How Video Repair Software Is Saving History One Clip at a Time
Have you ever opened a video file that looks fine, but refuses to play? Video files break for more reasons than people expect, but that doesn’t mean the footage is gone. From what we’ve seen, most “lost” clips still contain usable data; they just can’t be read correctly.
Today, we will explain how video repair software fixes broken video files and break down which tools make sense to try.
How Video Repair Software Works
Before we get into specific tools, let’s slow things down for a moment and look at what actually happens when a video “breaks.” In most cases, the situation is simpler than it looks. The file exists, the only problem is that the video player no longer understands how to interpret what’s inside. At that point, the issue usually lies in the video file metadata and structure, which defines how audio and video streams are stored and interpreted inside the container.
This is exactly where video repair software can help. When the data remains present but the structure becomes incomplete or inconsistent, repair tools restore the instructions that media players rely on. Despite the different interfaces, most video file repair software relies on the same core techniques to restore broken footage:
- Header and metadata rebuild restores the part of the file that tells media players how to interpret video and audio streams. When this information is missing or damaged, the video may remain intact, but it stays completely unplayable.
- Container repair fixes the outer structure of the video file so audio and video streams map correctly and follow the proper order. This approach applies when files open but freeze, skip sections, or stop during playback.
- Reference-based repair uses a healthy video recorded on the same device and with identical settings as a structural template. The software compares both files and reconstructs the corrupted one using information from the working sample.
- Stream realignment corrects timing issues between audio and video tracks. When timestamps drift or break, this technique restores synchronization so movement and sound match again.
- Remux or re-encode operations reorganize existing video data into a clean container or rewrite it with a new encoding process. This method helps when structural fixes alone cannot stabilize playback.
It might sound a little complicated at first, but fortunately, repair tools can handle the heavy lifting for you. In many cases, you only need to provide the broken file and, when available, a healthy sample from the same device. The software then applies the correct repair method automatically. Of course, not every file can be restored, but most playback issues fall well within the capabilities of modern repair tools.
