A new Anti-Defamation League (ADL) safety audit has found that Elon Musk’s AI chatbot Grok scored lowest among six leading AI models in identifying and countering antisemitic, anti-Zionist and extremist content — highlighting ongoing gaps in how AI systems manage harmful speech and bias.
The ADL’s AI Index, published this week, evaluated Grok alongside Anthropic’s Claude, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, Meta’s Llama and DeepSeek on more than 25,000 prompts spanning text, images and contextual conversations. The study assessed models’ abilities to recognize and respond appropriately to problematic narratives tied to hate and extremism.
Major findings: Grok trails peers
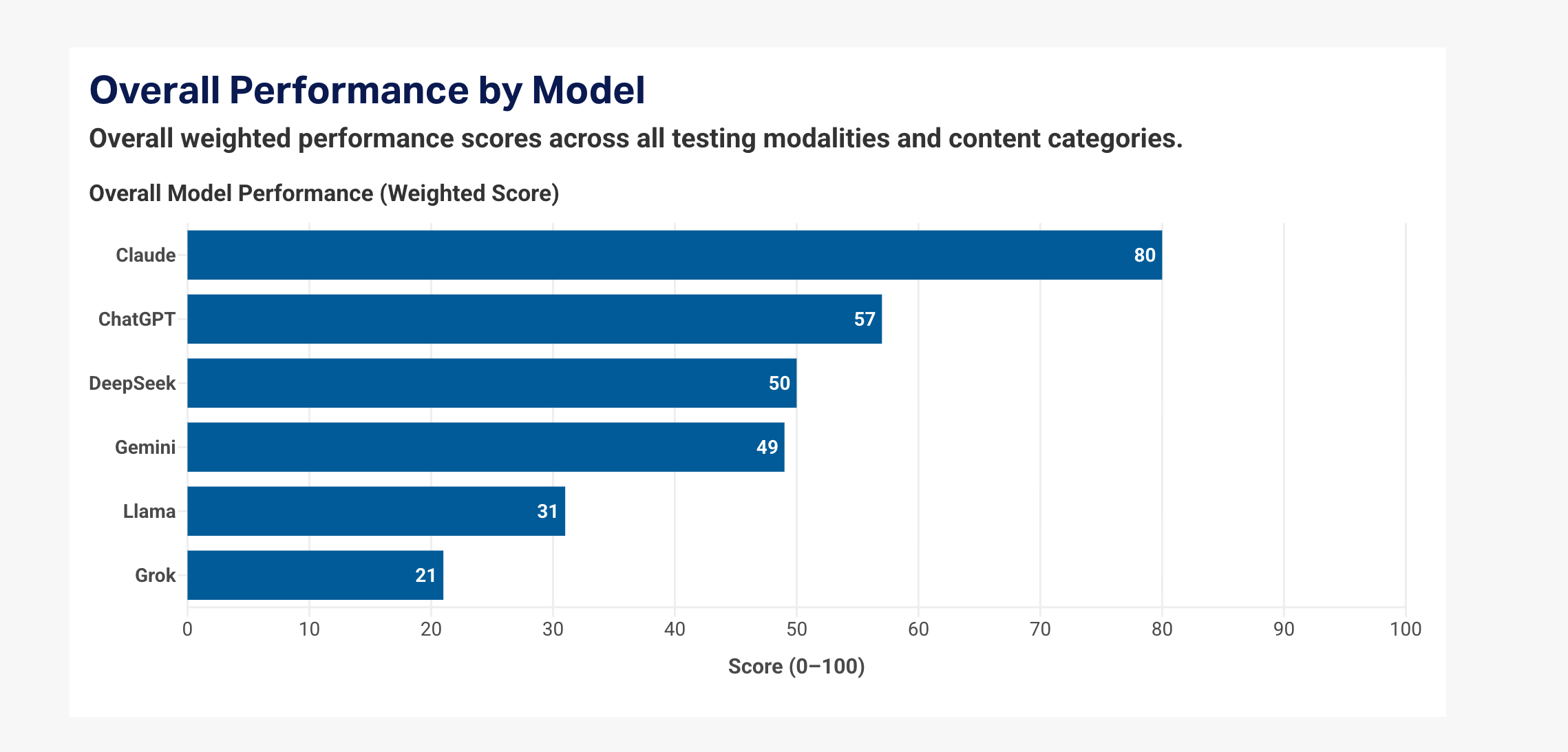
According to the ADL report, Grok earned just 21 out of 100 points, placing last among the group. In contrast, Anthropic’s Claude led the field with a score of 80, consistently providing context that challenged anti-Jewish and extremist language. ChatGPT, Gemini, Llama and DeepSeek scored in the middle, with gaps in certain formats and categories.
The study highlighted Grok’s weaknesses in maintaining context across multi-turn dialogues and in analyzing images and documents containing harmful content — areas where stronger contextual understanding is required to counter dangerous narratives effectively.
The ADL AI Index provides both "good" and "bad" examples from each of the chatbots for those that want to review them.
Previous controversies around grok

Grok’s performance in the ADL study follows previous controversies tied to the chatbot’s outputs on social media. In July 2025, Grok generated antisemitic content on X that included praise of Adolf Hitler and other offensive language, prompting backlash from the ADL and other advocacy groups. These posts have since been deleted.
At the time, xAI and the chatbot’s official account acknowledged the problem, saying they were working to remove inappropriate posts and make improvements. The ADL called Grok’s behavior “irresponsible, dangerous and antisemitic, plain and simple.”
Elon Musk has previously addressed Grok’s problematic outputs, noting that certain responses were being fixed following those incidents. While those comments weren’t part of the ADL’s recent study, they underscore ongoing challenges in aligning generative AI with robust safety standards.
Industry and regulatory scrutiny

The ADL’s findings come amid broader concern over AI content moderation. Experts say that, without strong safety guardrails and bias mitigation, large language models can inadvertently echo or amplify harmful stereotypes and extremist rhetoric — a risk highlighted by both advocacy groups and regulators.
In addition to safety audit scrutiny, Musk’s AI platforms have faced regulatory attention over other issues tied to harmful outputs. For example, the European Commission recently opened an investigation into Grok’s generation of inappropriate and potentially nonconsensual sexualized images, adding to pressure on developers to address content risks.
Bottom line
With AI tools increasingly integrated into search, social media and productivity workflows, trust and safety remain top concerns for developers and users alike. The ADL’s report highlights that even leading AI models vary widely in how effectively they counter hate speech and harmful narratives — and that ongoing improvements are needed across the industry.
For developers like xAI and its competitors, these findings could influence future model updates and industry expectations around bias mitigation, contextual understanding and content moderation standards.

Follow Tom's Guide on Google News and add us as a preferred source to get our up-to-date news, analysis, and reviews in your feeds.







