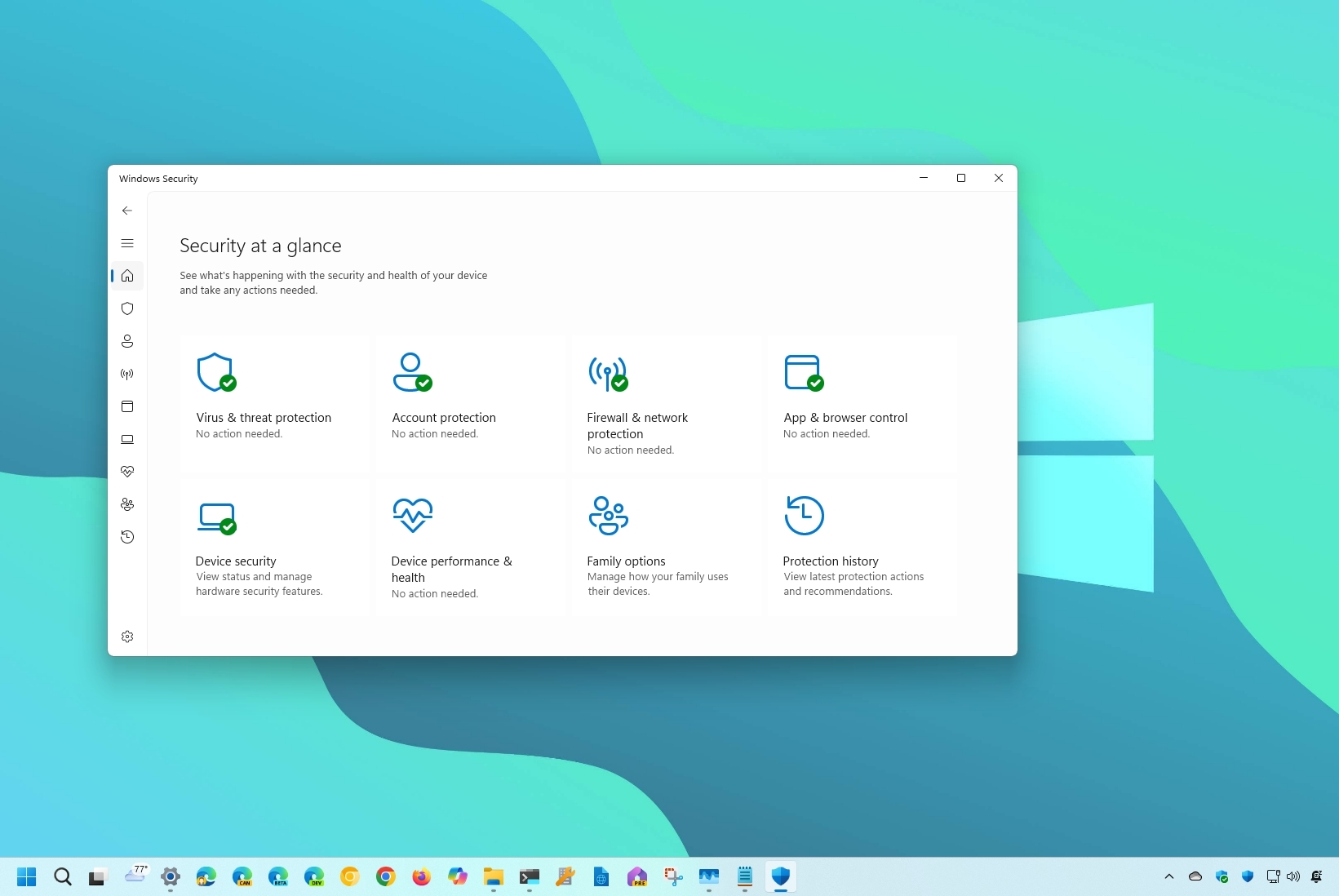
On Windows 11 (and 10), the "Windows Security" app provides a user-friendly interface and tools to manage common security features. For example, the experience includes the Microsoft Defender Antivirus, which offers real-time protection for your computer and data against viruses and many other kinds of malware.
You can also manage the Microsoft Defender Firewall to block intruders from sneaking in. With the account protection settings, you can monitor the device's performance and health, as well as your account and sign-in information, and you can access even more advanced features to keep everything a little more secure.
In this how-to guide, I will explain the steps to start using and perform everyday tasks with the security app to keep your system and data safe from malware and hackers.
Windows Security vs. Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Before diving into this guide, you must understand the difference between "Microsoft Defender Antivirus" and "Windows Security."
Windows Security is an app that offers a unified interface for viewing the status and managing security features, such as antivirus, firewall, performance, and others.
On the other hand, Microsoft Defender Antivirus is the default anti-malware engine that offers real-time protection against many forms of malware, including viruses, spyware, ransomware, and hackers.
Also, when you install another third-party antivirus, the system will disable the Microsoft Defender Antivirus automatically, but this will not affect the functionality of the Windows Security app. In the same way, disabling Microsoft Defender Antivirus or Microsoft Defender Firewall will not disable Windows Security.
How to navigate Windows Security
Windows Security is a straightforward application. You can open it from the Start menu or double-clicking the shield icon from the notification area in the Taskbar.
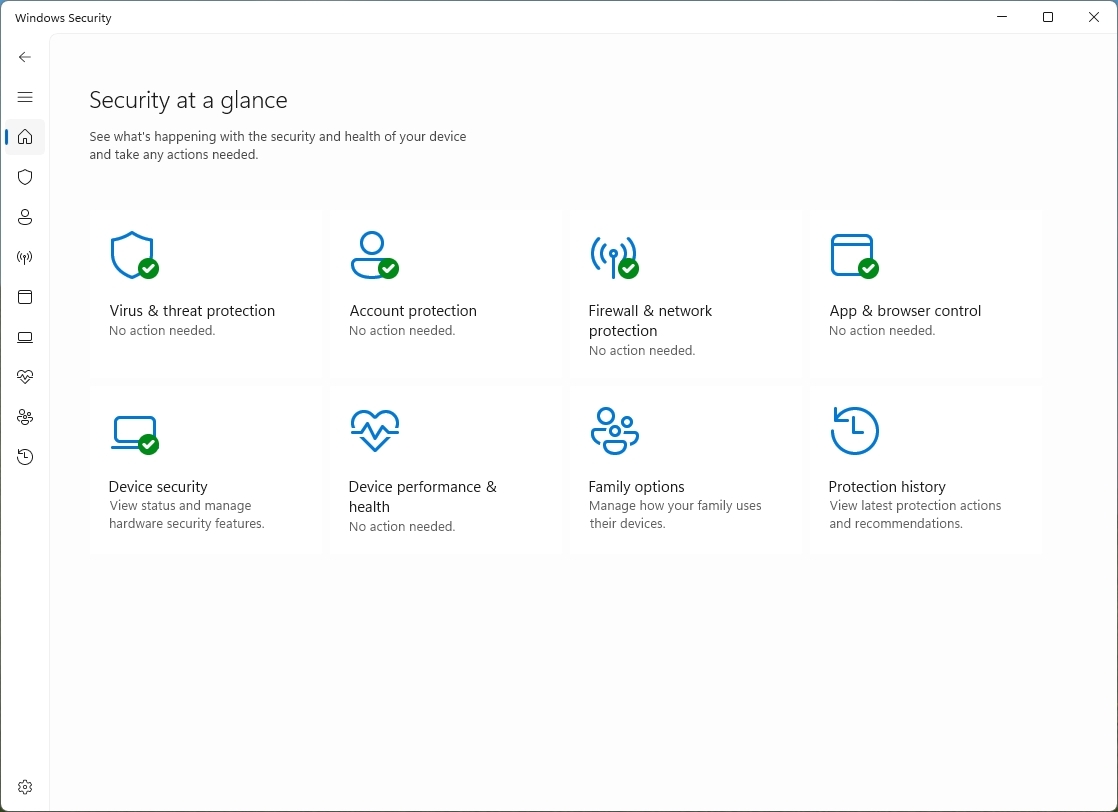
On the "Home" page, you can view the security status of the different protection features available by default on Windows 11 and 10. You can also see alerts of any action that needs to be taken to keep your computer secure.
The shield icon in the notification area can also alert you when an action needs to be taken. If there is more than one alert, only the most severe warning will appear. Also, if you right-click the app icon, you'll have access to actions, such as quick scan, download updates, adjust notifications, and access the dashboard.
Windows Security includes eight areas of protection that you can manage and monitor:
- Virus & threat protection: This section houses the Microsoft Defender Antivirus settings. It allows you to monitor malware protection, scan the device for threats, launch an offline scan, and set up the advanced anti-ransomware feature.
- Account protection: Allows you to see how to protect your identity on Windows 11 or 10.
- Firewall & network protection: This feature lets you monitor network connections and configure various Microsoft Defender Firewall settings.
- App & browser control: This section includes the settings to help you protect your device and data from malicious code hidden in apps, files, and websites.
- Device security: This area provides hardware-level security features, such as Core isolation and Security processor, to protect your computer from certain attacks.
- Device performance & health: This section displays your computer's health and performance report.
- Family options: This area offers easy access to manage your devices and kids' online experience using a Microsoft account.
- Protection history: This section gives you quick access to the latest actions and recommendations from the security feature.
How to scan computer for malware using Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Windows automatically updates and scans the device for malware regularly, but you can perform different scans manually.
Quick virus scan
A quick scan happens fast and only scans the parts of the system where malware is known to hide.
To start a virus scan with Microsoft Defender, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Quick scan button.
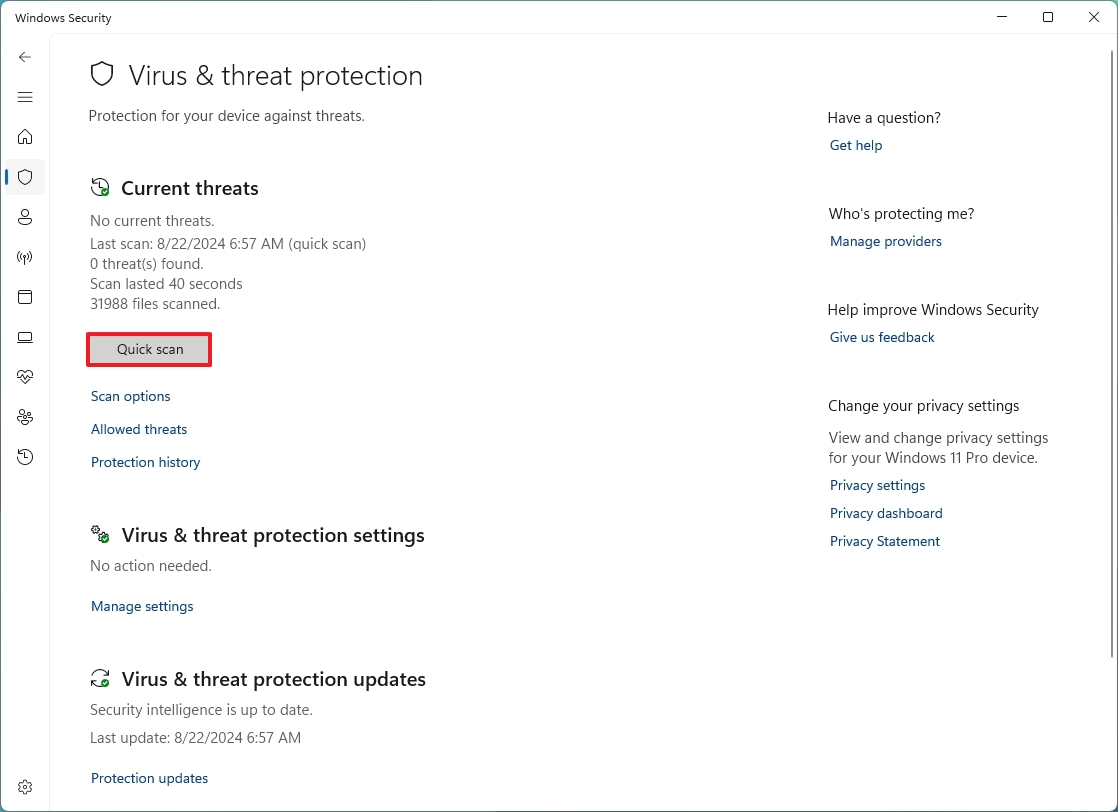
Once you complete the steps, under the "Current threats" section, you'll find any detected threats, as well as the time it took to complete the scan and the number of scanned files.