Top 5 Best Tools That Help Recover Video Footage
With the basics out of the way, it makes sense to look at the tools themselves. We selected five tools that, in our experience, handle the most common video file problems reliably. If you need to repair MOV file, you will find a suitable option on this list. The comparison table below helps you quickly see which tool fits your case.
|
Tool |
Type |
Best Use Case |
Reference Needed |
Price |
|
Clever Online Video Repair |
Online |
Interrupted camera or phone recordings |
Sometimes |
Free |
|
Untrunc GUI |
Desktop |
Truncated MP4/MOV with privacy needs |
Yes |
Free |
|
FFmpeg |
Desktop (CLI) |
Severe or unusual corruption |
No |
Free |
|
VLC Media Player |
Desktop |
AVI index issues, quick checks |
No |
Free |
|
Restore.Media |
Online |
Large or professional footage |
Not always |
Paid |
1. Clever Video Repair
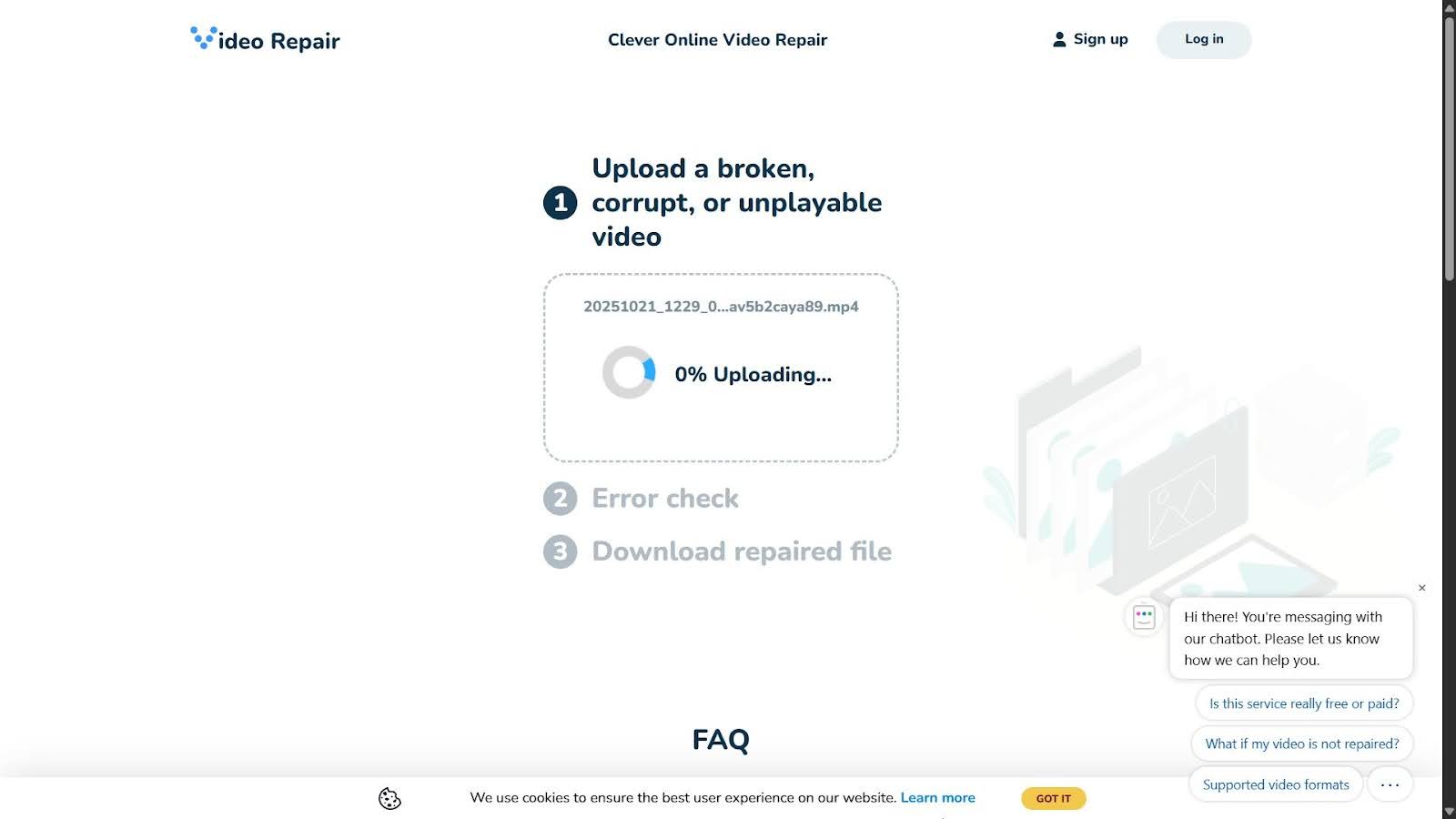
Clever Online Video Repair is a free browser-based video repair tool designed to fix files that become unplayable after an incomplete or interrupted recording. The tool works at the structural level. It rebuilds missing container information and restores playback metadata so media players can read the file again. Clever Online Video Repair supports a wide range of formats, including MP4, MOV, M4V, 3GP, 3G2, QT, DAT, and related variants, with a maximum file size of up to 5 GB.
Pros
- No software installation
- Works in any modern browser
- 5 GB file size limit is enough for most cases
- Strong results with MP4, MOV, and DAT files
- Accurate repair with a matching reference file
- Supports H.264 (AVC) and H.265 (HEVC)
- Preview available before download
Cons
- Best results depend on a reference file
We included Clever Online Video Repair in this list because it solves one of the most common real-world problems with a high success rate and minimal user effort. In our tests, it handled truncated MP4 and MOV files reliably, especially when corruption involved missing metadata or an incomplete container.
When a healthy sample recorded on the same camera with the same settings is available, this is the best-case scenario; it greatly helps the service rebuild the file correctly. That said, the repair can still succeed even without a reference clip.
2. Untrunc GUI
Untrunc GUI is a free video repair software. It is an open-source utility built specifically for truncated video files. These are files where recording stopped before the container finalized its structure, a situation we often see after sudden power loss, system crashes, or interrupted transfers. Unlike online tools, Untrunc runs entirely on your computer, which makes it suitable for large files and sensitive footage.
