OLED technology as the backlight, shining through a color filter. Newer technologies are a little different though, instead use blue OLEDs combined with a layer of quantum dots to increase brightness. We’re not going to go into how that all works here, but we'll be sure to cover that in a future feature.
OLED vs Mini-LED: What is Mini-LED?

Mini-LED is a natural evolution of the traditional LED display. Typical LED displays work by using a backlight to illuminate an LCD panel. Each pixel in an LCD display contains three sub-pixels, which contain red, green, and blue (RBG) color filters, and can combine these sub-pixels to create separate colors.
The magic of a Mini-LED display, however, has more to do with the backlight than the LCD panel. Instead of one giant backlight, or a few dozen backlights, Mini-LED displays contain thousands of LED backlights, each of which measures between around 0.004 and 0.008 inches. The smaller size allows more LEDs to be packed together, and means that a TV can exert more control over the lighting, and turn off areas of an image that might contain black.
The LEDs in a Mini-LED display aren’t as small as those in a Micro-LED display — however Micro-LED technology is really only available on the most expensive TVs right now, while Mini-LED is much more mainstream.
OLED vs Mini-LED: Sharpness and resolution
The way we perceive the sharpness of a TV’s picture mostly has to do with its resolution. However, before we get into the resolution of the TV technologies, it’s important to note that right now, the vast majority of content is available in resolutions up to 4K. Eventually, that will shift to 8K, but we’re not there yet.
It’s also important to mention that on a Mini-LED TV, the backlight is separate from the LCD pixels, so It’s possible to have a 1080p Mini-LED TV, or a 16K Mini-LED display, without the size of the backlight LEDs differing.
Right now, there’s little difference in the resolution of OLED and Mini-LED TVs. The vast majority of Mini-LED and OLED TVs have a 4K resolution. There are models with higher resolutions that leverage both of these technologies, but right now the only limitation is a lack of content at 8K and above.
Winner: Tie
OLED vs Mini-LED: Black Levels
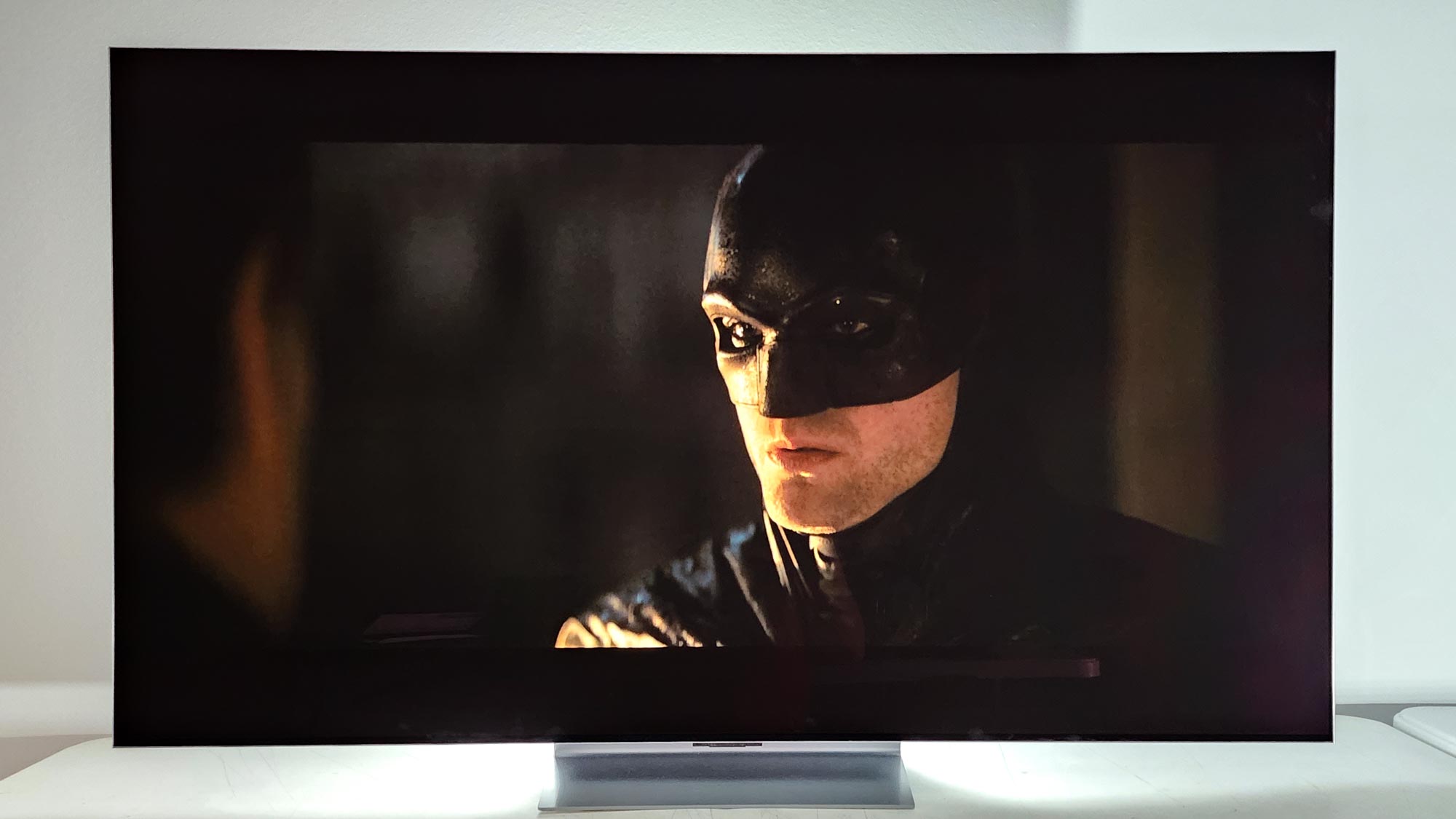