If you suspect that a virus is still on your computer, you should try to perform a full scan.
Full virus scan
A full virus scan takes longer, but it makes sure to check every file, folder, and application.
To start a full virus scan with Microsoft Defender, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Scan options option under the "Current threats" section.
- Select the Full scan option.
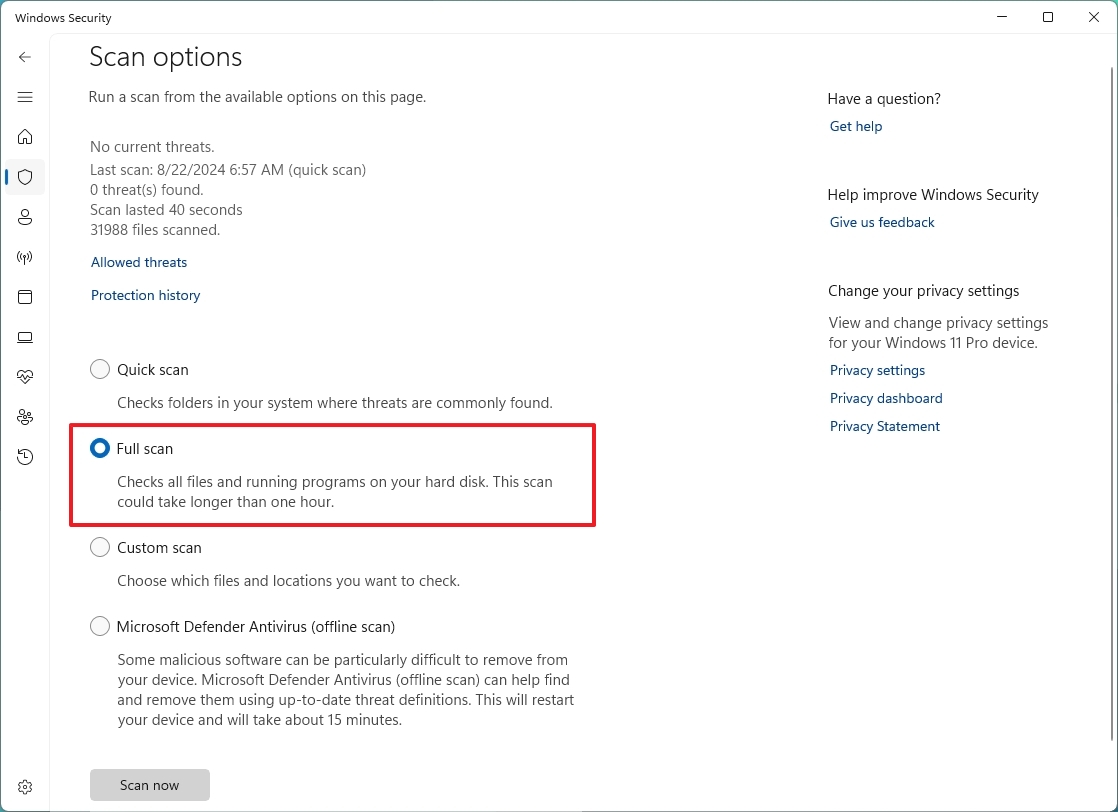
- Click the Scan now button.
After you complete the steps, you can continue using the device, while the antivirus will perform a full scan to detect any potential malware.
Custom virus scan
If you only want to scan a particular folder or location, the Windows antivirus includes an option to complete a custom scan.
To perform a custom virus scan, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & Threat Protection.
- Click the Scan options option under the "Current threats" section.

- Select the Custom scan option.
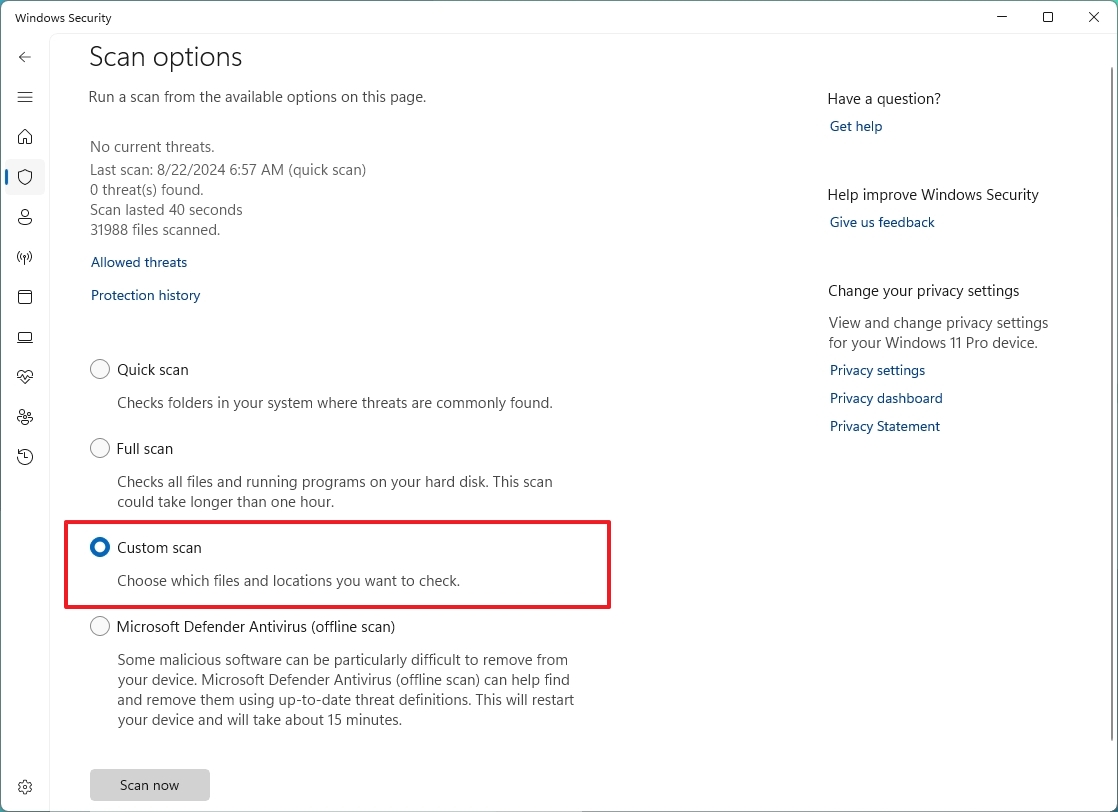
- Click the Scan now button.
- Select the location to be scanned.
- Click the Select Folder button.
Alternatively, you can just right-click on Windows 10 (or shift + right-click on Windows 11) a drive, folder, or file and select the "Scan with Microsoft Defender" option from the context menu to perform a custom scan.
Offline virus scan
Sometimes, if you're dealing with a tough virus or another type of malware, the antivirus software may be unable to remove it while the operating system is running. If so, you can use Microsoft Defender to perform an offline scan. When using this feature, the computer will restart automatically in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) and perform a full scan before the operating system starts.
To start an offline virus scan, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Scan options option under the "Current threats" section.

- Select the "Microsoft Defender Offline scan" option.
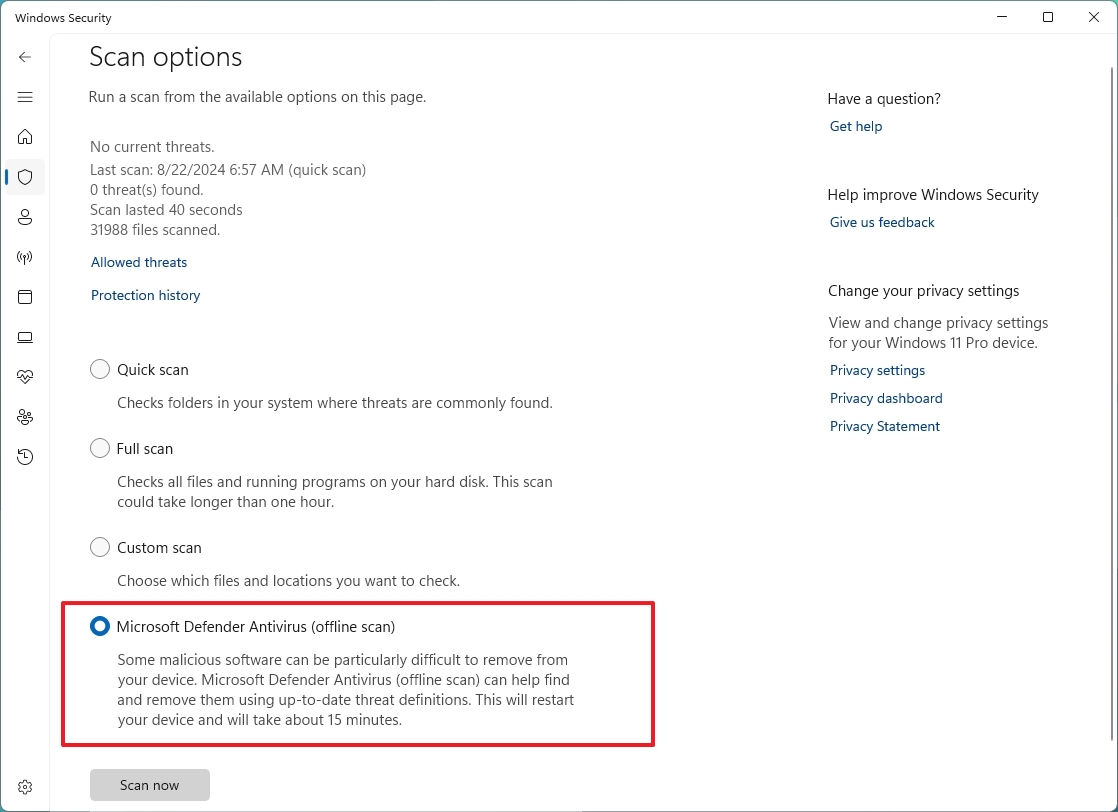
- Click the Scan now button.
- Click the Scan button.
Once you complete the steps, the device will restart and boot into a standalone version of the Microsoft Defender Antivirus, which will scan the entire machine. If malicious code is detected, it will be removed or quarantined automatically.
After the scan, the device will restart, and you can view a report in the Windows Security app.
How to view protection history using Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Microsoft Defender Antivirus also includes an area that you can view the latest protection actions and recommendations.
To view protection history, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Protection history option.