Pros
- Free and open-source
- Works fully offline
- High success rate for truncated files
- Lightweight and portable
- Does not modify the original file
Cons
- Limited format support
- Slower repair process than online tools
- Interface lacks polish
Untrunc GUI remains one of the most reliable free desktop options for structural video repair. In our tests, it handled damaged MP4 and MOV files consistently when a proper reference clip was available. The tool compares a healthy video recorded on the same device with the corrupted one and reconstructs missing structural elements, such as headers and indexes, based on that reference. However, in some real-world cases, people report that Untrunc may produce a broken output when the file lacks sufficient intact data, especially when an older version of the tool is used. Always check if the version you use is the latest one.
3. FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a professional-grade video and audio processing tool that also serves as a powerful repair option. It does not present itself as a video repair app, but its ability to rewrite containers, rebuild stream mappings, and re-encode damaged files makes it one of the most flexible tools available. However, many users note that the software feels complex since all operations rely on command-line input and precise parameters.
Pros
- Supports almost every video format and codec
- Works offline with no upload limits
- Offers granular control over repair methods
- Preserves the original file during repair attempts
- Large documentation base and active community
Cons
- No graphical interface
- Requires command-line knowledge
- Higher system resource usage during re-encode tasks
We included FFmpeg because it gives full control when automated repair tools fall short. In our tests, FFmpeg handled a wide range of corrupt files, including MP4, MOV, MKV, and AVI. Simple remux commands restored playback when corruption affected metadata or container structure. For deeper issues, controlled re-encode commands restored watchability when other tools failed.
4. VLC Media Player
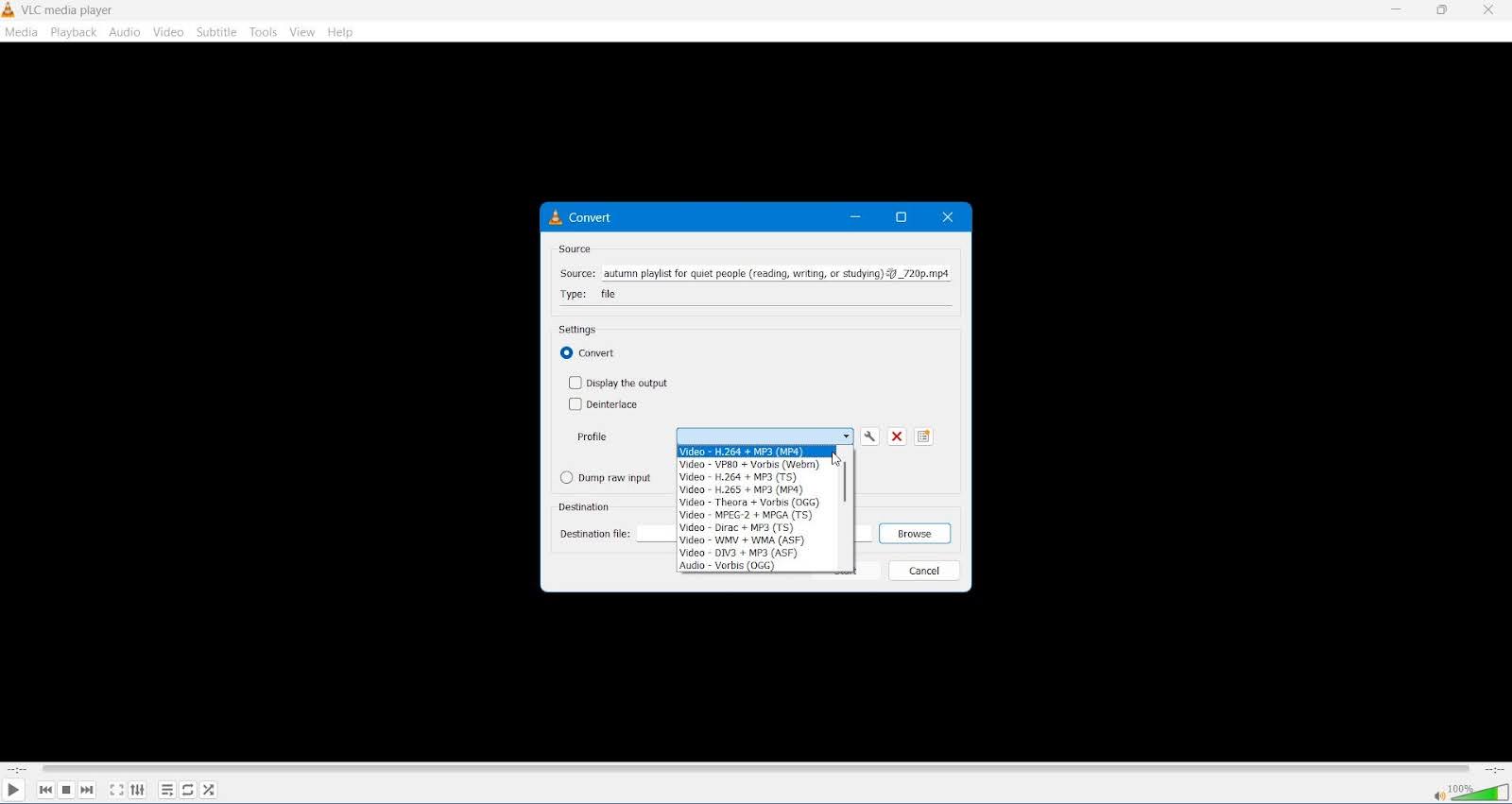
VLC Media Player is best known as a universal media player, but it also includes basic video repair capabilities. These features target container and index issues rather than deep structural damage, which places VLC in a supporting role rather than a primary repair solution.
