The U.S. Defense Department issued a memo on Feb. 17, 2023, warning service members to avoid eating poppy seeds because doing so may result in a positive urine test for the opiate codeine. Addiction and pain medicine specialist Gary Reisfield explains what affects the opiate content of poppy seeds and how they could influence drug tests.
What are poppy seeds?
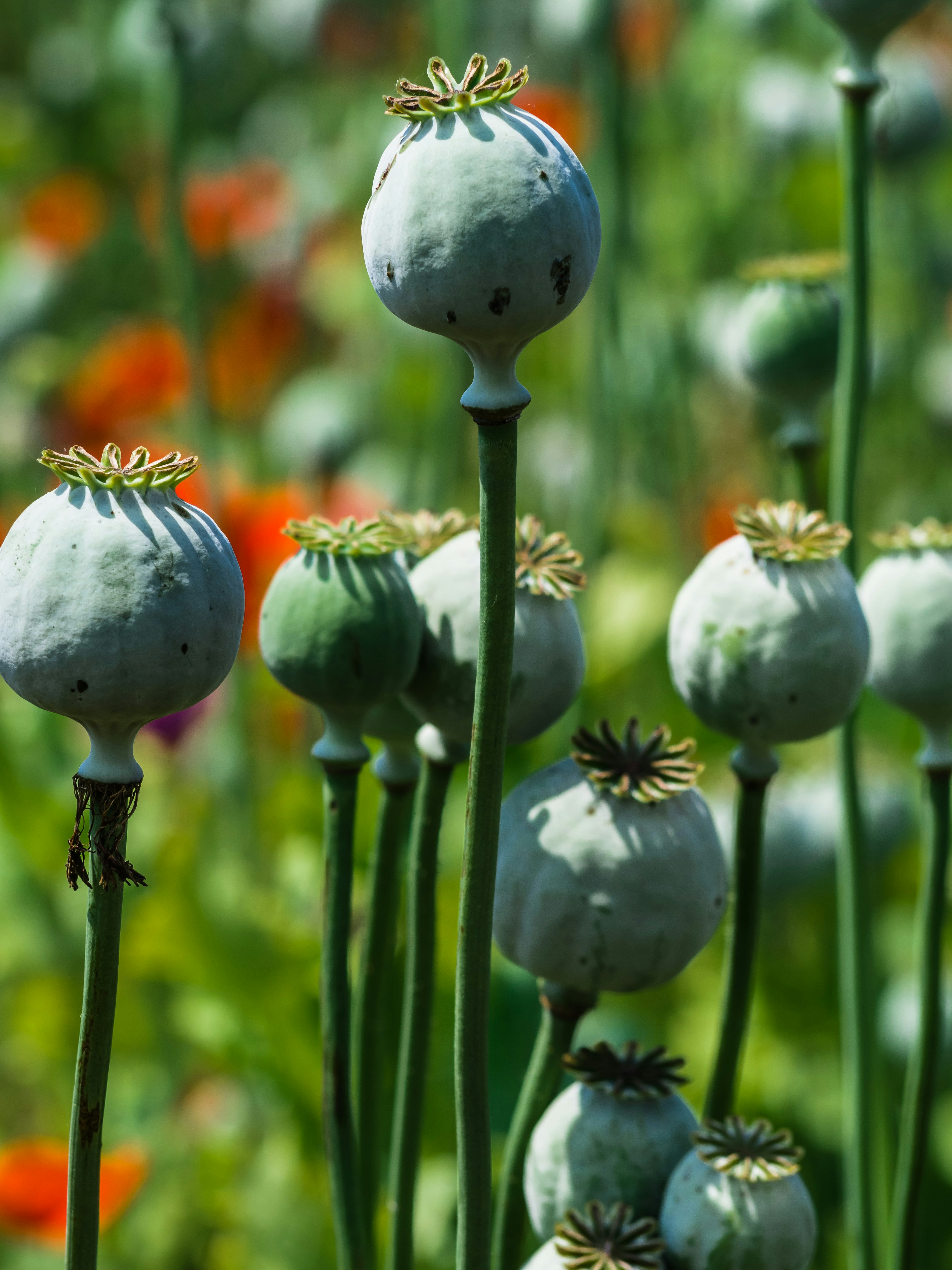
Poppy seeds come from a species of poppy plant called Papaver somniferum. “Somniferum” is Latin for “sleep-bringing,” which hints that it might contain opiates – powerful compounds that depress the central nervous system and can induce drowsiness and sleep.
There are two main uses for the opium poppy. It is a source of the opiates used in painkillers, the most biologically active of which are morphine and codeine. Its seeds are also used for cooking and baking.
Poppy seeds themselves don’t contain opiates. But during harvesting, the seeds can become contaminated with opiates contained in the milky latex of the seed pod covering them.
What affects opiate content in poppy seeds?
Many factors determine the opiate concentrations and ratios of poppies. As with wine grapes, the opiate profile of the poppy plant – and thus its seeds – is affected by its terroir: climate, soil, amount of sunshine, topography, and time of harvest.
Another factor is the variety or cultivar of the plant. For example, there are genetically engineered opium poppies that produce no morphine or codeine and others that produce no opium latex at all.
Can you get high from eating poppy seeds?
Practically speaking, you cannot eat enough poppy seeds to get you high. Furthermore, processing dramatically decreases opiate content – for example, by washing or cooking, or baking the seeds.

Do poppy seeds affect drug tests?
Poppy seeds don’t have nearly enough opiates to intoxicate you. But because drug tests are exquisitely sensitive, consuming certain poppy seed food products can lead to positive urine drug test results for opiates – specifically for morphine, codeine, or both.
Under most circumstances, opiate concentrations in the urine are too low to produce a positive test result. But certain food products – and it’s generally impossible to know which ones because opiate content does not appear on food labels – contain enough opiates to produce positive test results. Moreover, because of the overlap in opiate concentrations and morphine-to-codeine ratios, it can sometimes be challenging to distinguish test results that are due to the consumption of poppy seeds from those that are due to the use of opiate drugs.
This is not a problem with most workplace drug testing. Test results are reviewed by a specially trained physician called a medical review officer. Unless the physician finds evidence of unauthorized opiate use, such as needle marks or signs of opiate intoxication or withdrawal, even relatively high concentrations of opiates in the urine that produce positive test results are generally ruled to be negative.
It turns out, though, that drug testing in the military is different, and poppy seeds pose potential problems. One such problem, as highlighted in recent news reports, concerns service members who test positive for codeine and assert a “poppy seed defense.” They are still regarded as having taken codeine, sometimes with serious consequences, such as disciplinary action or discharge from the service.
This article was originally published on The Conversation by Gary Reisfield at the University of Florida. Read the original article here.