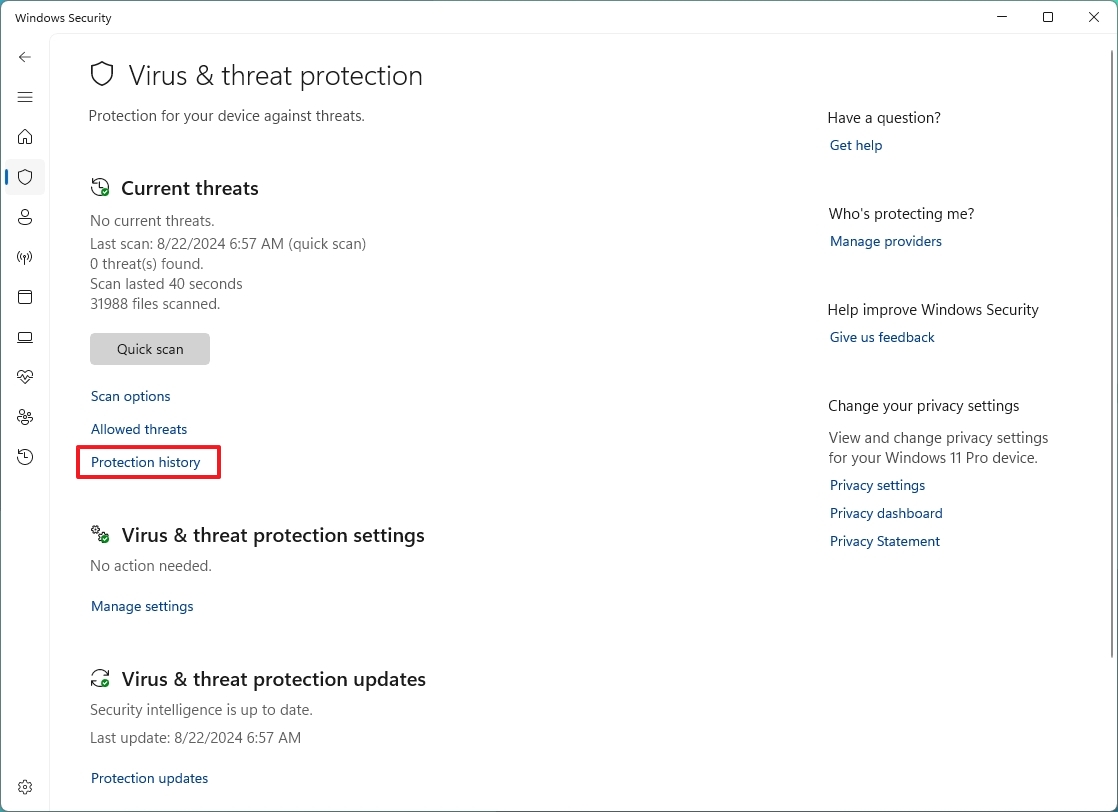
- Click the "Filters" drop-down menu and select the history you want to review, including:
- Recommendations.
- Quarantined items.
- Cleaned items.
- Blocked actions.
- Severity.
After you complete the steps, a report will be generated with items that have been removed, cleaned, or are still waiting for action.
How to temporarily disable Microsoft Defender Antivirus
It's not recommended to use a device without malware protection, but sometimes, the antivirus can prevent you from installing an app or update. If so, you can temporarily disable the antivirus to complete the installation.
To disable Microsoft Defender Antivirus on Windows, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Manage settings option under the "Virus & threat protection settings" section.
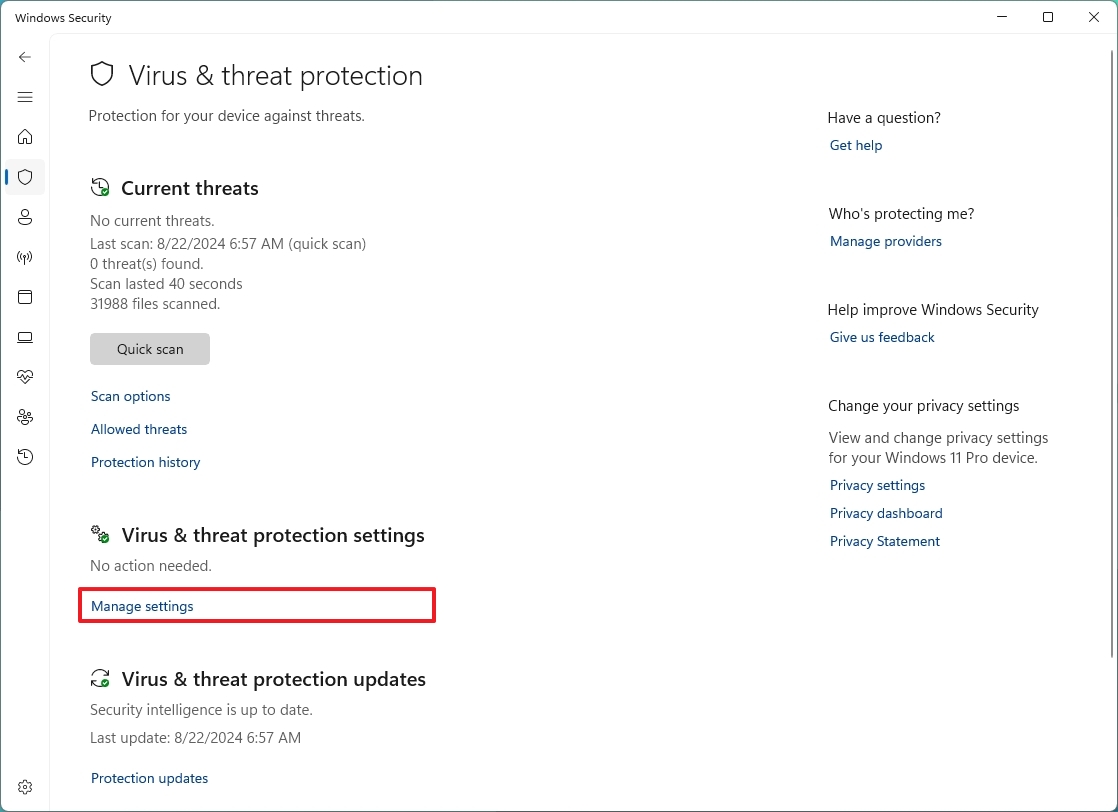
- Turn off the "Real-time protection" toggle switch.
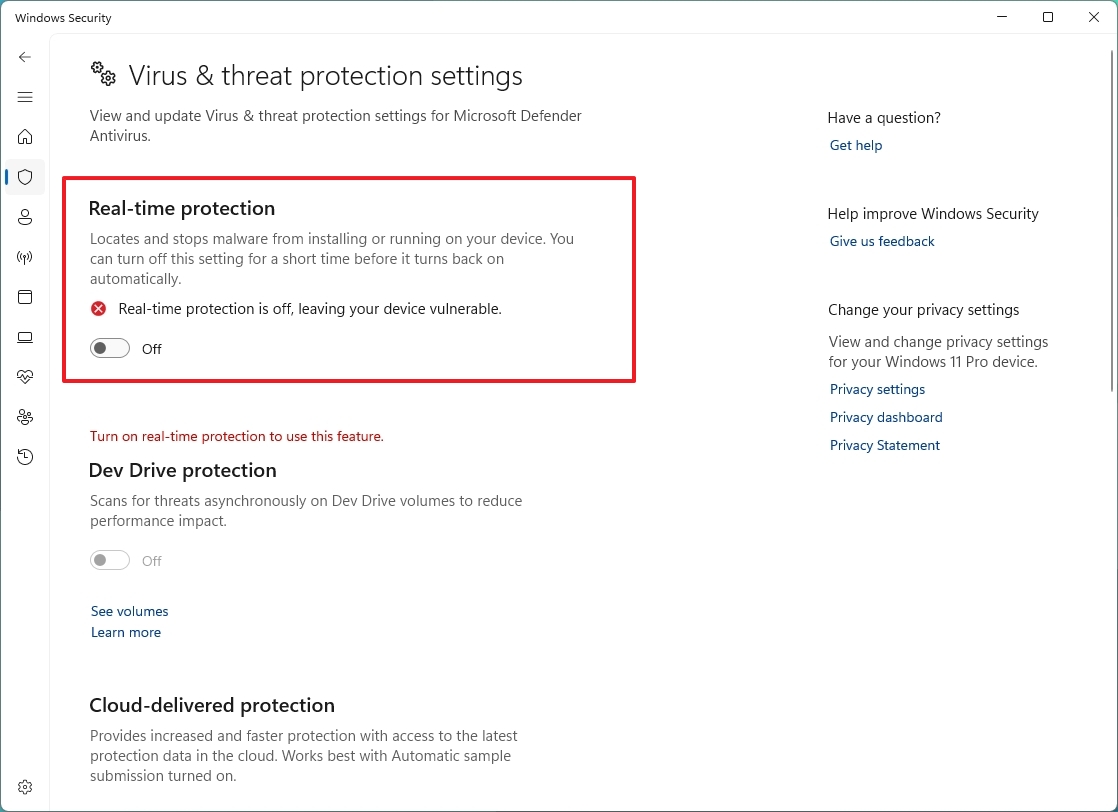
Once you complete the steps, you can perform tasks that may conflict with the antivirus. If you don't re-enable the antivirus, it'll restart automatically the next time you reboot your computer.
How to enable anti-ransomware using Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Microsoft Defender Antivirus includes a feature known as Controlled folder access, designed to monitor and protect your data against ransomware attacks and unwanted changes from malicious programs.
Since it's an advanced feature that can cause false positives, Controlled folder access is an opt-in feature, which means that you need to enable it manually using the Windows Security app.
To enable Controlled folder access on Windows 11 (or 10), use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Manage settings option nder the "Virus & threat protection settings" section.
- Quick tip: You can also access the settings by clicking the "Manage ransomware protection" option at the bottom of the page.

- Click the "Managed Controlled folder access" option under the "Controlled folder access" section.
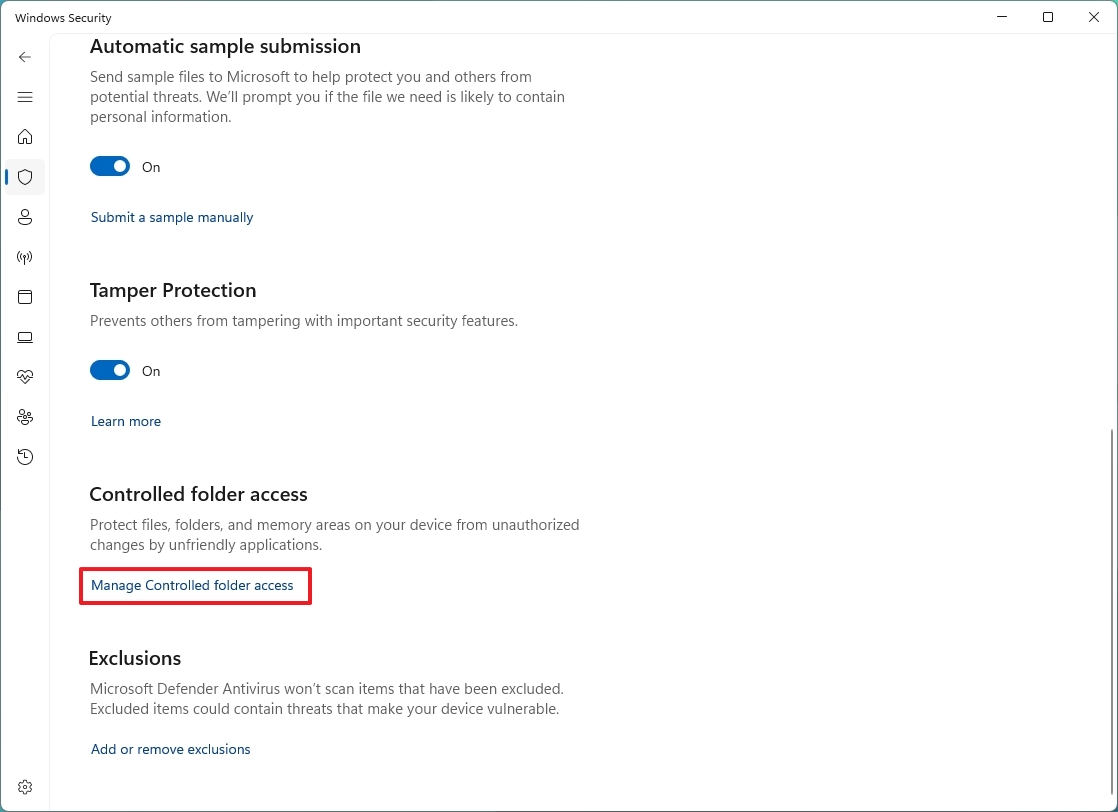
- Turn on the "Controlled folder access" toggle switch.