Pros
- Free and widely available
- Dedicated repair support for AVI files
- Includes playback, inspection, and conversion tools
- Allows partial playback of damaged files
Cons
- Repair success varies by format
- Primary repair function applies only to AVI
- Re-encode process may reduce quality
- Lacks advanced repair logic
VLC is widely available and sometimes resolves playback issues without additional tools. In our tests, VLC performed best with AVI files that contained broken indexes. Its built-in “Always fix” option restored playback in several cases where files refused to open in other players. For formats such as MP4 and MOV, VLC relies on re-encode. This approach occasionally restores usability but produces inconsistent results and may reduce quality. Still, VLC offers a fast way to assess damage and attempt basic repair.
5. Restore.Media
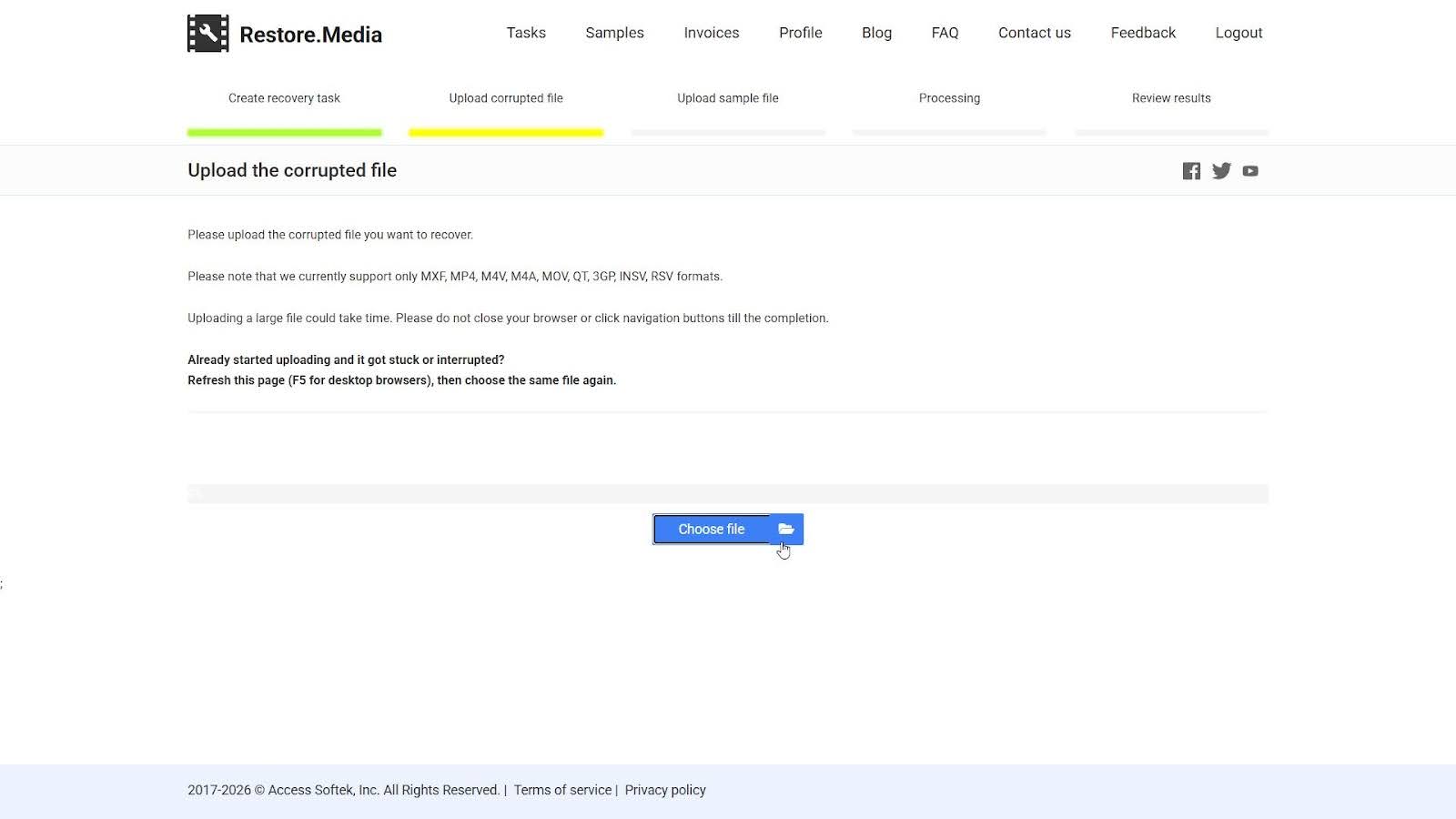
Restore.Media is a browser-based video repair service built for more complex corruption cases, especially those involving professional cameras and large files. Restore.Media focuses on structural reconstruction backed by device-specific profiles and optional manual review by engineers.
Pros
- Support for professional and action camera formats
- Handles very large files
- Works with MP4, MOV, MXF, INSV, and M4A
- Optional manual repair by engineers
- Preview available before payment
Cons
- Paid service with variable pricing, from $4.99 per file, with larger or more complex videos costing more
- Full download requires payment
- Repair time depends on file size and queue
- No batch processing
We included Restore.Media because it handled cases that simpler tools could not. In our tests, it showed strong results with MOV, MP4, MXF, and camera-specific formats where metadata damage or broken indexes blocked playback entirely. The platform analyzes the file first, then applies a repair method based on container structure, codec layout, and recording device data. When automatic repair did not fully restore playback, you can also use the option to request engineer review.
Conclusion
After we tested and compared all tools, one point stood clear: no single tool solves every repair case. If we had to suggest where to start, Clever Online Video Repair would be the best choice. It does not require installation or payment and works directly in the browser, which makes it accessible to almost anyone. Tools like FFmpeg or Untrunc offer more control but also require more experience and setup. Each option on this list has its strengths, which is exactly why all of them earned a place here.
