Flame retardants are added to a variety of products to prevent or slow the spread of fire. They have been added to many consumer and industrial products, including building materials, plastics, polyurethane-based foams in furniture, textiles and automotive parts, and electrical and electronic devices. They’re even in your iPhone.
Unfortunately, these product requirements are often poor predictors of actual fire risks and frequently lead to the misuse of these toxic chemicals.
When people dispose of consumer products that contain flame retardants, these chemical compounds end up in the environment, and contaminate, among other places, the St. Lawrence River, its estuary and wildlife. They can also travel great distances through the air to remote regions, including the Arctic. Flame retardants are now found in almost all species studied in the St. Lawrence River.

This article is part of our series, The St. Lawrence River: In depth. Don’t miss new articles on this mythical river of remarkable beauty. Our experts look at its fauna, flora and history, and the issues it faces. This series is brought to you by La Conversation.
In animals, exposure to certain types of flame retardants is associated with hormonal disruption, and developmental and reproductive disorders. Halogenated flame retardants (those containing bromine or chlorine atoms) are among the most widely used and environmentally harmful.
Many of them have now been banned, including polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), but a new generation of alternative flame retardants are taking their place. Their environmental impacts have not been sufficiently tested and are likely to cause similar effects.
À lire aussi : These chemicals are bad for babies and whales: Why haven't they been banned in Canada?
As a researcher in ecotoxicology, I focus part of my work on flame retardants in the environment and their impact on wildlife, including three of Québec’s iconic species: northern pike, minke whale and beluga whale.

St. Lawrence wildlife at great risk
When ingested or inhaled, PBDEs accumulate in animal tissues over time. Their concentrations are on the rise in species at the top of the food chain, especially in densely populated, heavily polluted areas.
River-dwelling organisms are exposed to flame retardants in municipal waste from large urban areas. For example, Northern pike, a predatory fish, which are exposed to effluent from Montréal’s wastewater treatment plant, had liver PDBE concentrations four times higher than northern pike at an upstream river site. New flame retardants (replacements for PBDEs), such as chlorinated chemicals that are similar to dechloranes and used mostly in cable and electrical wire sheathing, were also measured in these pike.
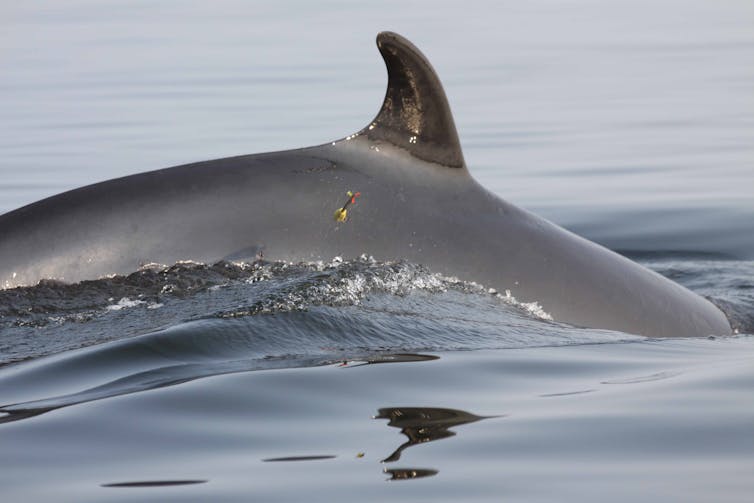
A study conducted downstream of major urban centres in the St. Lawrence estuary on beluga whales, a population currently considered endangered, revealed PBDE concentrations in their blubber that are among the highest in the world in marine mammals. These concentrations do not appear to be decreasing despite the nearly 15-year-old ban on the use of PBDEs.
In comparison, PBDEs in beluga fat were measured at concentrations about four times higher than in minke whales, a baleen whale that is a seasonal visitor to the St. Lawrence estuary. A number of next-generation flame retardants were also measured in the blubber of belugas and minke whales in the estuary. History is repeating itself.
Possible impacts on animal health?
PBDEs are toxic to animals upon exposure. Without confirming causal links, wildlife studies indicate that exposure to flame retardants are associated with a range of harmful bodily effects on their hormonal, immune and metabolic functions, and consequently on growth, reproduction and development. This is partially confirmed by studies on the impacts of flame retardants in St. Lawrence pike, beluga and minke whales.

For pike, exposure to flame retardants in Montréal’s effluent affected the regulation of their thyroid hormones and decreased the expression of some liver genes involved in lipid metabolism. Lipids are important sources of energy for several biological functions.
In belugas and minke whales, exposure to flame retardants, including some emerging compounds, has also been associated with hormonal effects. Researchers have found links between the concentrations of some flame retardants, such as PBDEs, in these two cetaceans, thyroid hormone levels and the expression of genes that play a key role in regulating the steroid and thyroid hormones involved in reproduction and metabolism.
However, chemical pollution in these species goes far beyond flame retardants. The cocktail of contaminants in the environment grows more complex year after year, and many of these accumulate in the tissues of marine animals, potentially creating compounding and even synergistic effects.
Sadly, the cycle of inadvisable substitutions — the replacement of one toxic compound with another that may eventually be deemed toxic in turn — seems to continue.
And that’s not good news for the health of our mighty St. Lawrence River and its priceless wildlife.
Jonathan Verreault has received funding from Fisheries and Oceans Canada and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