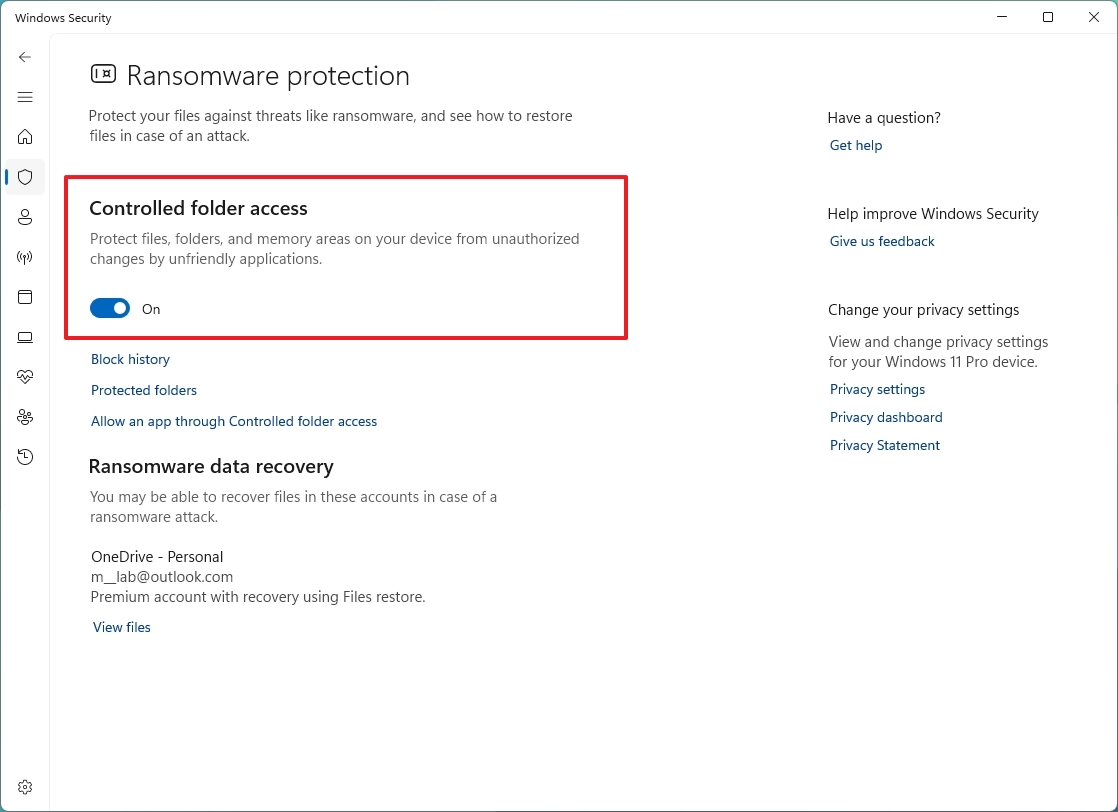
- Click the Block history option to access the "Protection history" page to view blocked folder access.
- (Optional) Click the Protected folders option to add (or remove) additional protected folders.
- (Optional) Click the "Allow an app through Controlled folder access" option to allow apps you trust to make changes to the protected folders.
After you complete the steps, the security feature will enable and monitor apps trying to make changes to files in the protected folders. If the app is flagged as malicious or unknown, Controlled folder access will block the attempt, and you'll receive an alert of the activity.
How to exclude scan locations using Microsoft Defender Antivirus
If you have a folder with files you don't want to scan for viruses, the anti-malware feature includes adding or removing scanning locations.
To prevent the antivirus from scanning specific folders, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Manage settings option under the "Virus & threat protection settings" section.

- Click the "Add or remove exclusions" option under the "Exclusions" section.
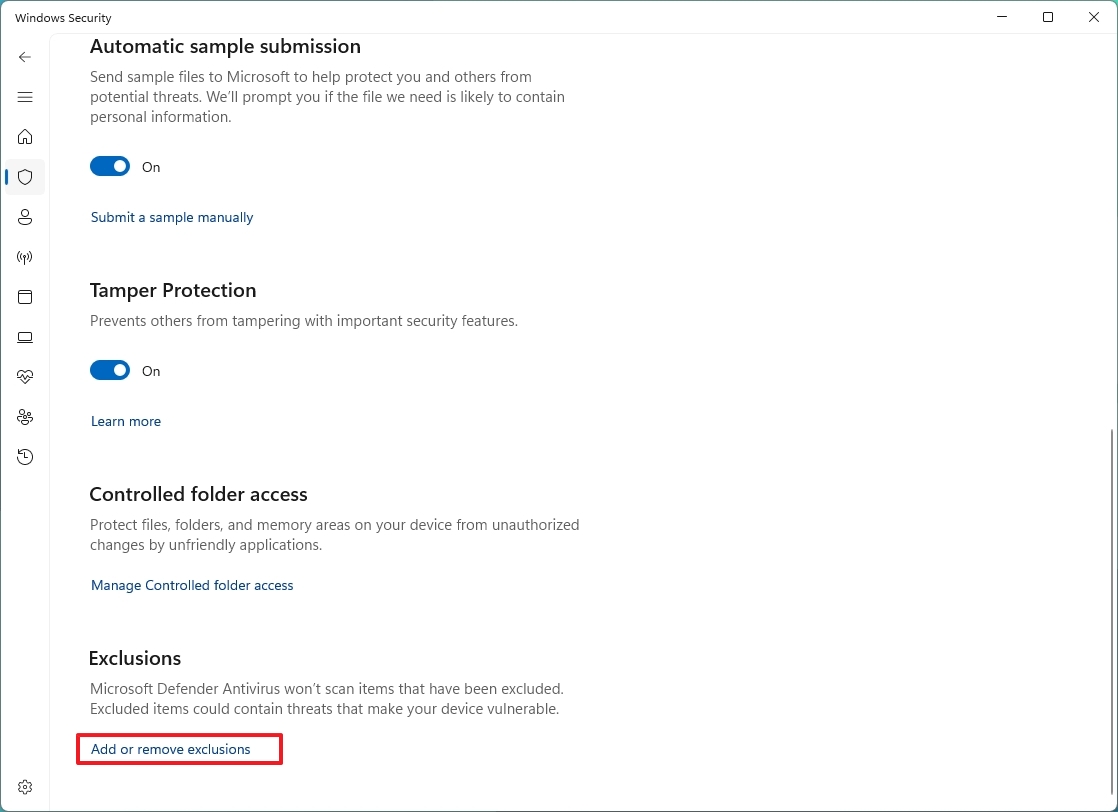
- Click the Add an exclusion button.
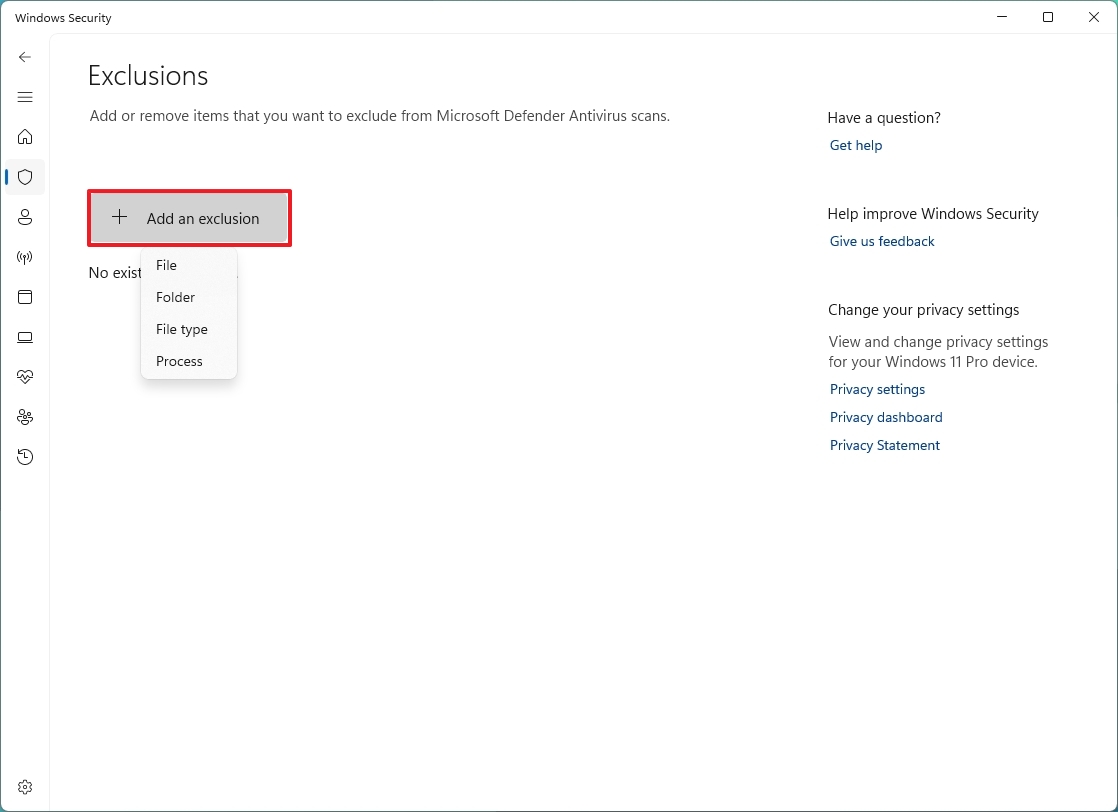
- Select the kind of exclusion you want to configure. For example, Folder, but you can select one of the following:
- File.
- Folder.
- File type.
- Process.
- Select the folder location.
- Click the Select Folder button.
Once you complete the steps, the security software will not scan the location you specified. You may need to repeat the steps to add more exclusions.
How to check account protection using Windows Security
The account protection feature available with Windows Security is designed to monitor and notify you of any problems with your account and signings to best protect your identity on Windows 11 (or 10).
To check the account protection on Windows, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Account protection.
- Confirm that Microsoft account, Windows Hello, and Dynamic lock have a green mark indicating that everything is working correctly.
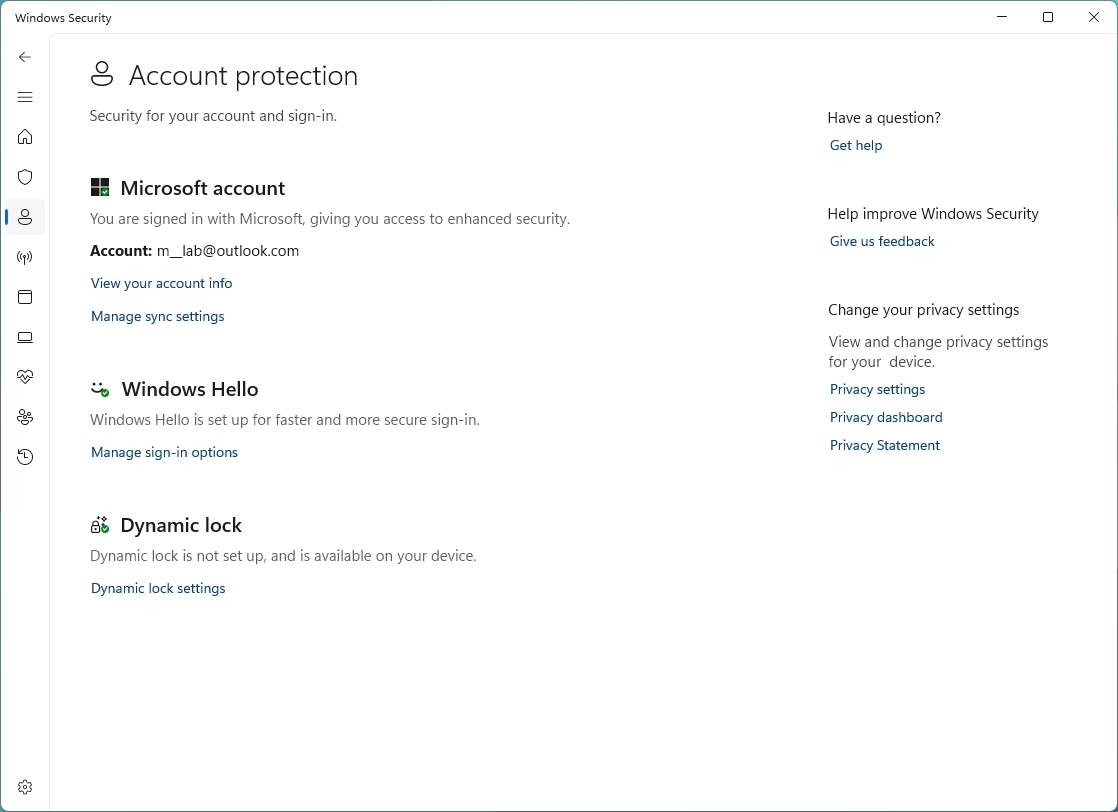
If one of the account security items requires attention, you'll receive an alert to take action to remedy the problem. For example, if you're using a password to sign in, the account protection system will recommend setting up the account with one of the available Windows Hello authentication methods, such as fingerprint, face, or PIN.
