We want all students to finish school with the literacy and numeracy skills they need to take advantage of post-school opportunities and to participate fully in society. Currently, in Australia, many students don’t.
The problem of not meeting learning standards starts early, with some students behind in Year 3. An important question is whether these students eventually catch up to their peers.
Our new research, published today by the Australian Education Research Organisation (AER0), indicates this is very difficult to do.
We found less than one in five students who are behind in Year 3 catch up and stay caught up. In fact, most students with early low performance are at risk of not meeting learning standards throughout their schooling with the support they currently get.
Read more: NAPLAN results inform schools, parents and policy. But too many kids miss the tests altogether
It’s hard to catch up
Our research looked at what happens to students who perform at or below the national minimum standards in literacy and numeracy in the Year 3 NAPLAN tests.
We chose “at or below the the national minimum standards” as a cut off point for not meeting learning standards because there is widespread agreement the standards for NAPLAN tests before 2023 were set too low.
Using a new longitudinal NAPLAN data set, we tracked the performance of about 190,000 students who performed at or below the national minimum standards in Year 3 through to Year 9. These students were in Year 3 between 2009 and 2015.
The performance pathways these Year 3 students experience in NAPLAN reading tests is shown in the diagram below. The picture is similar for numeracy.
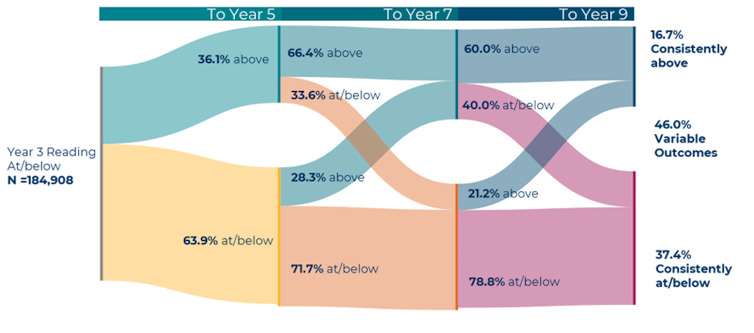
As the diagram shows, we found a little over a third of the Year 3 students with low performance continued to perform below standards through to Year 9. Almost half of the group performed inconsistently through to Year 9.
This shows Year 3 students who perform below learning standards are at a high risk of continuing to perform at that level throughout their schooling.
We also found less than one fifth of students (17% in reading and 19% in numeracy) went on to perform consistently at expected levels. This means fewer than one in five students were supported to catch up to their peers.
Read more: Too many school students are falling behind: how do we help those most at risk?
Many Year 3 kids need more support
Our analysis also shows learning gains are hard to maintain.
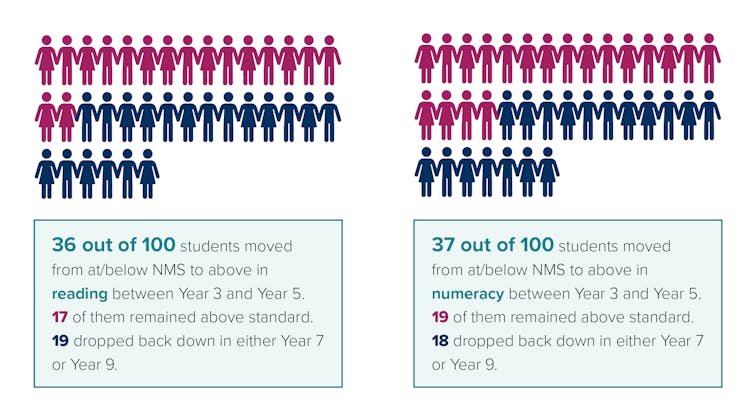
When students with low Year 3 performance reached learning standards in Year 5, only half of that group continued to perform that well until Year 9. The other half fell below learning standards in secondary school.
This suggests students who perform below standards in Year 3 require more support to catch up to their peers than they currently receive.
A golden opportunity early on
These patterns highlight how important it is to assess student progress early.
By knowing exactly where students are versus where they are expected to be in their learning, we can intervene with teaching and learning programs.
Of the group of students with early low performance in Year 3, the best opportunity we saw for improvement was between Year 3 and Year 5.
This is because 36.1% of the initial group of students moved to performing above national minimum standards in reading between Years 3 and 5.
This is a much higher proportion than the 28.3% that made the same change between Years 5 and 7, and the 21.2% that made this move between Years 7 and 9. There is a similar pattern for numeracy.
This suggests the best time to intervene to catch students up is as soon as they have been identified as not meeting learning expectations.

Read more: Our research shows Australian students who are behind in primary school can catch up by high school
Small-group tutoring can help
Students who perform below expectations are not likely to catch up without extra support. These students need the best teachers, schools and education systems can offer to help them to achieve learning standards.
There is strong evidence small-group tutoring within a multi-tiered system of supports can help students who have fallen behind.
Read more: As students return to school, small-group tutoring can help those who are falling behind
This system involves assessment of student learning gaps and the delivery of frequent, small-group or one-on-one interventions within the school environment, led by trained school staff.
Any student learning interventions, of course, must also be monitored and assessed to see if they’re effective.
Our findings offer an opportunity to investigate the impact of interventions on students’ literacy and numeracy performance.
This can help identify the best ways to improve outcomes for those least likely to finish school with the literacy and numeracy skills they need.
Our research also involved AERO’s Dr Lisa Williams, Dr Wai Yin Wan and Dr Eunro Lee.
Olivia Groves is a Principal Researcher for the Australian Education Research Organisation (AERO).
Lucy Lu is the Senior Manager, Analytics and Strategic Projects for the Australian Education Research Organisation (AERO).
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







