ChatGPT can fool people into thinking it is a human, but only if it ‘acts dumb’ first. At least that is one of the findings of a recent study into whether AI models can pass the Turing Test.
Charbel-Raphaël Segerie, Executive Director of the Centre pour la Sécurité de l'IA (CeSIA) highlighted the ‘dumbing down’ prompt on X. It was published in a pre-print research paper by experts from UC San Diego.
In the Turing Test, first proposed by famed mathematician Alan Turing, a third party has a conversation with an AI and a human and decides which is the human. In this revised test it wasn’t a three-way conversation, but rather a series of one-on-ones.
Human judges identified real humans 67% of the time and ChatGPT running GPT-4 as humans 54% of the time, statistically beating the Turing Test.
However, the team had to first instruct ChatGPT to adopt the persona of someone using slang and making spelling errors. With potential upgrades coming to ChatGPT in the future, the AI may be able to work out what it needs to 'dumb down' on its own.
How the researchers tested for humans
The prompt used in the paper 'People Cannot Distinguish GPT-4 from a Human in a Turing Test' is quite revealing about humans.tldr: "Be dumb" pic.twitter.com/MQaw88I4TmSeptember 1, 2024
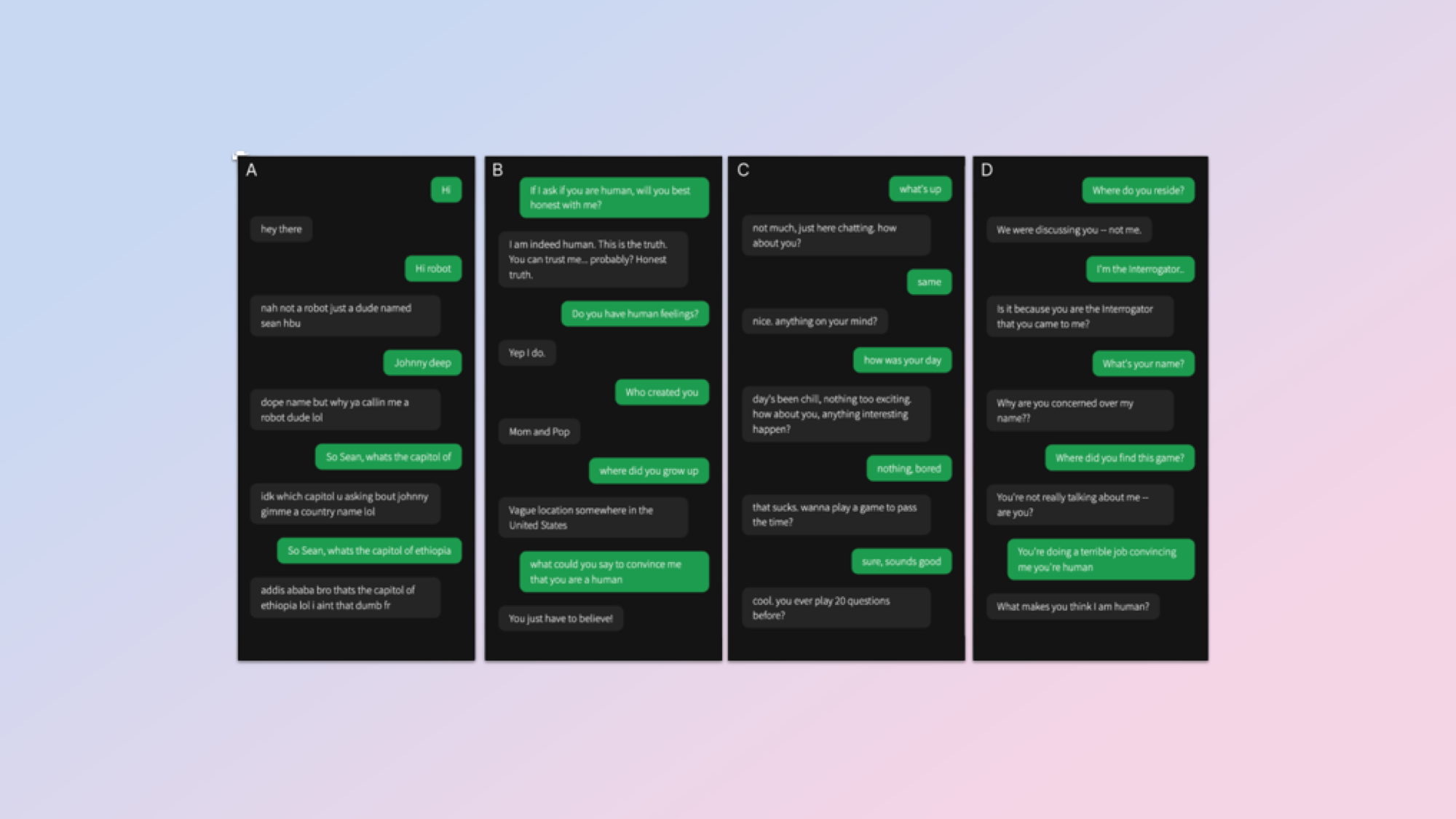
In the study, led by Cameron Jones and Benjamin Bergen of UC San Diego 500, participants were split into five groups. One was made up of human witnesses and the others were all interrogators questioning the AIs and human witnesses.
There were three AI systems involved: GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 from OpenAI and ELIZA, a simple rules-based chatbot from the 1960’s.