How to manage network security with Microsoft Defender Firewall
The app also includes an area to monitor and manage the Microsoft Defender Firewall settings.
View firewall status
To access the firewall settings with Windows Security, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Firewall & network protection.
On the page, you can view at a glance in which network profile the firewall is currently enabled and protecting you from unauthorized access. The one marked as "active" is the current network profile.
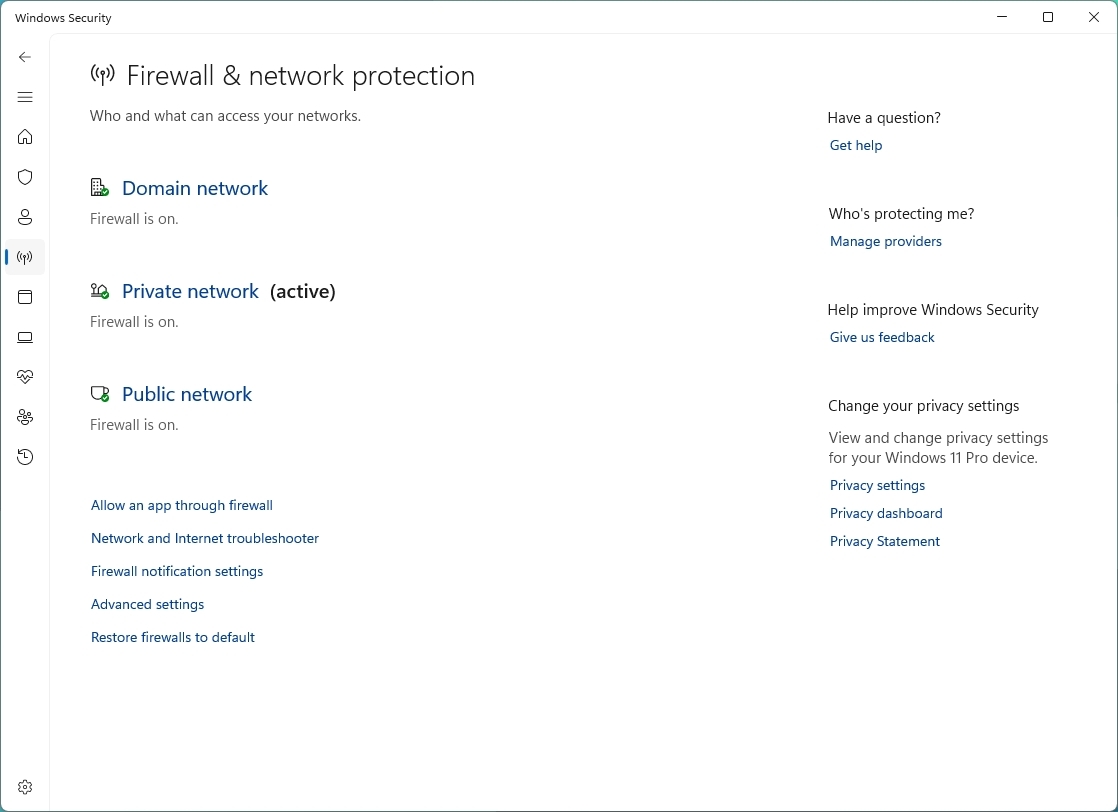
The page also includes options to adjust firewall settings to allow apps through the firewall and advanced settings. However, these settings are links to change configurations from the Control Panel.
Enable or disable firewall
To enable or disable the Microsoft Defender Firewall, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Firewall & network protection.
- Click the active firewall. For example, Private network.
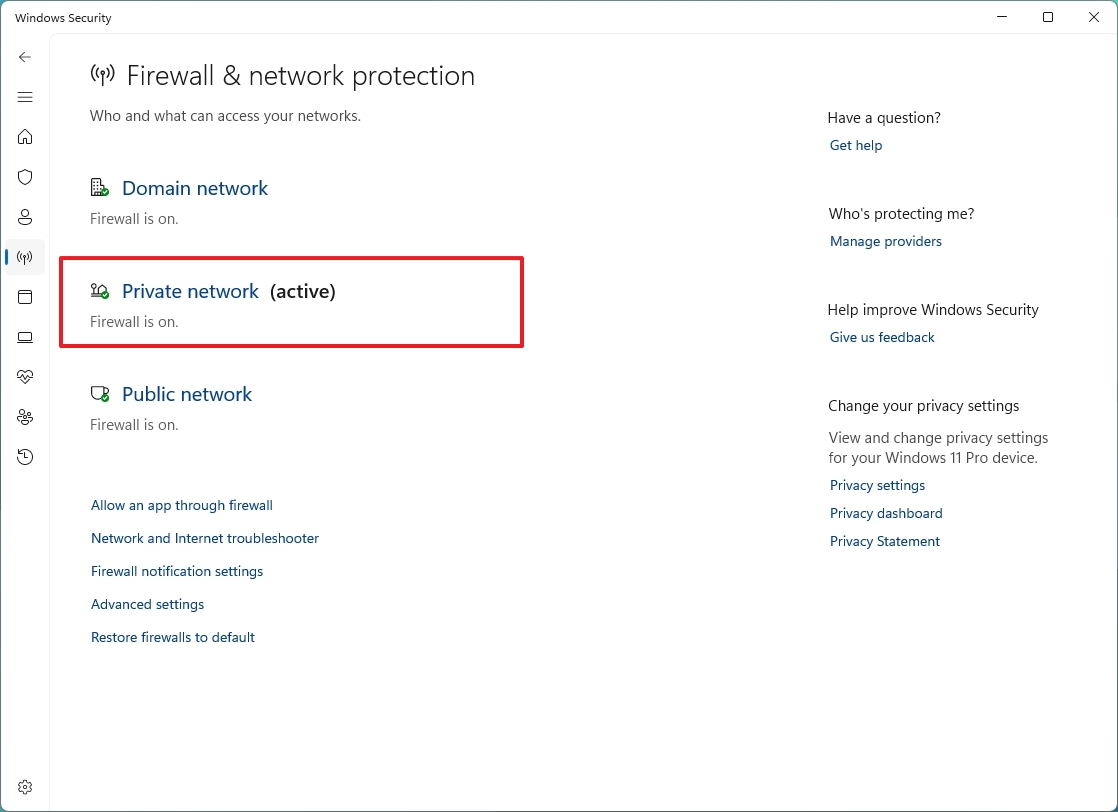
- Turn the "Microsoft Defender Firewall" toggle switch on or off to enable or disable the security feature.
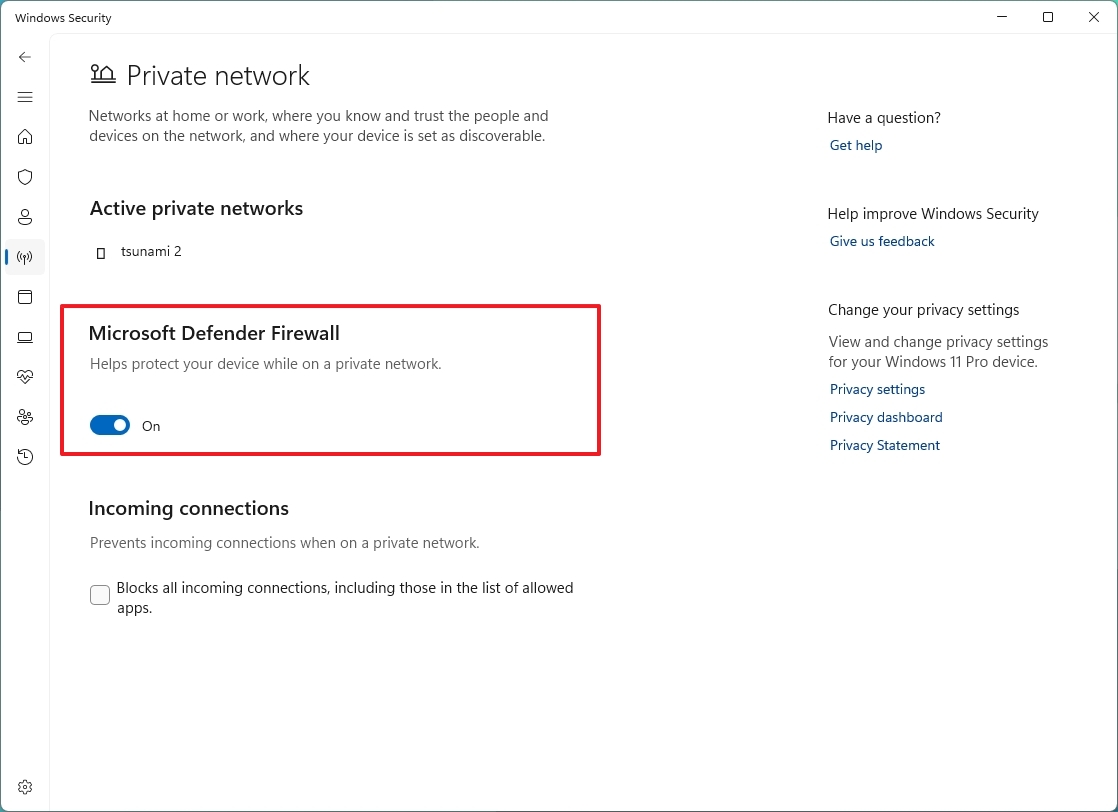
- (Optional) Check the "Blocks all incoming connections, including those in the list of allowed apps" option to block incoming connections quickly.
After you complete the steps, the firewall protection will be disabled on your computer.
If you disable the firewall to test an application, remember to re-enable it after the test. If the problem was the firewall, it's best to create a firewall rule instead of completely disabling the security feature.
How to protect device against malicious code using Windows Security
The "App & browser control" page is the place to configure app protection and online security settings that can help you protect your computer against sites, apps, and files that may contain malicious code.
The default settings are the recommended configuration you should be using, but you can always change them if you have a specific reason.
Smart App Control
Smart App Control is a feature only available on Windows 11, which has been designed to protect your computer by only allowing trusted apps while preventing the system from installing untrusted programs.
To enable Smart App Control on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on App & browse control.
- Click on Smart App Control settings under the "Smart App Control" section.