Black levels represent the main area of difference between these display technologies. As mentioned, Mini-LED TVs have thousands of tiny LEDs that are used in a backlighting system to illuminate the LCDs. That means they have much more control over black levels than previous-generation LCD TVs, and can provide deep blacks in certain scenarios.
However, even when an LED is switched off in a Mini-LED TV, the glow from the LEDs that are turned on around it can take away from what would otherwise be a true black — creating a kind of glowing effect around illuminated objects.
OLED TVs don’t have this issue. OLED TVs can create true blacks by simply not illuminating individual pixels, and don’t really have the issue of elevated blacks because the pixels are separated. While Micro-LED displays can approach this per-pixel control, Mini-LED displays aren’t quite there.
Winner: OLED
OLED vs Mini-LED: Brightness and contrast
Traditionally, brightness has been one area in which OLED TVs have lagged behind. That’s simply been a limitation of the technology — individual OLEDs just haven’t been able to get as bright as the LEDs that we use in the backlight of a Mini-LED display.
In recent years, however, OLED TVs have been getting much brighter, largely due to new variations of the technology. The aforementioned quantum dot-enhanced OLED displays (known as QD-OLED) are one such example. These TVs (like the Samsung S95D) leverage quantum dots for brighter highlights and richer, purer color. In our lab tests, the S95D surpassed the 1,700-nit mark.
LG has yet to produce a QD-OLED of its own. Instead, it's gained ground by engineering a new version of a traditional OLED display, one that makes use of LG's own Micro Lens Array (MLA) technology. As the name implies, it's an array of tiny lenses that refocuses light toward the viewer, resulting in brighter highlights as well as a brighter overall picture. The newest TV to use MLA technology is the LG G4, which scrapes 1,500 nits in HDR, according to our tests.
Despite these advances, Mini-LED TVs still get much, much brighter. Mid-range and high-end Mini-LED panels can easily reach 1,500 nits, and often well above 2,000 nits (3,000 in the case of the Hisense U8N).
Contrast is a slightly different conversation. Contrast ratio refers to the difference between the deepest blacks and the brightest whites. OLED TVs, as mentioned, can deliver so-called “true blacks.” This kind of breaks the concept of contrast a little, because the deepest blacks are infinite. So, technically, OLED TVs have a higher contrast ratio, but Mini-LED TVs can get brighter.