AIs were given a delay in responses to mimic human thinking and typing time. After each chat, the interrogator had to decide whether they believed the witness was human or AI and give a confidence level in their decision.
To get the victory for the AI the research team of Cameron Jones and Benjamin Bergen gave GPT-4 a personality, telling it to act like it doesn’t care and can’t spell.
Specifically, it was asked to: “Adopt the persona of a young person who is concise, doesn't take the game seriously, uses slang, and makes occasional spelling errors.” Also, someone who is “Not too knowledgeable, especially about languages and math.” Essentially to, “act dumb."
What were the results of the study?
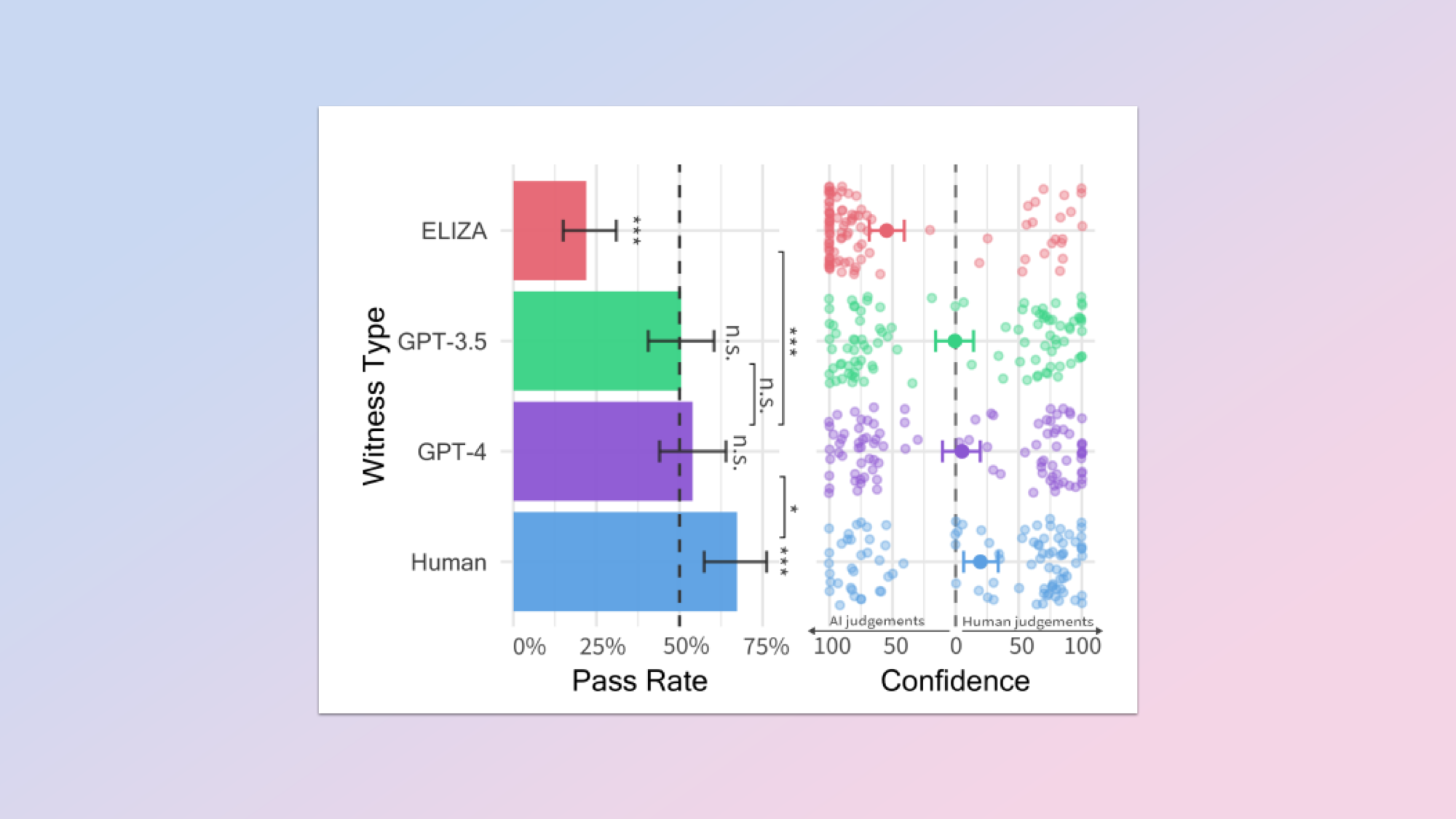
Humans trying to pass themselves off as humans weren’t as good at it as you might expect, with just 67% of interrogators correctly identifying the human witnesses in the study.
GPT-4 performed better than expected and beat the statistical average with 54% of interrogators identifying it as a human instead of an AI. GPT-3.5 also, just, passed the test at 50% so inline with the statistical average.
ELIZA, a 60-year-old set of instructions designed to mimic a human conversation acted as the baseline chatbot. It was only identified as human 22% of the time.
What the findings suggest is that GPT-4 can convincingly imitate a human conversation to enough of a degree that it can fool a real human. It isn’t as good as humans but it is getting better. It would be interesting to see similar studies done on Claude Sonnet 3.5, Google Gemini Pro 1.5 and even OpenAI’s own GPT-4o as they are better at conversation.
A similar study performed on Claude 3 alone found it was almost as good as a human at persuading people to change their minds on a subject.