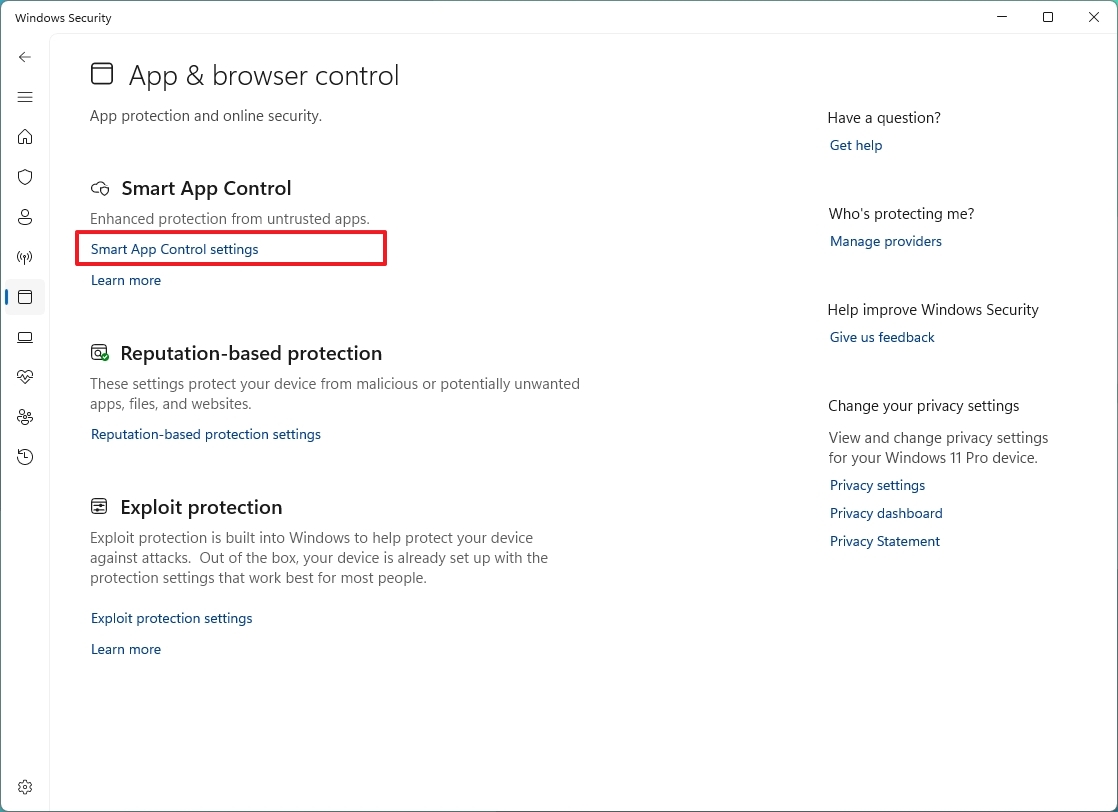
- Choose the Evaluation option.
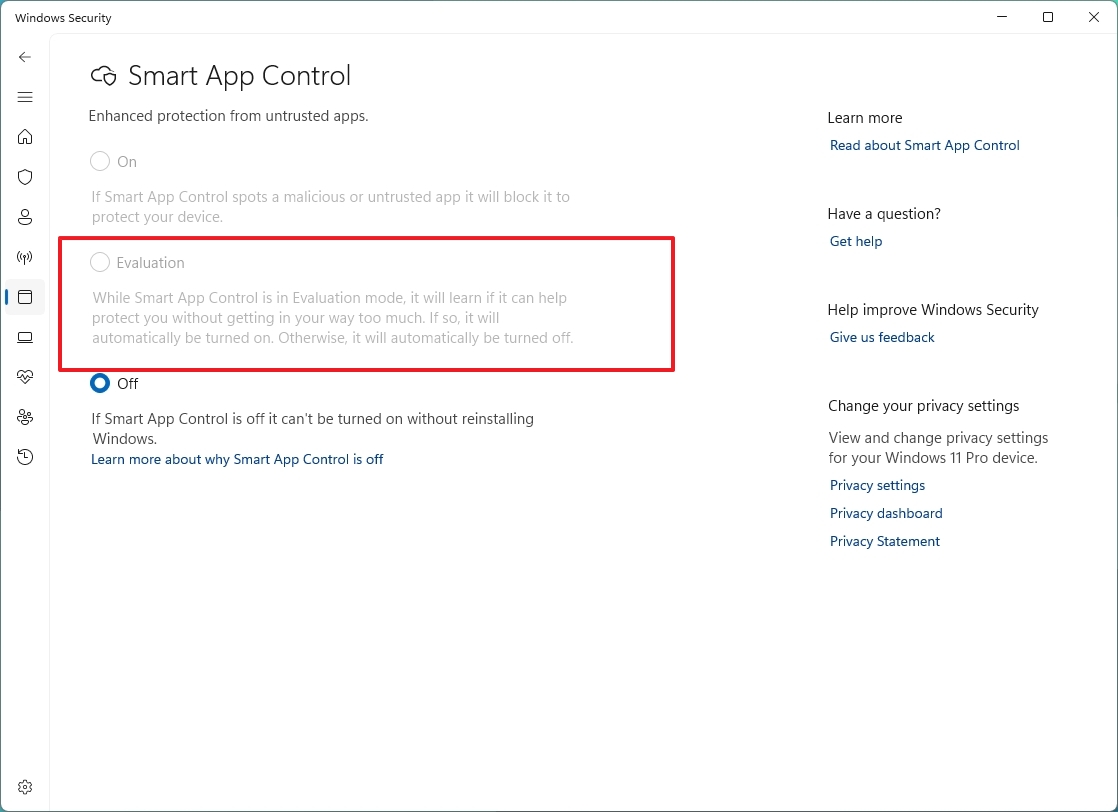
After you complete the steps, the feature will analyze the system to determine if it can run without negatively affecting the experience. Only if the feature can work correctly, it will enable automatically.
The only caveat with this feature is that once it's enabled, you cannot disable it. If you want to turn it off, you will have to reinstall the operating system.
Reputation-base protection
To protect the device using reputation-based protection, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on App & browser control.
- Click the Turn on button under the "Reputation-based protection" section.
- Click the "Reputation-based protection settings" option.
- Turn on or off the protection options according to your preferences:
- Check apps and files: provides protection against unrecognized apps and files from the internet.
- SmartScreen for Microsoft Edge: protects devices from malicious downloads and websites.
- Phishing protection: protects your account password from malicious apps and sites.
- Potentially unwanted app blocking: blocks low-reputation apps that can be responsible for unexpected behaviors.
- SmartScreen for Microsoft Store apps: checks web content that Microsoft Store apps use.
- Quick note: The operating system includes the optimal settings for this feature, but you can always manage the features depending on your preferences.
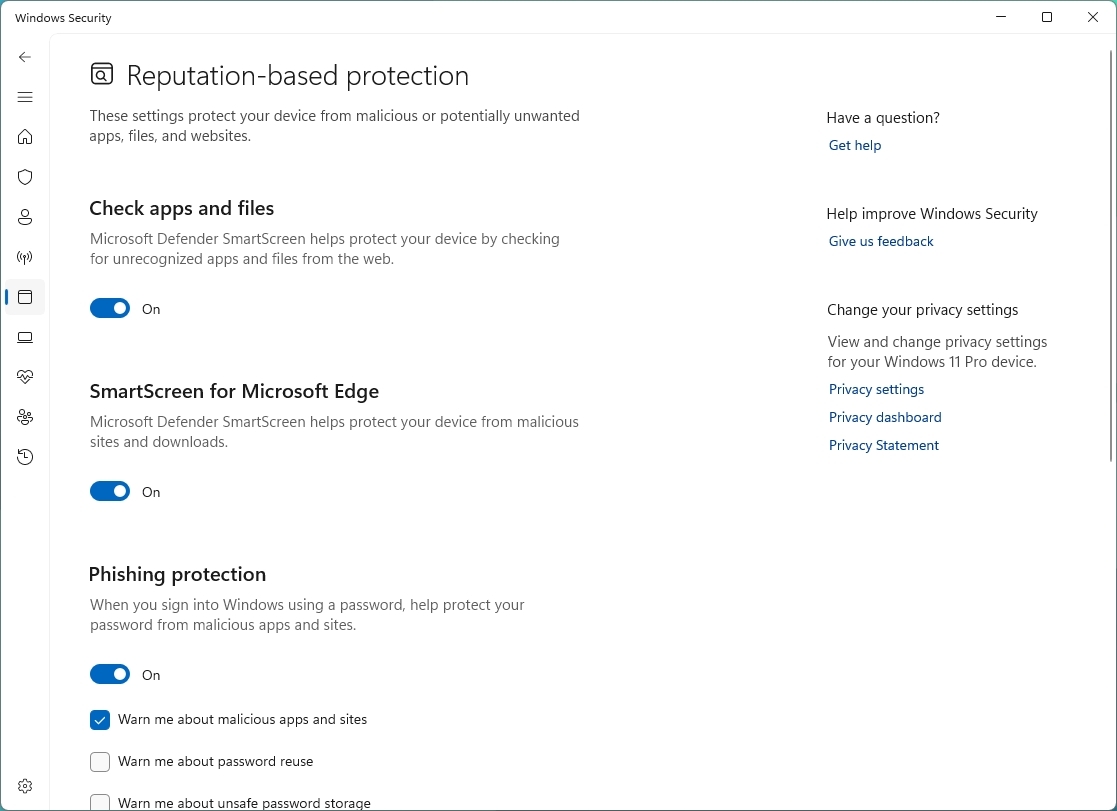
Once you complete the steps, Microsoft Defender Antivirus will protect your device from unwanted apps, files, and malicious websites.
Exploit protection
Exploit protection is an advanced feature that can help mitigate malware and vulnerabilities without having to wait for a malware or system update.
Windows 11 (and 10) includes the most optimal settings for Exploit protection, and you shouldn't be making any changes to these settings unless you know what you're doing.
To customize the Exploit protection settings, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on App & browser control.
- Click the "Exploit protection settings" option.
- Click the System settings tab.
- Configure the settings with your desire preferences.
- Click the Program settings tab.
- Configure the settings with your desire preferences.
Once you complete the steps, Exploit protection will run on the device according to your settings.
As part of the "App & browser control" settings, Windows Security also included the "Insolated browsing" feature to create a virtualized instance of Microsoft Edge to browse the web, but this feature is no longer maintained, so I'm not including it as one of the features for this application.
How to enable core isolation using Windows Security
Core isolation is a virtualization technology that adds an extra layer of security against sophisticated attacks. The available feature will depend on the device's capability. However, you'll usually find the memory integrity feature, which has been designed to minimize the chances of malware injection into memory.
Typically, you don't need to worry about the feature, but you can turn it on using these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Device security.
- Click the "Core isolation details" option.
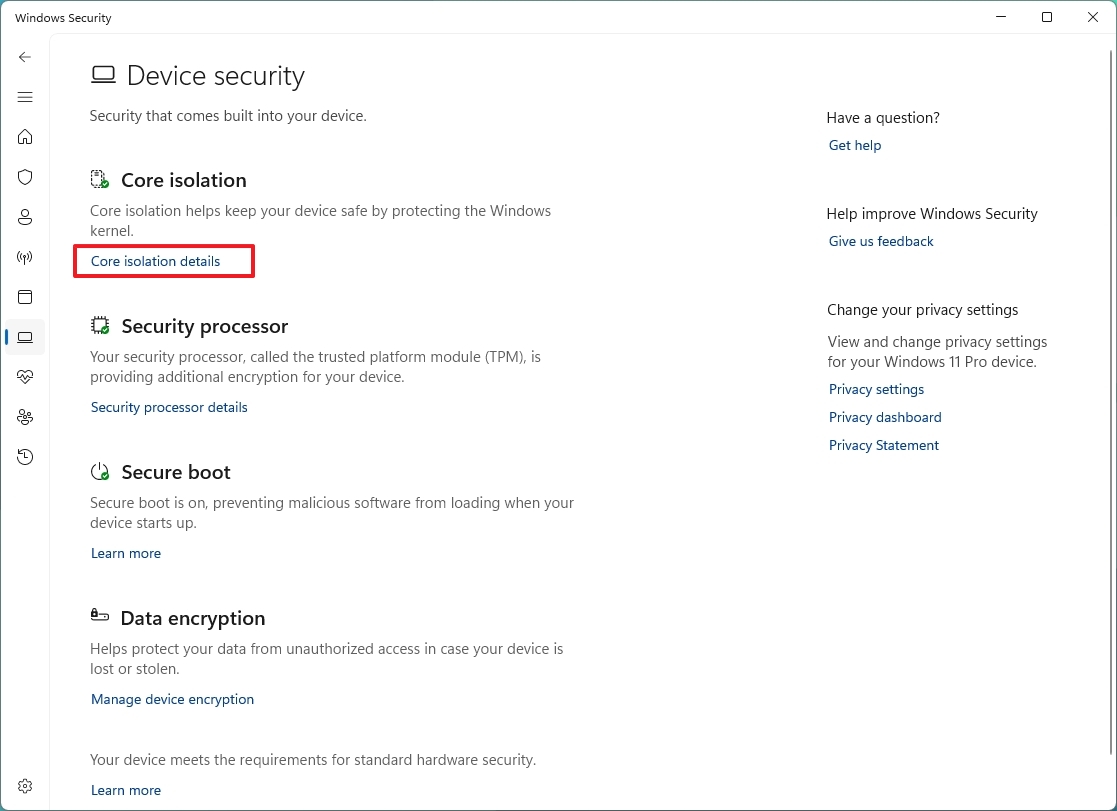
- Turn on the Memory integrity toggle switch.