FAQ
Can video restoration software fix audio that drifts out of sync over time?
Often, yes. From what we’ve seen, audio drift usually comes from broken or inconsistent timestamps rather than missing content. Repair tools rebuild timing data or realign streams so audio and video follow the same playback clock again. Success depends on how stable the remaining data stays across the full length of the clip.
What can I do when I don’t have any healthy sample clips at all?
You still have workable options. Many tools rely on internal format profiles instead of device-specific reference files, especially for common formats like MP4 and MOV. In these cases, the software rebuilds the file structure based on known container and codec standards rather than copied metadata from a sample clip.
When profile-based repair does not restore full playback, a clean remux or a re-encode often restores basic usability. If those methods still fail, you can try another repair tool, since different engines interpret damaged data in different ways.
Are online repair tools safe for private footage?
It depends entirely on the service and how it handles uploads. We usually advise that you verify the use of encrypted connections and transparency about file retention. Some tools remove files automatically after the repair completes, while others keep files longer for later support or inspection. For example, Clever Online Video Repair states that files are processed in secure sessions and can be removed by the user after repair.
Why do I see green blocks or heavy artifacts after repair, and how can I fix it?
This points to visual data that the software cannot reconstruct. Structural repair restores playback but cannot recreate image information that failed to decode correctly during recording or transfer. A re-encode with a different codec may reduce visible artifacts. When corruption affects large portions of the video, only manual restoration or professional analysis offers further improvement. It also helps to test playback on different players, since some handle imperfect streams better than others.