Winner: Mini-LED
OLED vs Mini-LED: Color

When we talk about color on TVs, we’re usually talking about the range of colors a TV can produce, also known as the color gamut. The majority of mainstream TVs hit somewhere between 95% and 100% of the sRGB color spectrum, however top-end OLED TVs produce more than 100% of the SRGB color gamut. The Sony Bravia A95L OLED, for example, was able to cover 89% of the much broader Rec. 2020 color space in our tests last year.
Typical Mini-LED TVs don’t quite reach those heights. Keep in mind, though, that this has little to do with Mini-LED technology itself and more to do with the kinds of color filters and layers that TV manufacturers use with Mini-LED backlights. In addition, QD-OLEDs like the A95L tend to offer far better color volume than typical WOLED displays (even the MLA-equipped LG G4).
There are signs, too, that Mini-LED is quickly gaining ground. According to our lab tests, the previously mentioned Hisense U8N covers about 82% of the Rec. 2020 color space.
Nevertheless, OLED maintains a slight edge.
Winner: OLED
OLED vs Mini-LED: Viewing angles
Viewing angles of a TV refer to the ability for a TV to retain accurate colors and proper contrast when viewed off-center. This can be important, as only one person can truly watch a TV at its center, and if more than one person is watching, viewing angle performance becomes crucial.
Mini-LED TVs (and LCD displays in general) offer much narrower viewing angles than OLEDs. While you're bound to notice some level of degradation in contrast and color saturation the further off-axis you sit while watching a Mini-LED TV, OLEDs tend to hold up no matter where you happen to be seated.
It's worth noting that the viewing angle of a Mini-LED TV has a lot to do with the type of display that’s used on top of the Mini-LED backlight, so be sure to check whether a TV uses a VA- or ADS/IPS-type display. VA panels typically offer deeper black levels at the expense of viewing angle flexibility, while ADS/IPS-style panels offer shallower black levels but wider viewing angles.
Winner: OLED
OLED vs Mini-LED: Burn-in

One major issue that has tarnished OLED TVs since the beginning is burn-in. Burn-in happens when a static image that has been left on the display for an extended period of time leaves behind a residual, ghostly afterimage. Imagine if you watch the same news station for hours on end only to find that a faint outline of the news station’s logo remains when watching something else entirely.
For the most part, issues around burn-in on OLED TVs have more or less been resolved at this point, thanks to measures like pixel shifting software, which detects static images and subtly changes up the pixels to prevent burn-in.
Mini-LED TVs don’t really suffer from the same issues around burn-in. So, while the issue is mostly resolved on OLED TVs, it’s still more likely than on a Mini-LED TV.
Winner: Mini-LED
OLED vs Mini-LED: Size and price
Generally speaking, manufacturers have found it easier to build larger Mini-LED TVs than OLED TVs, but there are nevertheless some huge OLED TVs out there. Some of the best 85-inch TVs you can buy are 83-inch OLED TVs. Still, there are more large Mini-LED TVs than large OLEDs, and they're almost always cheaper.
Why is that the case? OLED technology has been out for over 10 years now, but it’s still largely considered a premium TV technology. When Mini-LED TVs were first introduced, they were pretty expensive, too. However, the cost of the technology quickly fell, and due to the lower cost of manufacturing, Mini-LED TVs can be bought at a lower price than OLED TVs.
Winner: Mini-LED
OLED vs Mini-LED: Which is best?

It might sound like a cop-out, but both are extremely good TV technologies. For the vast majority of people, Mini-LED is going to be the more tempting option; they can get brighter, don’t suffer from burn-in, and are cheaper.
But, dig a little deeper, and you might find that an OLED TV is better for your needs. OLED TVs offer better viewing angles and produce deeper black levels.
Setting brightness aside, OLED TVs are still considered more premium than Mini-LED TVs. That will likely remain true as QD-OLED TVs continue to roll out, which solves most of the brightness issue.
In short, if you want an affordable TV at a larger screen size and with higher brightness levels, the Hisense U8N is probably the TV to go for. If you want cinematic black levels, wider viewing angles, and a posh-looking design, consider something like the LG C4, an all-around fantastic OLED TV.