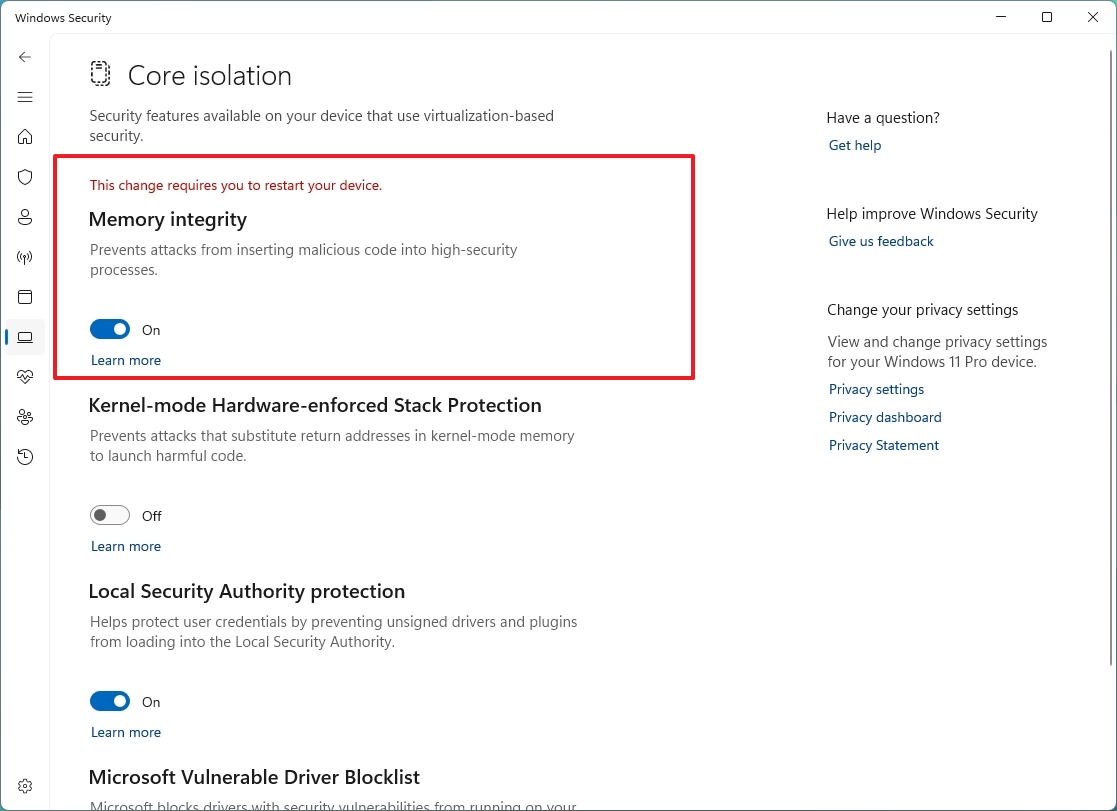
- (Optional) Turn on the "Kernel-mode Hardware-enforced Stack protection" toggle switch to prevent attacks on system memory.
- (Optional) Turn on the "Local Security Authority protection" toggle switch to prevent user credentials.
- (Optional) Turn on the "Microsoft Vulnerable Driver Blocklist" toggle switch to drivers with security vulnerabilities.
After you complete the steps, restart your computer to apply the changes.
If you don't see the option, it's likely because virtualization isn't enabled inside the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI).
How to check security processor details using Windows Security
To view TPM (Trusted Platform Module) specifications on devices with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface ), use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Device Security.
- Click the "Security processor details" setting.
- Confirm the TPM details, such as manufacturer, version, and TCG specs.
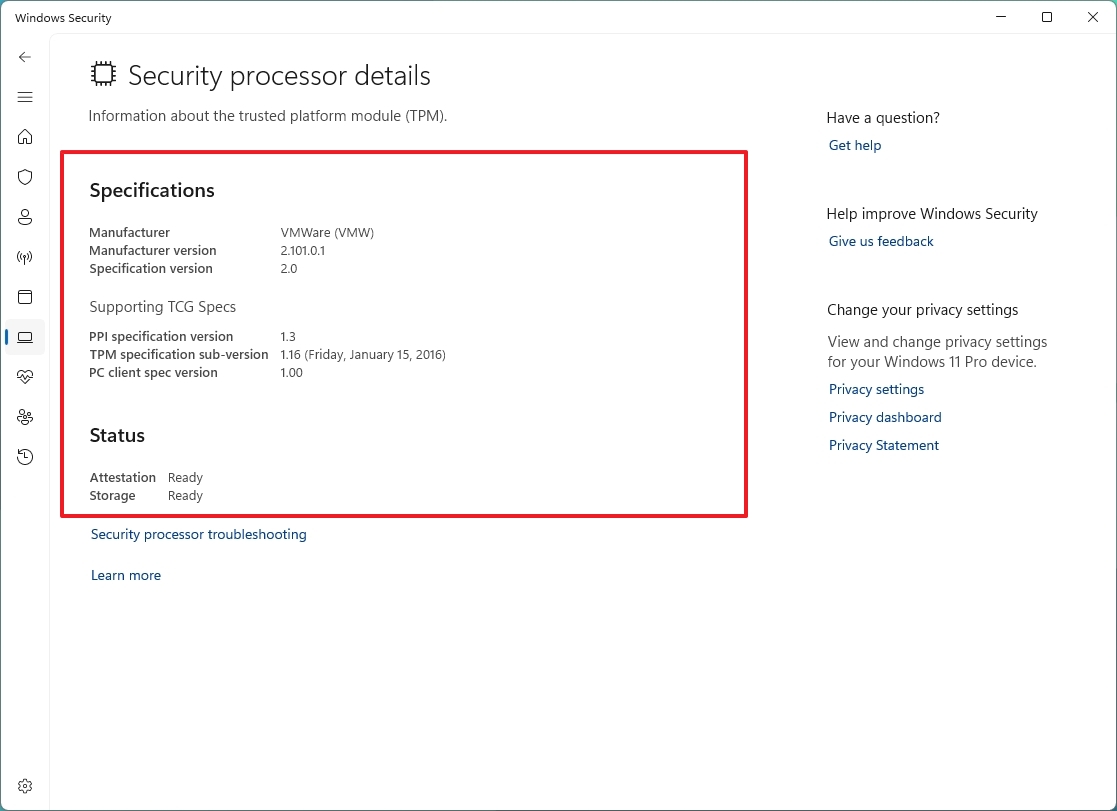
Once you complete the steps, you will better understand your computer's security chip specifications.
As part of the "Device security" settings, you can also use this page to confirm whether "Secure boot" is enabled, and there's an option to access the "Device encryption" feature in the Settings app.
How to view device health and performance report using Windows Security
Windows Security also includes an area that surfaces information about the health and performance of your computer.
To view the health and performance report of a device, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Device performance & health.
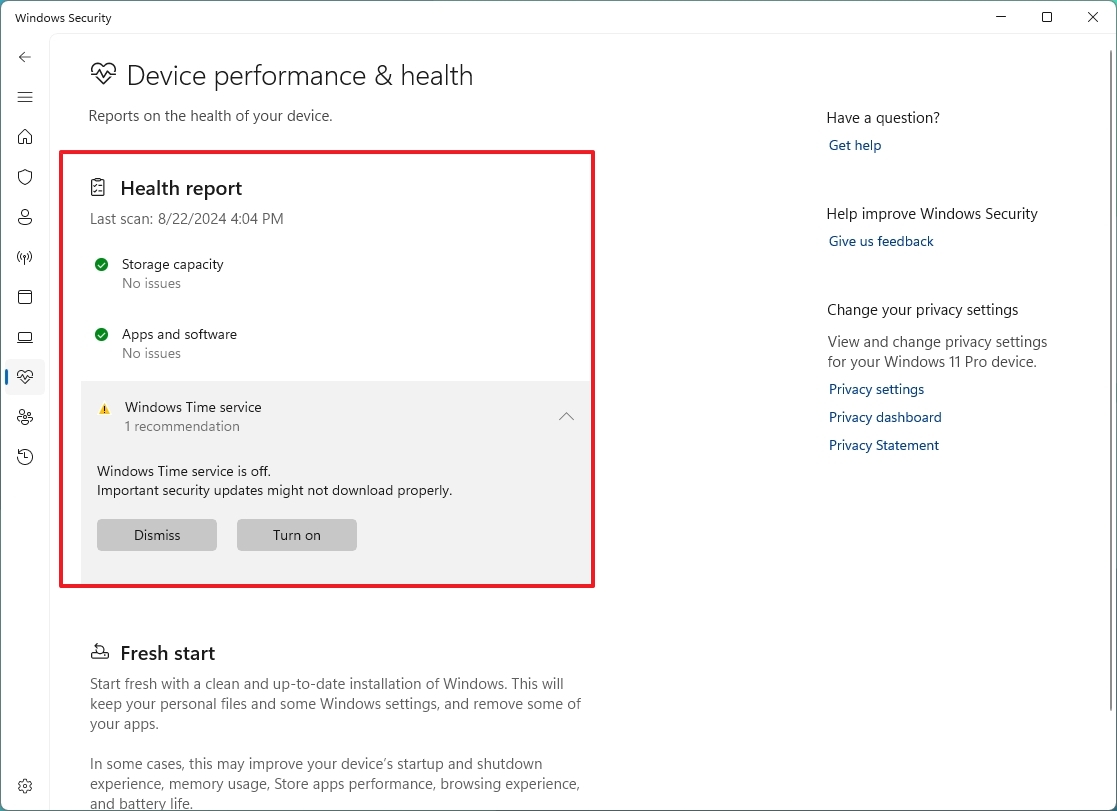
- Check the health port of the device.
The report includes statuses for Windows Update, storage, device driver, and battery. If action needs to be taken, you'll see an alert with a recommendation on how to remedy the issue.
Here are the meanings for each possible status state:
- Green: everything is working correctly.
- Yellow: recommendation is available.
- Red: warning that requires immediate attention.
How to manage parental control and track devices using Windows Security
Windows Security also has a "Family options" area, but it's not a place where you can manage any settings. Instead, it offers access to your Microsoft account to manage parental control and other devices connected to the account.
