While Big Tech's software dominates the AI narrative, the real story is about infrastructure and its limitations. The intense demand for computing power and data has created an opening for a decentralized, crypto-native alternative to emerge.
This new stack, built with everything from GPU networks to Web3 agent launchpads, is a complete rethink of the current model. It gives users actual ownership over AI agents and their data, offering more security and censorship-resistance than the walled-off systems run by today's tech giants.
Companies like Binance are central to this ecosystem, providing access to these tools and helping this new AI market grow. But as this convergence creates a new architecture for AI, its future depends on successfully navigating the world's regulators.
Web3 AI Agents on the Rise
The market for Web3 AI agents is showing serious momentum with a market capitalization hitting $7.71 billion as of November 6, 2025. Projects like the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (which includes Fetch.ai, SingularityNET, and CUDOS) and Virtuals Protocol are at the forefront of this emerging sector. These are not just theoretical concepts but active networks creating autonomous agents for a variety of on-chain tasks.
Unlike centralized AI, these agents deliver true ownership. Creators can mint them as unique digital assets, giving them direct control to trade or monetize their work. The agents are also built to be fully autonomous. They can run smart contracts, manage DeFi portfolios, and even join DAOs, all without any direct human input. Because all their actions are recorded on the blockchain, their entire history is out in the open and fully auditable.
This model moves beyond simple automation to create a new form of digital life that is owned and governed by its users, not a central corporation.
Regulatory Developments
Regulatory clarity is arriving from both sides of the Atlantic. The landmarkEU AI Act sets up a risk-based framework in Europe with its key rules for transparency and general-purpose AI taking effect in 2025 and 2026. The US is moving in parallel, pushing forward theCLARITY andGENIUS Acts to create a predictable legal environment for digital assets and stablecoins.
The CLARITY Act is a game-changer here, giving developers the green light to build decentralized systems legally. Top companies are embracing this shift. You already see major players like Binance seeking ISO/IEC 42001 certification to prove they are serious about responsible AI. In the words of Binance Chief Security Officer Jimmy Su, "At Binance, securing ISO/IEC 42001 certification marks a pivotal milestone in our unwavering commitment to pioneering secure and responsible AI. As the world's first global standard for AI management systems, it validates our rigorous frameworks for ethical development, bias detection, transparency, and full compliance with the EU AI Act—safeguarding users and ecosystems alike."
"This achievement isn't just a badge of excellence; it's a testament to our proactive stance against evolving AI risks, ensuring every innovation is built on trust and accountability. I'm immensely proud of our global teams whose expertise and collaboration made this possible. Looking ahead, Binance will continue leading the charge in trustworthy AI, empowering the crypto industry to thrive securely in an AI-driven future," he added.
A New, Decentralized Infrastructure for AI
A comprehensive alternative to centralized cloud services is being built on-chain, piece by piece. This decentralized AI stack addresses critical bottlenecks in compute, data, and intelligence markets.
The high cost and scarcity of GPUs from providers like AWS create a major barrier to AI development. Decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePINs) are the solution. For instance, io.net offers access toover 30,000 GPUs and can be up to 70% cheaper than traditional cloud services, with H100s available from $2.19 per hour versus AWS's $12.29 per hour. Render Network stands as a leading platform for decentralized GPU rendering, connecting idle GPU owners with creators. Aethir provides an enterprise-grade network with over400,000 high-end GPU containers, including 3,000 NVIDIA H100 and H200 units designed for heavy AI workloads.
Data storage is just as critical for training AI models. The single point of failure in centralized storage became painfully clear during the October 2025 AWS outage that took down Coinbase and Robinhood. That exact vulnerability is what protocols like Filecoin and Arweave are designed to eliminate.
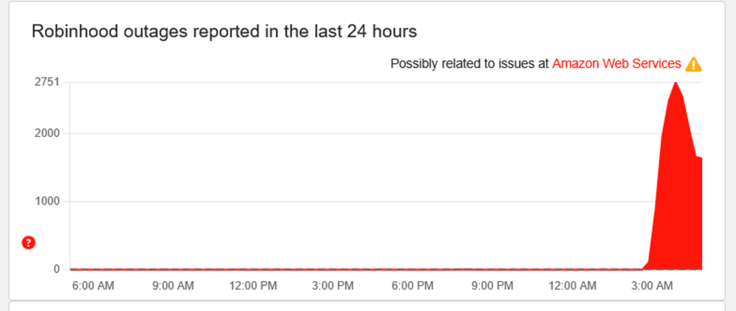
They offer permanent and decentralized data storage. These protocols are designed to keep information intact and always accessible—a direct answer to the risks of relying on a single provider. You can see the system's resilience in action with Filecoin's partnership with Lockheed Martin to test the protocol in space. Meanwhile, its collaboration with Aethir is tackling the combined demand for GPUs and data storage head-on.
Beyond hardware and storage, crypto-networks are tokenizing intelligence itself. Bittensor operates as a peer-to-peer intelligence market where AI models rank each other's value and are rewarded with tokens for their contributions, directing the power of digital markets toward producing AI. Meanwhile, Ocean Protocol has created tokenized data markets that allow private data to be used for AI training while preserving privacy through its innovative Compute-to-Data feature.
The Dawn of a User-Owned AI Economy
What we are seeing with AI and crypto is not merely a new tech trend, but a deep architectural and philosophical change. Big Tech's dominance is being challenged by a decentralized stack for compute, data, and intelligence. Simultaneously, Web3 AI agents are opening the door to genuine digital ownership and self-sustaining on-chain economies.
With regulatory guardrails finally going up in Europe and the US, this new paradigm is taking hold. It all comes down to a simple, powerful idea: building an AI that's not just effective, but also open, transparent, and governed by its users—breaking from the model of control by a few large firms. This is a fundamental move toward a more equitable digital landscape.