To access the Family options, use these steps:
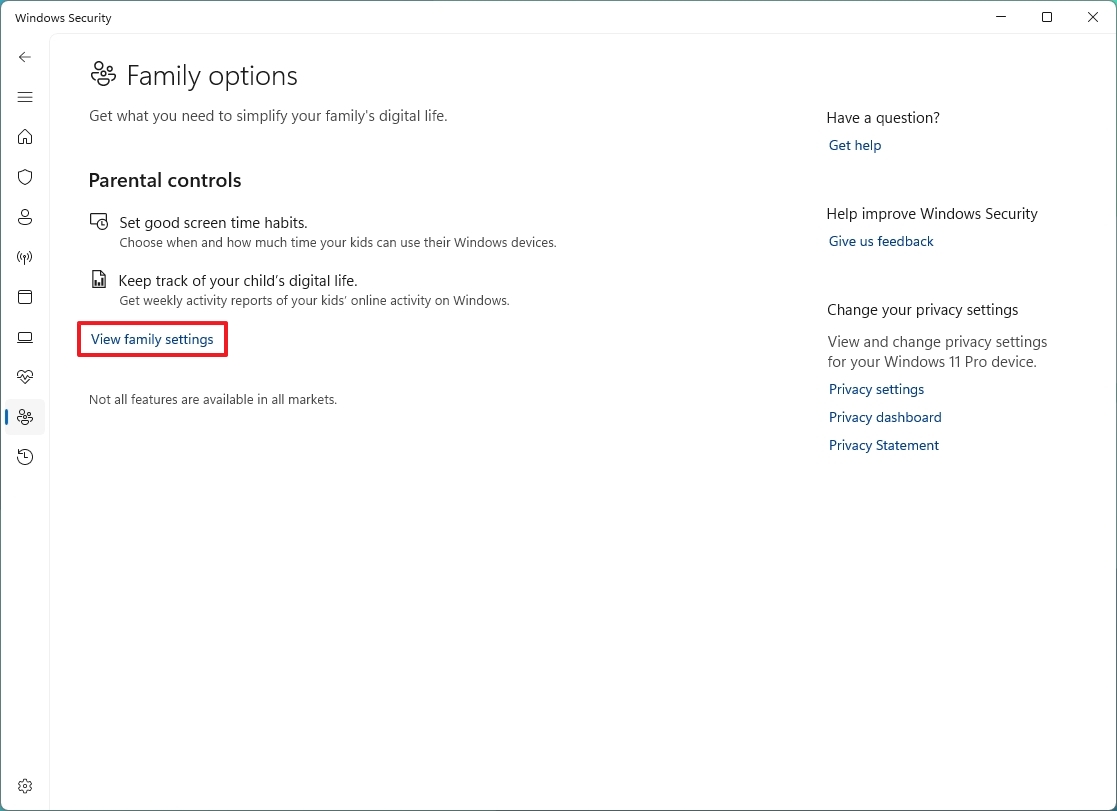
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Family options.
- Click the "View family settings" option to open these settings in your Microsoft account online under the "Parental controls" section.
How to view protection history for Windows Security
The app also includes the "Protection history" page, which is similar to the history view for the antivirus, but this page offers actions and commendations for features available on Windows Security.
To access the Windows Security history, use these steps:
- Open Windows Security.
- Click on Protection history.
- Review the actions and recommendations.
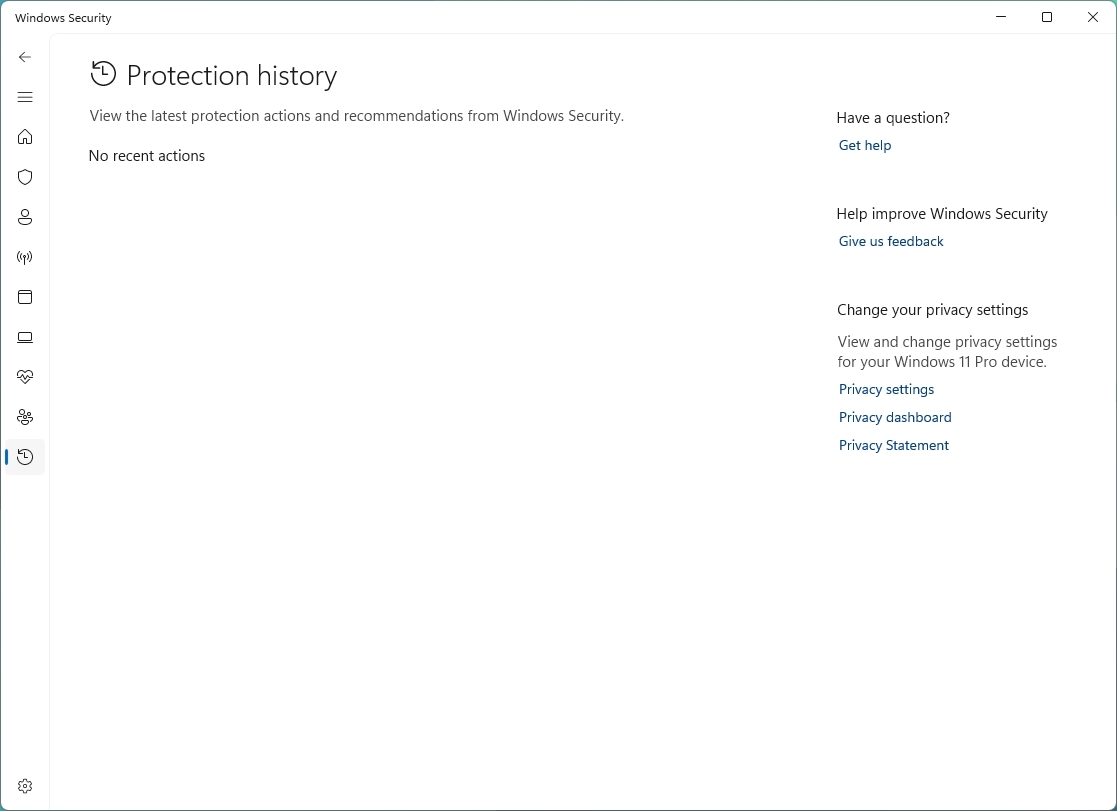
The actions and recommendations will only appear when available. Usually, this page will remain empty.
How to adjust notifications for Windows Security
Finally, there's the Settings page that allows you to manage security providers and notifications settings.
To change the notifications settings on Windows Security, use these steps:
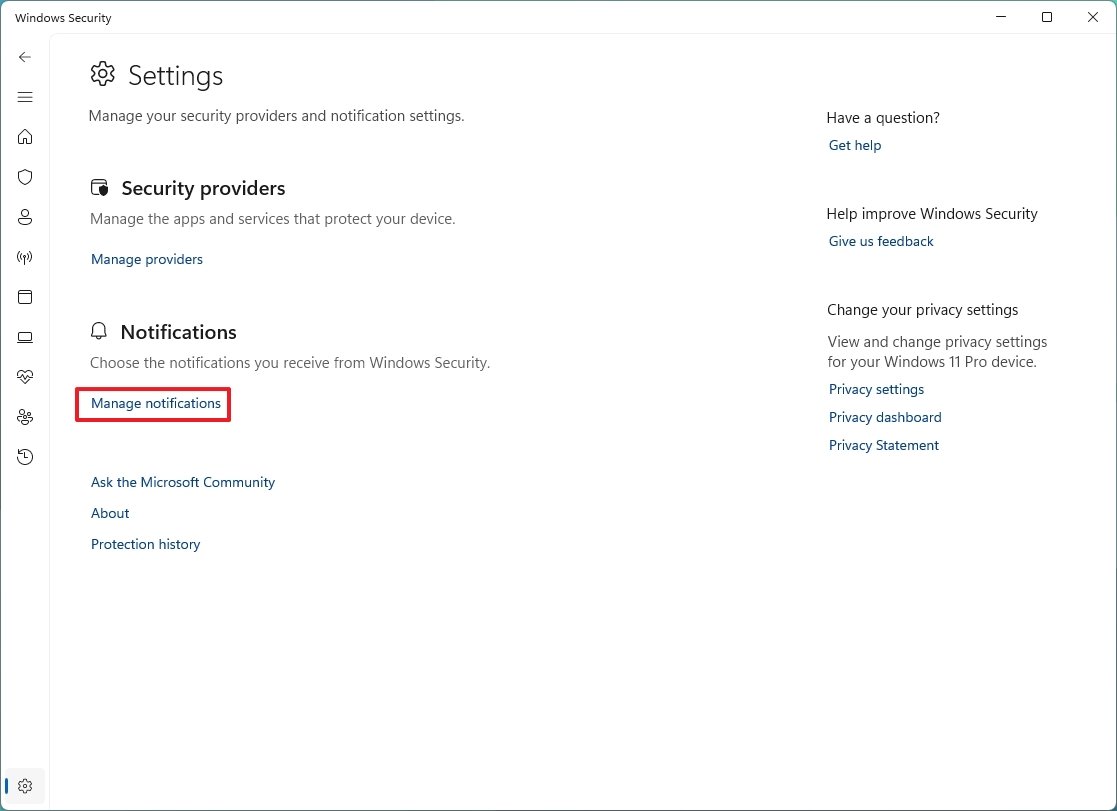
- Open Windows Security.
- Click the Settings button at the bottom of the page.
- Click the Manage notifications option under the "Notifications" section.
- Customize the notifications to your preferences for the Microsoft Defender Antivirus, account protection, and firewall.
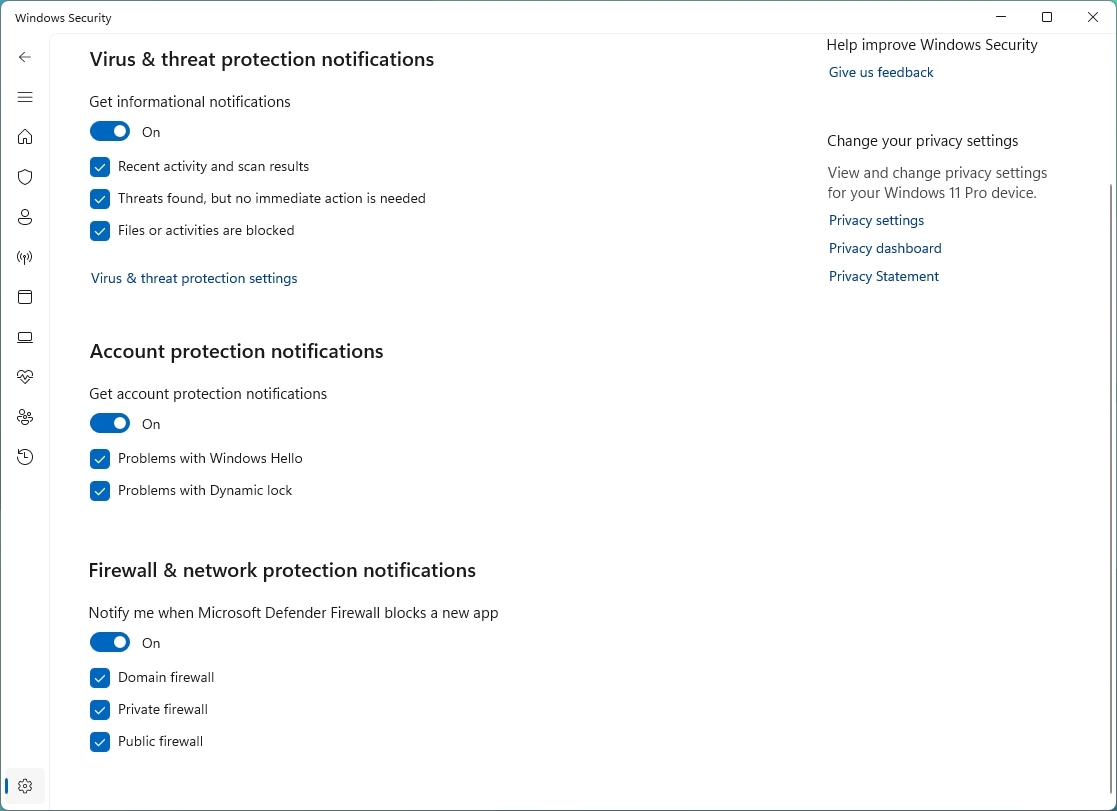
Once you complete the steps, the settings will apply according to your configuration.
In the Settings page for Windows Security, you'll also notice a "Security providers" section. This section allows you to access another page where you will find a list of other security providers, such as web protection, firewall, and antivirus. Although you can't customize any settings, you can use this page to open the security app and adjust its settings.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:







